Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DC Conductivity Studies On Polyethylene Oxide/ Nickel Ferrite Composites
Uploaded by
Jai SagarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DC Conductivity Studies On Polyethylene Oxide/ Nickel Ferrite Composites
Uploaded by
Jai SagarCopyright:
Available Formats
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering | Volume 3 | Issue 02 | August 2016
ISSN (online): 2349-784X
DC Conductivity Studies on Polyethylene Oxide/
Nickel Ferrite Composites
Jakeer Husain M. Anvarullha
Department of Science & Humanities Department of Mechanical Engineering
Farah Institute of Technology, Chevella, JNTUH, India- Farah Institute of Technology, Chevella, JNTUH, India-
501503 501503
Nagalli Raghu Jai Sagar
Department of Mechanical Engineering Department of Mechanical Engineering
Farah Institute of Technology, Chevella, JNTUH, India- Farah Institute of Technology, Chevella, JNTUH, India-
501503 501503
Bushra Anjum
Department of Physics
Gulbarga University Gulbarga 585106 Karnataka, India
Abstract
Nanocomposite of polyethylene oxide/nickel ferrite nanoparicles were synthesized by Sol-Gel method these nanocomposites
were characterized by employing .X-ray diffraction (XRD), infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and TEM. The conductivity was
found to increase with the increase in temperature indicating the semiconducting behavior of all the compositions. Maximum
conductivity was observed in 1.5 wt%.
Keywords: Synthesis, X-Ray Diffraction, TEM, FT-IR
________________________________________________________________________________________________________
I. INTRODUCTION
Recent years polyethylene oxide based polymer electrolytes composite are showing great interest due to their optical as well as
theoretical importance for making of solid state batteries, sensors. electronic etc. (1-4). PEO is an exceptional polymer which
dissolves with concentrations of a wide variety of salts to form polymer electrolytes (5) Spinel Ferrite nanoparticles are belongs
to soft magnetic materials these ferrites are most attractive class of materials due to important properties such as low melting
point, high specific heating, large expansion coefficient, low saturation magnetic moment and low magnetic transition
temperature, etc. Because of these properties, the spinel ferrites have many technical applications, such as in photoelectric
devices, catalysis, sensors, nano devices, microwave devices and magnetic pigments. Nickel ferrite is one of the important soft
ferrite materials because of its typical ferromagnetic properties, low conductivity and thus lower eddy current losses, high
electrochemical stability, catalytic behavior, abundance in nature, etc. (6-14). PEO has the simplest structure of water-soluble
polymers. Its salt complexes have shown to be solid electrolytes and have attracted considerable research attention because they
are promising for applications in solid-state batteries and electrochromic devices.(15)
In this present work authors have carried out the synthesis, characterization, DC conductivity studies of PEO/Nickel ferrite
nanocomposites. The dc conductivity shows that N3 has high conductivity among all composites. It is observed that N3
composites have high current compare to other composites due to more feasibility for ion moments.
II. EXPERIMENTAL
Materials
Polyethylene oxide (relative molecular mass of 5 x 105) was obtained from Shanghai Research Institute of Chemicals, China and
dried under vacuum at 50 C for 24 h before use.
Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles Were Prepared by the Solgel Method
Using Nickel nitrate and ferric nitrate in the molar ratio 1: 2. A certain amount of citric acid was dissolved in distilled water, A
small amount of ammonia was then added to the solution to adjust the pH value to 7 and stabilize the nitrate-citrate solution.
During this process the solution was continues stirring using magnetic stirrer for 56 h at 1200C. Finally, a gel is formed. This
gel is heated at a temperature of about 300 C for 1 h to remove water molecules. Finally, the gel is completely transformed into a
foam powder. The foam powder was then ground into a fine powder. The synthesized powder was ground and calcinate for 2
hour to remove impurities finally get pure nickel ferrite nanoparticles.
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org 223
DC Conductivity Studies on Polyethylene Oxide/ Nickel Ferrite Composites
(IJSTE/ Volume 3 / Issue 02 / 035)
Preparation of Nickel Ferrite/PEO Nano Nanocomposites
The prepared nickel ferrite gel was continuously stirrer by adding different weight percentage PEO solution such as
(0.5,1.5,2.5)This gel is heated at a temperature of about 80 C for 1 h to remove water molecules. Finally, the gel is completely
transformed into a foam powder. The foam powder was then ground into a fine powder. The synthesized powder was ground and
calcinate for 2 hour to remove impurities finally get PEO/Nickel ferrite nanocomposite.
III. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
FTIR Spectra
Fig. shows the FTIR spectra of the polyethylene oxide /nickel ferrite composites ,. The absorption bands around 629.12 cm-1 in
NiFe2O4 are attributed to the stretching vibration of tetrahedral and octahedral group complexes of ferrites, respectively . The
bands at 1690.39 and 1487.89cm-1 in pure NiFe2O4/PEO are the characteristics bands of nitrogen quinoid and benzoid forms due
to the conducting state of the polymer. The bands at 2541 to 2931 cm-1 is due to hydrogen bonding . The interaction of nickel
ferrite with polyaniline is confirmed from IR spectra of the nanocomposites.
95
90
85
2 5 4 1 .8 1
2 6 3 4 .4 4
1 6 0 6 .4 9
1 1 7 7 .6 3
80
6 3 9 .7 1
9 2 1 .5 8
2 9 3 1 .6 5
75
%T
1 3 0 9 .0 8
70
1 2 0 1 .1 2
65
1 4 1 6 .2 7
60
55 1 6 9 0 .1 7
50
4000 3500 3000 2500 2000 1500 1000
Wavenumbers (cm-1)
Fig. 1: Shows the FTIR spectra of the polyethylene oxide /nickel ferrite composites
X Ray Diffraction
The reinforcement of PEO is done by fillers like ferrite nanoparticles which play a major role in strengthening properties of
polymer nanocomposites. When nanosized ferrite particles are magnetic in polymer matrix, then such nanocomposites show
enhanced magnetic and transport properties over their individual constituents. XRD pattern of nickel ferrite (NF) shows all the
peaks corresponds to spinnel ferrite phase matches well with JCPDS data 10-325. The average crystallite size of the NiFe 2O4 was
found to be 30 nm. NiFe2O4 belongs to the class of ferrites with inverse spinel structure.
6000
PEO/Nickel ferrite composite
5000
4000
Intensity (a.u.)
3000
2000
1000
0
0 20 40 60 80
2 (degree)
Fig. 2: Shows the XRD spectra of the polyethylene oxide/nickel ferrite composites
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org 224
DC Conductivity Studies on Polyethylene Oxide/ Nickel Ferrite Composites
(IJSTE/ Volume 3 / Issue 02 / 035)
Scanning Electron Microscopy
TEM analysis revealed that the particles are nearly spherical. The particle size determined from TEM was found to be in close
agreement with that obtained from XRD studies.
Fig. 3: Shows the TEM Image nickel ferrite
DC Conductivity
Conductivity DC electrical conductivity of the Ni-PEO system was found to increase from 8.04 X10-05 (-cm) to 4.71 X10-03
(-cm) at room temperature with the increase in Cu concentration form 0.5 to 2.5 This increase in conductivity is due to the fact
that PEO has smaller value of resistivity as compared to that of Ni (7.010-6 -cm) .The increase in conductivity may be due to
the hopping of electrons between Fe2+ Fe3+ on tetrahedral sites that increases the conduction as PEO is added, which are
produced during sintering.
5
1.4x10 0.5
1.5
5
1.2x10 2.5
5
1.0x10
dc conductivity(S/cm)
4
8.0x10
4
6.0x10
4
4.0x10
4
2.0x10
0.0
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Temprature
Fig. 4: Shows the DC Conductivity of polyethylene oxide /nickel ferrite composites
IV. CONCLUSION
The polyethylene oxide /nickel ferrite composites with different weight percentages of NiFe2O4 in PEO were synthesized by Sol-
Gel method. Detailed characterizations of the nanocomposites were carried out using the techniques such as XRD, FTIR and
TEM,. The results of XRD, FTIR and TEM reveals that the crystalline nature of the NiFe2O4 nanocomposites. FTIR spectra of
the nanocomposites show the characteristic absorption bands which confirm the formation of NiFe2O4/PEO nanocomposites.
The DC conductivity as a function of temperature NiFe2O4/PEO nanocomposites was studied in the temperature range from
30oC-160oC. At higher temperatures, DC conductivity increases because of hopping of polarons from one localized state to
other localized states. The DC conductivity of the nanocomposites increases with an increase in temperature, which is
characteristic behavior of semiconducting materials.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The First author is working as faculty in the Department of S&H and grateful to the management of Farah Institute of
Technology, Chevella for the financial support in the research work.
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org 225
DC Conductivity Studies on Polyethylene Oxide/ Nickel Ferrite Composites
(IJSTE/ Volume 3 / Issue 02 / 035)
REFERENCES
[1] M.A.Ratner, D.F.Shriver, Chem. Rev. 1988, 88,109. DOI: 10.1021/cr00083a006
[2] M.Armand, Polymer Electrolytes Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1986, 16, 254. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.ms.16.080186.001333
[3] Appetecchi G B, Hassoum J, Scrosati B, Croce F, Cassel F and Salomon M J. Power Sources 2003, 124, 246 DOI: 10.1016/S0378-7753(03)00611-6
[4] A. Tiwari, V. Singh, Carbohydrate Polymers 2008, 74, 427 DOI:10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.03.015
[5] K. Hanai, K. Kusagawa, M. Ueno, T. Kobayashi, N. Imanishi, A. Hirano, Y. Takeda, O. Yamamoto, (2010) J. Power Sources 195:2956.
DOI:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.08.087
[6] Xu Q, Wei Y, Liu Y, Ji X, Yang L, Gu M: Preparation of Mg/Fe spinel ferritenanoparticles from Mg/Fe-LDH microcrystallites under mild conditions.Solid
State Sci 2009, 11(2):472-478.
[7] Tian MB: Magnetic Material Beijing: Tsinghua University Press; 2001.
[8] Hu J, Li L-s, Yang W, Manna L, Wang L-w, Alivisatos AP: Linearly PolarizedEmission from Colloidal Semiconductor Quantum Rods. Science 2001,
292(5524):2060-2063.
[9] Sloczynski J, Janas J, Machej T, Rynkowski J, Stoch J: Catalytic activity of chromium spinels in SCR of NO with NH3. Appl Catal B 2000, 24(1):45-60.
[10] Pena MA, Fierro JLG: Chemical Structures and Performance of PerovskiteOxides. Chem Rev 2001, 101(7):1981-2018.
[11] Ajayan PM, Redlich P, Ru"hle M: Structure of carbon nanotube-basednanocomposites. J Micro 1997, 185(2):275-282.
[12] Baykal A, Kasapoglun , Durmus Z, Kavas H, Toprak MS, Koseoglu Y: CTABAssistedHydrothermal Synthesis and Magnetic Characterization ofNiXCo1-
xFe2O4 Nanoparticles (x = 0.0, 0.6, 1.0). Turk J Chem 2009, 33:33-45.
[13] Gunjakar JL, More AM, Gurav KV, Lokhande CD: Chemical synthesis ofspinel nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nano-sheets. Appl Surf Sci 2008,254(18):5844-
5848.
[14] Wang X, Yang G, Zhang Z, Yan L, Meng J: Synthesis of strong-magneticnanosized black pigment ZnxFe3-xO4. Dyes Pigm 2007, 74(2):269-272.
[15] Polymer Electrolyte Reviews; McCallum, J. R., Vincent, C. A.,Eds.; Elsevier Applied Science: London, 1987, 1989; Vols. 1 and 2.
All rights reserved by www.ijste.org 226
You might also like
- Design and Analysis of Magneto Repulsive Wind TurbineDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Magneto Repulsive Wind TurbineIJSTENo ratings yet
- Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Iron Ore Tailings and Glass PowderDocument7 pagesPartial Replacement of Fine Aggregate With Iron Ore Tailings and Glass PowderIJSTENo ratings yet
- Effect of RIB Orientation in Isogrid Structures: Aerospace ApplicationsDocument9 pagesEffect of RIB Orientation in Isogrid Structures: Aerospace ApplicationsIJSTENo ratings yet
- An Implementation and Design A Customized Advanced Image Editor Using Image Processing in MatlabDocument5 pagesAn Implementation and Design A Customized Advanced Image Editor Using Image Processing in MatlabIJSTENo ratings yet
- Development of Relationship Between Saturation Flow and Capacity of Mid Block Section of Urban Road - A Case Study of Ahmedabad CityDocument6 pagesDevelopment of Relationship Between Saturation Flow and Capacity of Mid Block Section of Urban Road - A Case Study of Ahmedabad CityIJSTENo ratings yet
- A Mixture of Experts Model For ExtubationDocument4 pagesA Mixture of Experts Model For ExtubationIJSTENo ratings yet
- Using The Touch-Screen Images For Password-Based Authentication of IlliteratesDocument6 pagesUsing The Touch-Screen Images For Password-Based Authentication of IlliteratesIJSTENo ratings yet
- Onerider The Bike TaxiDocument3 pagesOnerider The Bike TaxiIJSTENo ratings yet
- Wireless Information Process and Power Transfer in Single-User OFDM SystemDocument6 pagesWireless Information Process and Power Transfer in Single-User OFDM SystemIJSTENo ratings yet
- Technology Advancement For Abled PersonDocument9 pagesTechnology Advancement For Abled PersonIJSTENo ratings yet
- Duplicate Detection Using AlgorithmsDocument3 pagesDuplicate Detection Using AlgorithmsIJSTENo ratings yet
- Research On Storage Privacy Via Black Box and Sanitizable SignatureDocument6 pagesResearch On Storage Privacy Via Black Box and Sanitizable SignatureIJSTENo ratings yet
- Study On The Properties of Aerated Concrete Incorporating Fly Ash and Rubber PowderDocument6 pagesStudy On The Properties of Aerated Concrete Incorporating Fly Ash and Rubber PowderIJSTENo ratings yet
- An Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithms For Photovoltaic Systems Using Matlab and Arduino Based RTOS SystemDocument5 pagesAn Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Algorithms For Photovoltaic Systems Using Matlab and Arduino Based RTOS SystemIJSTENo ratings yet
- An Implementation of Matlab Based Platform For The Evaluation of Modulation Techniques Using Multiuser MIMO-OFDM For Visible Light Communications Using MatlabDocument5 pagesAn Implementation of Matlab Based Platform For The Evaluation of Modulation Techniques Using Multiuser MIMO-OFDM For Visible Light Communications Using MatlabIJSTENo ratings yet
- Privacy Preserving: Slicer Based SchemeDocument3 pagesPrivacy Preserving: Slicer Based SchemeIJSTENo ratings yet
- Coupled Shear Wall: A ReviewDocument2 pagesCoupled Shear Wall: A ReviewIJSTE100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Softening & BitumenDocument6 pagesSoftening & Bitumen2020890244No ratings yet
- KOD - Plus-Neo: Store at - 20°CDocument12 pagesKOD - Plus-Neo: Store at - 20°CArga GuruNo ratings yet
- ICLEEN Air PurificatoryDocument20 pagesICLEEN Air PurificatoryWalid ZiadeNo ratings yet
- David Besser - Cambridge IGCSE™ Chemistry Study and Revision Guide Third Edition-Hodder EducationDocument172 pagesDavid Besser - Cambridge IGCSE™ Chemistry Study and Revision Guide Third Edition-Hodder EducationSuha DawNo ratings yet
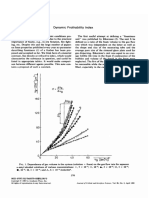
- Dynamic Frothability IndexDocument3 pagesDynamic Frothability IndexjvchiqueNo ratings yet
- Resonance (Q.B.) 13th - PMDDocument12 pagesResonance (Q.B.) 13th - PMDRajeev KaushikNo ratings yet
- SOP 75v4 Specific-Gravity FinalDocument22 pagesSOP 75v4 Specific-Gravity FinalAldwiNo ratings yet
- OlinDocument16 pagesOlinA AhmedNo ratings yet
- Protective & Marine Coatings: General Polymers 3746Document2 pagesProtective & Marine Coatings: General Polymers 3746Efrain Israel Arroyo AlaniaNo ratings yet
- SpectrumPhysicsNovember2015 Ebook3000 PDFDocument84 pagesSpectrumPhysicsNovember2015 Ebook3000 PDFjagannivasNo ratings yet
- Omc Notes 2Document96 pagesOmc Notes 2polypeptideNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Wps OfficeDocument20 pagesLesson Plan-Wps OfficeMargielyn RagosNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Titration NotesDocument3 pagesAcid Base Titration NotesaminahNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Activity of Vitamin e PDFDocument7 pagesAntioxidant Activity of Vitamin e PDFdewiNo ratings yet
- Keerthi M.Nair, Vignesh Kumaravel, Suresh C Pillai Carbonaceous Cathode Materials For Electro-Fenton TechnologyDocument142 pagesKeerthi M.Nair, Vignesh Kumaravel, Suresh C Pillai Carbonaceous Cathode Materials For Electro-Fenton TechnologyVăn Thành MaiNo ratings yet
- Siemens Dishwasher ManualDocument28 pagesSiemens Dishwasher ManualChrister NilssonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CausticizerDocument7 pagesIntroduction To CausticizerMageshwaran NNo ratings yet
- Basics in NMRDocument75 pagesBasics in NMRPrashant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Momentum LabDocument3 pagesMomentum LabSam Anderson50% (4)
- SF6 Circuit BreakerDocument2 pagesSF6 Circuit BreakerkashifNo ratings yet
- Teacher: Mervi Vera Buitron de Gratal Trabajo Grupal: 1) Giron Ugarte, Luis AurelioDocument3 pagesTeacher: Mervi Vera Buitron de Gratal Trabajo Grupal: 1) Giron Ugarte, Luis AurelioNaomi HerreraNo ratings yet
- 03 Doetsch PDFDocument10 pages03 Doetsch PDFNeelima MishraNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word Document جديد Document6 pagesMicrosoft Word Document جديد seraj ibramemNo ratings yet
- LG Pqrcvsl0qw Owners ManualDocument34 pagesLG Pqrcvsl0qw Owners ManualThanhquy NguyenNo ratings yet
- ChromatographyDocument15 pagesChromatographyManogna Sai PadiNo ratings yet
- JPCB Salt Praveen - 2Document2 pagesJPCB Salt Praveen - 2Vahid SarfarazNo ratings yet
- The Performance Evaluation On The Effectiveness of Nspri's IceFish BoxDocument5 pagesThe Performance Evaluation On The Effectiveness of Nspri's IceFish BoxInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Welding - Fissures DefectDocument12 pagesWelding - Fissures DefectthanhNo ratings yet
- A Simplified Method For Analysis of Inorganic Phosphate in The Presence of Interfering Substances.Document9 pagesA Simplified Method For Analysis of Inorganic Phosphate in The Presence of Interfering Substances.muratout3447No ratings yet