Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rockmount ASTM Steel Grades PDF
Uploaded by
kanteron6443Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rockmount ASTM Steel Grades PDF
Uploaded by
kanteron6443Copyright:
Available Formats
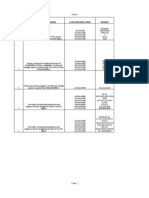
ASTM - SPECIFIED PLATE STEELS
1-800-272-7637
ASTM Content
Number
A36 Carbon steel: Plates and other structural steel products melted and rolled to give 36,000 lb/in2 yield strength minimum.
Composition: 0.26 C, 0.80 - 1.20 Mn plus silicon and copper, if specified.
A131 Carbon steel: Twelve grades, compositions and properties of which coincide with those listed in steel specs of the
American Bureau of Shipping. Ordinary-strength grades (A, B, CS, D, DS, and E) offer yield points, minimum, of
34,000 lb/in2 plates for structural uses, and 30,000 lb/in2, plates to be riveted or cold-flanged. Higher-strength grades
provide minimum yield strengths of 46,000 lb/in2 (Grades AH32, DH32 and EH32) and 51,000 lb/in2 (Grades AH36,
DH36, and EH36). Impact and bend testing required. Steels contain carbon, manganese, and silicon; grain-size control
comes from aluminum, for low-strength grades, plus columbium and vanadium, for high strength grade.
A242 High-strength low-alloy (hsla) steel: Two types; four times the resistance to atmospheric corrosion of carbon steels.
Yield strengths, minimum; 42,000 and 50,000 lb/in2 . Composition: 0.15 - 0.20 C, 1.00 - 1.35 Mn, 0.20 Cu min.
A283 Carbon steel: Four grades for plates, shapes and bars. Yield strengths, minimum (lb/in2) 24,000 (Grade A),
27,000 (B), 30,000 (D). No carbon, manganese, or silicon specs.
A284 Carbon steel: Two grades with yield strengths, minimum (lb/ in2) of 30,000 (Grade C) and 33,000 (D). Carbon contents,
maximum, vary from 0.24 percent, for plates less than 1 in. thick, to 0.36 percent, for plates from 8 to 12 in. thick.
A514 Alloy steel: Sixteen grades quenched and tempered to yield strengths, minimum of 90,000 and 100,000 lb/ in2,
depending on thickness (to 6 in.). Composition: 0.12 - 0.21 C max., plus varying amounts of Mn, Ni, Cr, Mo, V, Ti, Zr,
Cu, and B, added for strength, grain-size control, and corrosion resistance. A517 lists pressure-vessel specs for these
steels.
A529 Carbon steel: One grade - 42,000 lb/ in2 yield strength, minimum. Composition: 0.27 C max., 1.20 Mn max., 0.20 Cu
min.
A572 Hsla steel: Four grades containing columbium, vanadium, and nitrogen, singly and together, for grain-size control.
Yield strengths, minimum, are 42,000 (Grade 42), 50,000 (50), 60,000 (60), and 65,000 lb/ in2 (65).
A573 Carbon steel: Three grades. Tensile strength ranges, lb/in2, are 58,000 - 72,000 (Grade 58), 65,000 - 77,000 (65), and
70,000 - 90,000 (70). Composition: 0.23 - 0.28 C, 0.60 - 1.20 Mn, 0.10 - 0.40 Si, depending on grade. Bend tests verify
ductility and toughness.
A588 Hsla steel: Nine grades containing copper to raise resistance to atmospheric corrosion to four times that of conventional
carbon grades - known as weathering steels. Tensile strengths and minimums vary with thickness, from 70,000 lb/in2
(thicknesses under 4 inches) to 63,000 lb/in2 (5 to 8 inches). Composition: 0.11 - 0.20 C max plus varying amounts of
Mn, Si, Ni, Cr, Mo, Cu, V, Cb, and Ti for strength, corrosion resistance and grain-size control.
A633 Hsla steel: Four grades, normalized to improve low-temperature toughness, to - 50 F. Yield strengths, minimum lb/in2 -
42,000 (Grade A); 46,000 and 50,000, depending on thickness to 6 in. (Grades C and D); and 55,000 and 60,000 (Grade
E, depending on thickness). Composition: 0.18 to 0.22 C max, 1.00 to 1.50 Mn, 0.15 to 0.50 Si, plus copper and varying
amounts of grain-refining elements.
A656 Hsla steel: Seven types featuring formability for forming of shapes. Composition, varying with types (1 - 7): 0.18 C
max, 1.65 Mn max, 0.30 to 0.90 Si, depending on type, plus varying amounts of V, N, Ti, Cb, Zr, Mo, Cr, and B, singly
and together. Yield strengths, minimum (lb/in2) - 50,000 (Grade 50), 60,000 (60), 70,000 (70), and 80,000 (80).
A678 Carbon and hsla steels: Four grades, quenched and tempered to yield strengths, minimum (lb/in2) of 50,000 (Grade A),
60,000 (B), 65,000 to 75,000, depending on thickness - to 2 in. (C), and 75,000 to 3 in. (D). Composition: 0.16 - 0.22 C
max, 0.90 - 1.50 Mn, 0.15 - 0.50 Si, 0.20 Cu min (when specified), 0.15 - 0.50 V - Grade D also contains Cb, N, and B
when specified.
A709 Carbon and hsla steels: Twenty-one grades for bridge applications, listed in ASTM 36, A514, A572, and A588 -
compositions and properties. A709 adds specs covering fine-grain practice, tension testing, notch-toughness testing,
proof of resistance to atmospheric corrosion, ultrasonic inspection, and the need for freedom from mill-made weld
repairs.
A808 Hsla steel: One grade containing columbium and vanadium for grain-size control. Yield strengths, minimum (lb/in2) -
50,000 to 1 - in. thick, 46,000 over 1- to 2 in., 42,000 over 2 to 2 - in. Notch toughness to -50 F; bend and
impact testing required.
A829 Alloy steel: AISI grades 1330 - 1345 (4 grades), 4118 - 4145 (7), 4340, 4615 - 4620 (3), 5160, 6150, 8615 - 8655 (10),
and 8742. Supplied to AISI-specified compositions; mechanical properties may be specified.
A830 Carbon steel: AISI grades 1006 to 1095 (51 grades), 1524 to 1552 (6). Generally furnished to AISI-specified
compositions; mechanical properties may be specified.
A852 Hsla steel: One grade, quenched and tempered to a yield strength, minimum, of 70,000 lb/in2) in plate to 4 in. thick.
Composition: 0.19 C max, 0.80 - 1.35 Mn, 0.20 - 0.65 Si, 0.40 - 0.70 Cr, 0.20 - 0.40 Cu, 0.02 - 0.10 V. Impact testing
required - 20 ft-lb min at 40 F.
A871 Hsla steel: Two grades, as-rolled, normalized, or quenched-and-tempered to yield strengths, minimum (lb/in2) of 60,000
(Grade 60) or 65,000 (65). Composition (max): 0.20 C, 1.50 Mn, 0.90 Si, 1.25 Ni, 0.90 Cr, 0.25 Mo, 1.00 Cu, 0.10 V,
0.15 Zr, 0.05 Cb, 0.05 Ti. Impact testing required - 15 ft-lb min at 0 F to 1/2 in. thick, at -20 F over 1/2 in.
9808-41 Weld Tips
You might also like
- Rockmount ASTM Steel GradesDocument1 pageRockmount ASTM Steel Gradesjesus_frimontNo ratings yet
- Steel Properties (Notes)Document27 pagesSteel Properties (Notes)ellesor macalamNo ratings yet
- 02.classifications and SpecificationsDocument8 pages02.classifications and SpecificationsShendi Kiki PratamaNo ratings yet
- Oxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonFrom EverandOxy-Acetylene Welding and Cutting: Electric, Forge and Thermit Welding together with related methods and materials used in metal working and the oxygen process for removal of carbonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Steels For Seismic Applications: Astm A913 Grade 50 and Grade 65Document10 pagesSteels For Seismic Applications: Astm A913 Grade 50 and Grade 65Edwin RamirezNo ratings yet
- Boiler Making for Boiler Makers - A Practical Treatise on Work in the ShopFrom EverandBoiler Making for Boiler Makers - A Practical Treatise on Work in the ShopRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Carbon Hollow BarDocument3 pagesCarbon Hollow Barscrane@No ratings yet
- Lesson2 STEEL PROPERTIES CDocument87 pagesLesson2 STEEL PROPERTIES CMaqMaikNo ratings yet
- The Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelFrom EverandThe Working of Steel: Annealing, Heat Treating and Hardening of Carbon and Alloy SteelNo ratings yet
- Material Cross Reference TableDocument3 pagesMaterial Cross Reference TableLuis Pol SistiNo ratings yet
- Alloy Steel Castings Table 1Document16 pagesAlloy Steel Castings Table 1takumi_zNo ratings yet
- AISI Designation: Stainless Tool Steels Killed Carbon SteelsDocument14 pagesAISI Designation: Stainless Tool Steels Killed Carbon SteelsShankar JhaNo ratings yet
- SMAW Electrode IdentificationDocument2 pagesSMAW Electrode IdentificationAsim AliNo ratings yet
- Astm A283 Carbon Steel PlateDocument1 pageAstm A283 Carbon Steel Platefikry arifandaniNo ratings yet
- SteelDocument1 pageSteelSinhro018No ratings yet
- 16 ApllicationsDocument57 pages16 ApllicationsBoni PrakasaNo ratings yet
- NO. Material Description Astm Specification GradesDocument3 pagesNO. Material Description Astm Specification GradesFer VFNo ratings yet
- Astm A500Document2 pagesAstm A500Liquor Liam0% (1)
- MaterialsDocument26 pagesMaterialsbadesharamkNo ratings yet
- Ce 2014 Fundamental of Concrete, Steel and Timber StructureDocument22 pagesCe 2014 Fundamental of Concrete, Steel and Timber StructureKyaw Zin HeinNo ratings yet
- LTCS Vs CSDocument2 pagesLTCS Vs CSMuhammad ShahzadNo ratings yet
- A36 Steel Composition Applications and Properties of ASTM A36 Steel PDFDocument6 pagesA36 Steel Composition Applications and Properties of ASTM A36 Steel PDFYudha Andrie Sasi ZenNo ratings yet
- Worldwide Guide To Equivalent Irons & Steels, 5th Ed: SumberDocument1 pageWorldwide Guide To Equivalent Irons & Steels, 5th Ed: SumberMuhamad NurNo ratings yet
- Materials For Mechanical Parts-Steel & StandardsDocument31 pagesMaterials For Mechanical Parts-Steel & StandardsKhantoNo ratings yet
- 003 Steel Plate SHTDocument26 pages003 Steel Plate SHTFebri VictorNo ratings yet
- Smaw Welding Electrode ClassificationDocument2 pagesSmaw Welding Electrode ClassificationsamyNo ratings yet
- 60Si2Mn Spring Steel PDFDocument4 pages60Si2Mn Spring Steel PDFShubhamNo ratings yet
- Materials and Cold Work of Forming: 2.1 Steel StandardsDocument23 pagesMaterials and Cold Work of Forming: 2.1 Steel Standardshunter8080No ratings yet
- HR Sheet Metal Steel TableDocument1 pageHR Sheet Metal Steel TablercastrohNo ratings yet
- As-Rolled Plate Product With Improved Yield Strength, Toughness, and Weldability For Pressurized Railroad Tank CarsDocument16 pagesAs-Rolled Plate Product With Improved Yield Strength, Toughness, and Weldability For Pressurized Railroad Tank CarssurendarNo ratings yet
- API Vs A53 Vs A106 Vs A333Document8 pagesAPI Vs A53 Vs A106 Vs A333Ibrahim BashaNo ratings yet
- A516 NormalizedDocument3 pagesA516 Normalizediran1362No ratings yet
- Carbon and Low-Alloy SteelsDocument46 pagesCarbon and Low-Alloy SteelsSuphi YükselNo ratings yet
- Sa765 - VS-350LF2Document2 pagesSa765 - VS-350LF2rtrajan_mech5408No ratings yet
- GX300CrMo15 3Document1 pageGX300CrMo15 3jdash0904No ratings yet
- 3 Steel PDFDocument16 pages3 Steel PDFSohanur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Standard (Kuliah 17)Document12 pagesStandard (Kuliah 17)Bowby JoNo ratings yet
- API 2hgr50Document3 pagesAPI 2hgr50Jym GensonNo ratings yet
- Us 5326527Document8 pagesUs 5326527Hugo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Piping MaterialDocument45 pagesPiping MaterialLcm TnlNo ratings yet
- 2205 InfoDocument6 pages2205 InfoMave75No ratings yet
- Welding Steel Alloys: Low-Carbon SteelsDocument3 pagesWelding Steel Alloys: Low-Carbon SteelsRathnakrajaNo ratings yet
- Steel Products and Structural Shapes - OptDocument12 pagesSteel Products and Structural Shapes - OptmurdicksNo ratings yet
- Steel SpecificationsDocument4 pagesSteel Specificationsgaurav tiwariNo ratings yet
- Steel Reinforcing BarsDocument3 pagesSteel Reinforcing BarsALI ZUBAIRNo ratings yet
- MaterialDocument4 pagesMaterialAmit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fabrication WeldingDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Fabrication WeldingKevinNo ratings yet
- Astm A588 1979 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm A588 1979 PDFNuno Telmo LopesNo ratings yet
- Types of Structural SteelDocument4 pagesTypes of Structural SteelPti RaheelNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy of MaterialsDocument15 pagesMetallurgy of Materialscal2_uniNo ratings yet
- Cast IronDocument5 pagesCast IronPetroenNo ratings yet
- SA36Document6 pagesSA36el10bgNo ratings yet
- SMAW Electrode ClassificationDocument2 pagesSMAW Electrode ClassificationHarold GillNo ratings yet
- ALLOY 6082: Understanding Extruded Aluminum AlloysDocument0 pagesALLOY 6082: Understanding Extruded Aluminum Alloysetamil87No ratings yet
- S/A 106 Spec Sheet A106 Pipe Specifications: ScopeDocument7 pagesS/A 106 Spec Sheet A106 Pipe Specifications: ScopeyanurarzaqaNo ratings yet
- Alloy 6060Document2 pagesAlloy 6060SuryaNo ratings yet
- No Magic Quick Reference Guide BPMN PDFDocument2 pagesNo Magic Quick Reference Guide BPMN PDFkanteron6443No ratings yet
- Bandy NAAIM PaperDocument30 pagesBandy NAAIM Paperkanteron6443No ratings yet
- Technical Data: Base Price Ex Works (Excl. Vat) 128.900,00Document6 pagesTechnical Data: Base Price Ex Works (Excl. Vat) 128.900,00kanteron6443No ratings yet
- Bavaria C38: Product Management: Pascal KuhnDocument24 pagesBavaria C38: Product Management: Pascal Kuhnkanteron6443No ratings yet
- Syegon Leaflet 2012Document2 pagesSyegon Leaflet 2012kanteron6443No ratings yet
- Alexander Brem, Éric Viardot (Eds.) - Adoption of Innovation - Balancing Internal and External Stakeholders in The Marketing of Innovation-Springer International Publishing (2015) PDFDocument230 pagesAlexander Brem, Éric Viardot (Eds.) - Adoption of Innovation - Balancing Internal and External Stakeholders in The Marketing of Innovation-Springer International Publishing (2015) PDFkanteron6443No ratings yet
- Markforged Mark TwoDocument8 pagesMarkforged Mark Twokanteron6443No ratings yet
- Data Table Cheat Sheet PDFDocument1 pageData Table Cheat Sheet PDFkanteron6443No ratings yet
- Create ISOMETRIC View of Given MultiviewsDocument3 pagesCreate ISOMETRIC View of Given Multiviewskanteron6443No ratings yet
- Autodesk Simulation Mechanical IIDocument1 pageAutodesk Simulation Mechanical IIkanteron6443No ratings yet
- A CFD Model For Orbital Gerotor MotorDocument13 pagesA CFD Model For Orbital Gerotor Motorkanteron6443No ratings yet
- Modifications To The Mean Maximum Pressure SystemDocument17 pagesModifications To The Mean Maximum Pressure Systemkanteron6443No ratings yet
- The Transition To Model Based Enterprise AIAGDocument20 pagesThe Transition To Model Based Enterprise AIAGkanteron6443No ratings yet
- Gerotor Selection Pump DesignDocument28 pagesGerotor Selection Pump Designkanteron6443100% (1)
- Geometric Design For A Gerotor Pump With High Area EfficiencyDocument9 pagesGeometric Design For A Gerotor Pump With High Area Efficiencykanteron6443No ratings yet
- Data Sheet ASTM A514 Grade B 2017-04-19 221 371857150 enDocument2 pagesData Sheet ASTM A514 Grade B 2017-04-19 221 371857150 enkanteron6443No ratings yet
- 8,000 RPM APU Size To 30,000 RPM Miniature, Aerospace ApplicationsDocument9 pages8,000 RPM APU Size To 30,000 RPM Miniature, Aerospace Applicationskanteron6443No ratings yet
- Section 9 - Ground Combat Systems TechnologyDocument96 pagesSection 9 - Ground Combat Systems Technologykanteron6443100% (1)
- Edward Dobson - Understanding Bollinger BandsDocument27 pagesEdward Dobson - Understanding Bollinger Bandskanteron6443No ratings yet
- Battle Tested Forex Trading StrategiesDocument73 pagesBattle Tested Forex Trading Strategieskanteron6443No ratings yet
- Trading With Bollinger Bands - Toni Turner PDFDocument32 pagesTrading With Bollinger Bands - Toni Turner PDFteresasNo ratings yet
- Michelin Truck DataBookDocument101 pagesMichelin Truck DataBookkanteron6443100% (1)
- Aussie Def Veh Mob CatDocument39 pagesAussie Def Veh Mob Catkanteron6443No ratings yet
- Prevention of Waterborne DiseasesDocument2 pagesPrevention of Waterborne DiseasesRixin JamtshoNo ratings yet
- Hướng Dẫn Chấm: Ngày thi: 27 tháng 7 năm 2019 Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề) HDC gồm có 4 trangDocument4 pagesHướng Dẫn Chấm: Ngày thi: 27 tháng 7 năm 2019 Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề) HDC gồm có 4 trangHưng Quân VõNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Mortality - A Community ApproachDocument13 pagesNeonatal Mortality - A Community ApproachJalam Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- 1 in 8.5 60KG PSC Sleepers TurnoutDocument9 pages1 in 8.5 60KG PSC Sleepers Turnoutrailway maintenanceNo ratings yet
- Business Plan in BDDocument48 pagesBusiness Plan in BDNasir Hossen100% (1)
- Safety Procedures in Using Hand Tools and EquipmentDocument12 pagesSafety Procedures in Using Hand Tools and EquipmentJan IcejimenezNo ratings yet
- Epson Stylus Pro 7900/9900: Printer GuideDocument208 pagesEpson Stylus Pro 7900/9900: Printer GuideJamesNo ratings yet
- Lamentation of The Old Pensioner FinalDocument17 pagesLamentation of The Old Pensioner FinalRahulNo ratings yet
- Music 10 (2nd Quarter)Document8 pagesMusic 10 (2nd Quarter)Dafchen Villarin MahasolNo ratings yet
- C2 - Conveyors Diagram: Peso de Faja Longitud de CargaDocument1 pageC2 - Conveyors Diagram: Peso de Faja Longitud de CargaIvan CruzNo ratings yet
- Test 51Document7 pagesTest 51Nguyễn Hiền Giang AnhNo ratings yet
- Catedral de SevillaDocument28 pagesCatedral de SevillaAnonymous LkgNmKeNo ratings yet
- Eloy-Stock English Full PDFDocument0 pagesEloy-Stock English Full PDFR.s. WartsNo ratings yet
- Bom Details FormatDocument6 pagesBom Details FormatPrince MittalNo ratings yet
- Sample Resume For Supply Chain Logistics PersonDocument2 pagesSample Resume For Supply Chain Logistics PersonAmmar AbbasNo ratings yet
- PFEIFER Angled Loops For Hollow Core Slabs: Item-No. 05.023Document1 pagePFEIFER Angled Loops For Hollow Core Slabs: Item-No. 05.023adyhugoNo ratings yet
- 2014 - A - Levels Actual Grade A Essay by Harvey LeeDocument3 pages2014 - A - Levels Actual Grade A Essay by Harvey Leecherylhzy100% (1)
- Pathology of LiverDocument15 pagesPathology of Liverערין גבאריןNo ratings yet
- Anemia in PregnancyDocument5 pagesAnemia in PregnancycfgrtwifhNo ratings yet
- An Annotated Bibliography of Timothy LearyDocument312 pagesAn Annotated Bibliography of Timothy LearyGeetika CnNo ratings yet
- Cable To Metal Surface, Cathodic - CAHAAW3Document2 pagesCable To Metal Surface, Cathodic - CAHAAW3lhanx2No ratings yet
- Head Coverings BookDocument86 pagesHead Coverings BookRichu RosarioNo ratings yet
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument10 pagesPityriasis Versicolorketty putriNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument1 pageDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesJonathan CayatNo ratings yet
- Genetics Icar1Document18 pagesGenetics Icar1elanthamizhmaranNo ratings yet
- Tesco True Results Casing Running in China Results in Total Depth PDFDocument2 pagesTesco True Results Casing Running in China Results in Total Depth PDF123456ccNo ratings yet
- Sveba Dahlen - SRP240Document16 pagesSveba Dahlen - SRP240Paola MendozaNo ratings yet
- Implementation of E-Governance To Improve The Civil Administration Service Quality in Public SectorDocument11 pagesImplementation of E-Governance To Improve The Civil Administration Service Quality in Public SectorChristie YohanaNo ratings yet
- Cisco BGP ASPATH FilterDocument115 pagesCisco BGP ASPATH FilterHalison SantosNo ratings yet
- Performance Monitoring and Coaching FormDocument3 pagesPerformance Monitoring and Coaching Formjanine masilang100% (2)