Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients in Heat Exchangers
Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients in Heat Exchangers
Uploaded by
blondonantonio0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesOriginal Title
Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients in Heat Exchangers.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesTypical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients in Heat Exchangers
Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients in Heat Exchangers
Uploaded by
blondonantonioCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients in Heat Exchangers
U U
Type Application and Conditions 2 Btu/(ft2 F
1)
W/(m K)
h)1)
Tubular, heating or Gases at atmospheric pressure inside and
5 - 35 1-6
cooling outside tubes
Gases at high pressure inside and outside 150 -
25 - 90
tubes 500
Liquid outside (inside) and gas at atmospheric
15 - 70 3 - 15
pressure inside (outside) tubes
Gas at high pressure inside and liquid outside 200 -
35 - 70
tubes 400
150 -
Liquids inside and outside tubes 25 - 200
1200
300 -
Steam outside and liquid inside tubes 50 - 200
1200
Tubular, 1500 - 250 -
Steam outside and cooling water inside tubes
condensation 4000 700
Organic vapors or ammonia outside and 300 -
50 - 200
cooling water inside tubes 1200
steam outside and high-viscous liquid inside 300 -
Tubular, evaporation 50 - 150
tubes, natural circulation 900
steam outside and low-viscous liquid inside 600 - 100 -
tubes, natural circulation 1700 300
steam outside and liquid inside tubes, forced 900 - 150 -
circulation 3000 500
Air-cooled heat 600 - 100 -
Cooling of water
exchangers2) 750 130
400 -
Cooling of liquid light hydrocarbons 70 - 95
550
Cooling of tar 30 - 60 5 - 10
Cooling of air or flue gas 60 - 180 10 - 30
200 -
Cooling of hydrocarbon gas 35 - 80
450
700 - 125 -
Condensation of low pressure steam
850 150
350 -
Condensation of organic vapors 65 - 90
500
1000 - 150 -
Plate heat exchanger liquid to liquid
4000 700
Spiral heat 700 - 125 -
liquid to liquid
exchanger 2500 500
900 - 150 -
condensing vapor to liquid
3500 700
http://www.cheresources.com/uexchangers.shtml
http://www.engineeringtoolbox.com/heat-transfer-coefficients-exchangers-d_450.html
You might also like
- 02 - Cabin Slim Ac Ug 2 D - 21 enDocument13 pages02 - Cabin Slim Ac Ug 2 D - 21 enkdc termice100% (1)
- Overall Heat TransferDocument9 pagesOverall Heat TransferRahul S. ChandrawarNo ratings yet
- Coeficientes de Calor 2Document3 pagesCoeficientes de Calor 2Hector BarriosNo ratings yet
- Engineering Page - Heat Exchangers - Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients PDFDocument2 pagesEngineering Page - Heat Exchangers - Typical Overall Heat Transfer Coefficients PDFJahidul IslamNo ratings yet
- HeatExchanger Part2Document81 pagesHeatExchanger Part2mohammad abusarhanNo ratings yet
- Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient TableDocument2 pagesOverall Heat Transfer Coefficient TableooichinhuiNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Coefficients For Submerged CoilsDocument70 pagesHeat Transfer Coefficients For Submerged CoilsAdam JinNo ratings yet
- Hvac Assignment: Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient, Compressor, Effects of Bend On DuctDocument29 pagesHvac Assignment: Overall Heat Transfer Coefficient, Compressor, Effects of Bend On DuctNeerajaNo ratings yet
- Buhar Boru Teknik - TablolarDocument19 pagesBuhar Boru Teknik - TablolarEnes BayramNo ratings yet
- Burner Start-Up Quick Guide: Appendix ADocument3 pagesBurner Start-Up Quick Guide: Appendix ADIAGNENo ratings yet
- Convective Heat Transfer Coefficients Table Chart - Engineers Edge - WWW - EngineersedgeDocument4 pagesConvective Heat Transfer Coefficients Table Chart - Engineers Edge - WWW - Engineersedgenikhil3005No ratings yet
- Increasing Heat Exchanger PerformanceDocument13 pagesIncreasing Heat Exchanger Performanceimtinan mohsinNo ratings yet
- HF 745 02 T eDocument4 pagesHF 745 02 T eNuñez JesusNo ratings yet
- Type Application and Conditions: W/ (M K) Btu/ (FT °F H)Document2 pagesType Application and Conditions: W/ (M K) Btu/ (FT °F H)Debkumar958No ratings yet
- ITT Standard Gould SpecDocument12 pagesITT Standard Gould SpecDendi DenisNo ratings yet
- Appendix B & CDocument3 pagesAppendix B & CJohn Louie PimentelNo ratings yet
- Pengolahan Pipa Bengkok Dan Pipa UDocument3 pagesPengolahan Pipa Bengkok Dan Pipa UnoviNo ratings yet
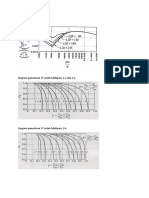
- Penentuan Koefisien H: Diagram Penentuan FT Untuk Multipass 1-2 Dan 1-4Document3 pagesPenentuan Koefisien H: Diagram Penentuan FT Untuk Multipass 1-2 Dan 1-4Novianti NoviNo ratings yet
- Parker B Series Ball ValvesDocument12 pagesParker B Series Ball ValvesCesar ZarateNo ratings yet
- HeatPump enDocument4 pagesHeatPump enArunee SombatjindaNo ratings yet
- Gas Quality INGAA Presentation 2004Document34 pagesGas Quality INGAA Presentation 2004sabrineNo ratings yet
- UFK W AftercoolerDocument3 pagesUFK W AftercoolerLiem NguyenNo ratings yet
- MidsemwasteheatrecoveryDocument11 pagesMidsemwasteheatrecoveryPranav OmkarNo ratings yet
- Setyo KalorDocument2 pagesSetyo KalorstyoNo ratings yet
- Ebara PumpDocument25 pagesEbara PumpMark CentenoNo ratings yet
- Fluxes: Forms of Filler MetalsDocument7 pagesFluxes: Forms of Filler MetalsWilly UioNo ratings yet
- الرسومات و الجداول الخاصة بالمبادل الحراريDocument11 pagesالرسومات و الجداول الخاصة بالمبادل الحراريمحمد عليNo ratings yet
- Thermo Dynamics Sheet3Document3 pagesThermo Dynamics Sheet3Kerro MankoNo ratings yet
- Some Practical Considerations in The Design of Steam Injection WellsDocument8 pagesSome Practical Considerations in The Design of Steam Injection Wellsfjflores26No ratings yet
- Different Types of Refrigeration SystemDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of Refrigeration SystemRavi Shankar67% (3)
- How To Select The Right Flange Gasket - Projectmaterials PDFDocument1 pageHow To Select The Right Flange Gasket - Projectmaterials PDFWiskusa NarudeanNo ratings yet
- Corrosion and Cracking in Recovery BoilersDocument23 pagesCorrosion and Cracking in Recovery BoilersAndy Herdyal SitumorangNo ratings yet
- 9000 SeriesDocument32 pages9000 SeriesTechnical A-Star Testing & Inspection MalaysiaNo ratings yet
- LPG Flex ENDocument4 pagesLPG Flex ENSEBASDAZACNo ratings yet
- Multi-Rifled Seamless Cold Drawn Boiler Tubes For Power GenerationDocument8 pagesMulti-Rifled Seamless Cold Drawn Boiler Tubes For Power GenerationAgniva DuttaNo ratings yet
- Ex Air Vortex TubeDocument8 pagesEx Air Vortex TubeSyed AmirNo ratings yet
- 2015 L14 Distillation Applications - Refinery Distillation PDFDocument27 pages2015 L14 Distillation Applications - Refinery Distillation PDFfegcopNo ratings yet
- Dehumidifiers For Radiant Cooling Systems With Heat Recovery: VersionsDocument6 pagesDehumidifiers For Radiant Cooling Systems With Heat Recovery: VersionsNikosNo ratings yet
- Spray Water - Rev 00Document2 pagesSpray Water - Rev 00Jacky KaruppaiahNo ratings yet
- Keller & BohacekDocument3 pagesKeller & BohacekCarlos TomeyNo ratings yet
- Is S SE E E SE S SE S SE S: Water Storage - CalorifierDocument4 pagesIs S SE E E SE S SE S SE S: Water Storage - CalorifierJust RysdanNo ratings yet
- Air Treatment Product Line Cross ReferenceDocument1 pageAir Treatment Product Line Cross Referenceingenieria_377024831No ratings yet
- Data Sheet-FIREMIKS-FM-14000-GP-F-Aut 2016-02-23Document3 pagesData Sheet-FIREMIKS-FM-14000-GP-F-Aut 2016-02-23appril26No ratings yet
- CLM Series Steam & Water BoilersDocument4 pagesCLM Series Steam & Water BoilersAlexánder Muñoz FerrerNo ratings yet
- Madukismo Water TreatmentDocument119 pagesMadukismo Water TreatmentFadli Ryan ArikundoNo ratings yet
- Catalog Deaerator, Model Deg 8000 PDFDocument2 pagesCatalog Deaerator, Model Deg 8000 PDFHưng QuangNo ratings yet
- Valve Classification SchedulesDocument1 pageValve Classification SchedulesAbd Elrahman HamdyNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Cooling Units For Door or Wall Mounting: Characteristics M.U. EMO04BM1B EMO04CM1B Accessories/OptionsDocument1 pageOutdoor Cooling Units For Door or Wall Mounting: Characteristics M.U. EMO04BM1B EMO04CM1B Accessories/OptionsTomasz KownackiNo ratings yet
- Iti Thermjet Usa (Eclipse)Document38 pagesIti Thermjet Usa (Eclipse)exergicNo ratings yet
- Sno Service Pipe Material: 4. Non Ibr PipingsDocument1 pageSno Service Pipe Material: 4. Non Ibr PipingsArun KumarNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Network Synthesis (HENS/)Document56 pagesHeat Exchanger Network Synthesis (HENS/)vijendra mauryaNo ratings yet
- Chloride Ball Valve FLVDocument7 pagesChloride Ball Valve FLVLenin MagañaNo ratings yet
- Etaline Type SeriesDocument48 pagesEtaline Type SeriesChristopher Greg PermisonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document12 pagesChapter 2Shreshth BhargavaNo ratings yet
- Solimpeks Solar Water HeaterDocument8 pagesSolimpeks Solar Water HeaterInter Solar EgyptNo ratings yet
- Dati Tecnici TB EDocument2 pagesDati Tecnici TB ExilentstrikeNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Non-Stationary Heat Transfer Through Walls, Measurement of Thermal Conductivity, Heat Transfer with Two Phase RefrigerantsFrom EverandHeat Transfer: Non-Stationary Heat Transfer Through Walls, Measurement of Thermal Conductivity, Heat Transfer with Two Phase RefrigerantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- Resco Product Brochures (Usa) Aluminum Melting and Holding FurnaceDocument4 pagesResco Product Brochures (Usa) Aluminum Melting and Holding FurnaceWill DNo ratings yet
- Valves & Fittings PDFDocument24 pagesValves & Fittings PDFFahad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Indicators & PH CurvesDocument35 pagesIndicators & PH CurvesSairam PrasathNo ratings yet
- Debutanizer Reb FoulingDocument4 pagesDebutanizer Reb FoulingAmit YadavNo ratings yet
- Stance 161 - Valves For Special ChemicalsDocument5 pagesStance 161 - Valves For Special ChemicalsPhyu Mar Thein KyawNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument34 pagesChemical EquilibriumLala Rifa0% (1)
- Din 7603Document10 pagesDin 7603Marcin100% (1)
- Emulsion LectureDocument55 pagesEmulsion Lecturehermella tegegneNo ratings yet
- Maintain Training FacilitiesDocument14 pagesMaintain Training Facilitiesrodel megollasNo ratings yet
- Identification of Rocks and Minerals PDFDocument22 pagesIdentification of Rocks and Minerals PDFIkhwan Z.80% (15)
- Extraction of Active Principles From Natural SourcesDocument9 pagesExtraction of Active Principles From Natural SourcesSiddarth PalletiNo ratings yet
- System Bekaplast™: Plastics EngineeringDocument5 pagesSystem Bekaplast™: Plastics EngineeringMau Atenas PerezNo ratings yet
- Outline: Junction and MOS Electrostatics (III)Document17 pagesOutline: Junction and MOS Electrostatics (III)garu1991No ratings yet
- BoltsDocument6 pagesBoltsJuragan IwalNo ratings yet
- 187-19 Wpqc-W161-2''-Asme XiDocument1 page187-19 Wpqc-W161-2''-Asme Xibouchoucha jebaliNo ratings yet
- DS 9303 e OWAtecta Installation Guide 121400Document40 pagesDS 9303 e OWAtecta Installation Guide 121400DianaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Surface Roughness and Cutting Force Components in Hard Turning With CBN Tool - Prediction Model and Cutting Conditions OptimizationDocument10 pagesAnalysis of Surface Roughness and Cutting Force Components in Hard Turning With CBN Tool - Prediction Model and Cutting Conditions OptimizationadarshgitamNo ratings yet
- Swagelok-Hose and Flexible Tubing CatalogDocument109 pagesSwagelok-Hose and Flexible Tubing CatalogDağhan ArpacıNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Air PressureDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 6 Air PressureSanjana ShahNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Generale FPD 100 Ea4Document76 pagesCatalogue Generale FPD 100 Ea4Achraf BoudayaNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAjay EadakeNo ratings yet
- Kilns and Furnaces Used in Ceramic and Refractory IndustriesDocument4 pagesKilns and Furnaces Used in Ceramic and Refractory IndustriesDwiky SuryaNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design and Ductile Detailing - BIT WardhaDocument109 pagesSeismic Design and Ductile Detailing - BIT WardhaDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATENo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY 2 Monduli District Pre NationDocument5 pagesCHEMISTRY 2 Monduli District Pre NationJackson KilasiNo ratings yet
- Ceplattyn Cleaner - Pi - (Gb-En)Document2 pagesCeplattyn Cleaner - Pi - (Gb-En)Michael KimNo ratings yet
- Standardization NaOHDocument5 pagesStandardization NaOHgiyagirlsNo ratings yet
- ICON - Sandwich PanelsDocument32 pagesICON - Sandwich Panelsnu.arabiaNo ratings yet
- 11th STD Chemistry TN BoardDocument103 pages11th STD Chemistry TN Boardpriya gopalakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Physics Hooke's LawDocument11 pagesLab Report Physics Hooke's LawAbu Huzaifah100% (1)
- Foot and Leg Protectors Ð Requirements and Test Methods For Toecaps and Metal Penetration Resistant InsertsDocument19 pagesFoot and Leg Protectors Ð Requirements and Test Methods For Toecaps and Metal Penetration Resistant InsertsArif Hasnat JonyNo ratings yet