Professional Documents
Culture Documents
T H e Multipole Expansion: Today
Uploaded by
EddieOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
T H e Multipole Expansion: Today
Uploaded by
EddieCopyright:
Available Formats
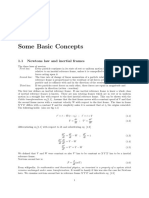
3.
9 T h e Multipole Expansion 83
We set
y1 = 21 + 2 2 , y2 = 21 -22,
so that
1 1
21 = -(Y1
2
+ Y d , 2 2 = -(Y1
2
- YZ),
and E is then diagonalised, i.e.
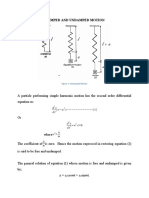
Quantum mechanically this is
For the difference with Eo, i.e. with no dipole-dipole interacion, we obtain for the ground state of
the system (N1 = 0, N2 = 0 )
= ; h o ( / G + / - - 2 )
N -1h o (
2
- $) K -.1
R6
This is an energy similar to that of a van der Waals force. One can look at this calculation as a
rough physical model of the Casimir effect in producing the potential K l / R 6 , at least this was
suggested in the 1iterature.q Actually the Casimir effect is a boundary effect, as we shall see in
Chapter 20.
qSee D. Kleppner, Physics Today (Oct. 1990) 9; cf. also the Casimir effect in Chapter 20.
You might also like
- 2 BhthermoDocument11 pages2 Bhthermorajarshi234No ratings yet
- Notes On Solving The Black-Scholes EquationDocument20 pagesNotes On Solving The Black-Scholes EquationCaroline YanNo ratings yet
- Wavelets and Subband Coding Solutions ManualDocument90 pagesWavelets and Subband Coding Solutions Manualwilliam_windsor100% (8)
- Example 21.12: Field of A Uniformly Charged DiskDocument3 pagesExample 21.12: Field of A Uniformly Charged Diskعبدالرحمن التميميNo ratings yet
- CM 17 Small OscillationsDocument6 pagesCM 17 Small Oscillationsosama hasanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21: The One Dimensional Wave Equation: D'Alembert's SolutionDocument5 pagesLecture 21: The One Dimensional Wave Equation: D'Alembert's SolutionBryan NanaNo ratings yet
- ScatteringDocument23 pagesScatteringDeniz MostaracNo ratings yet
- Physics 430: Lecture 15 Lagrange's Equations: Dale E. GaryDocument16 pagesPhysics 430: Lecture 15 Lagrange's Equations: Dale E. GaryfaniNo ratings yet
- Physics, General Relativity: Homework Due Wednesday, NovemberDocument5 pagesPhysics, General Relativity: Homework Due Wednesday, NovemberMaci CostaNo ratings yet
- Special FunDocument10 pagesSpecial FunJHNo ratings yet
- Homework 5 Progressive Wave ShapeDocument2 pagesHomework 5 Progressive Wave ShapeSwathi BDNo ratings yet
- MA1512 Tutorial 5 SolutionsDocument7 pagesMA1512 Tutorial 5 SolutionsWeiyen NgNo ratings yet
- Peat8002 - Seismology: Lecture 5: Surface Waves and DispersionDocument37 pagesPeat8002 - Seismology: Lecture 5: Surface Waves and DispersionAhmad Maulana SidikNo ratings yet
- RHO Periodic PDFDocument4 pagesRHO Periodic PDFPrabhat NarangNo ratings yet
- Goldstein 31 32 7Document8 pagesGoldstein 31 32 7Dijana TolićNo ratings yet
- Action PDFDocument12 pagesAction PDFHugo VentimigliaNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter2Document65 pagesHeat Chapter2Ab AnNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts: 1.1 Newtons Law and Inertial FramesDocument16 pagesSome Basic Concepts: 1.1 Newtons Law and Inertial Framestbrackman99No ratings yet
- Coupled OscillationDocument26 pagesCoupled OscillationSwarnava BaruiNo ratings yet
- Phase Velocity and Group VelocityDocument29 pagesPhase Velocity and Group VelocityDebanuj BasakNo ratings yet
- bk978 0 7503 1401 5ch1Document19 pagesbk978 0 7503 1401 5ch1Putu IndraNo ratings yet
- 3 Partial Differential EquationsDocument8 pages3 Partial Differential EquationsRoy VeseyNo ratings yet
- 0054 Handout 8Document12 pages0054 Handout 8zcaptNo ratings yet
- Wave EquationDocument14 pagesWave EquationSawon KhanNo ratings yet
- Torus Magnetic MomentDocument6 pagesTorus Magnetic MomentBen WaterglowNo ratings yet
- Energy Is Static Electric Fields:: N M M MDocument4 pagesEnergy Is Static Electric Fields:: N M M MJoel DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Educative Jee (Mathematics) : Errata For Second EditionDocument2 pagesEducative Jee (Mathematics) : Errata For Second EditionDheeraj MauryaNo ratings yet
- Jackson Electrodynamics Chapter 1 SolutionDocument13 pagesJackson Electrodynamics Chapter 1 SolutionHayanNo ratings yet
- 7.16 (Bourjaily)Document1 page7.16 (Bourjaily)harrypotter403No ratings yet
- My Favorite Number:: John Baez September 19, 2008 The Rankin Lectures Supported by The Glasgow Mathematical Journal TrustDocument50 pagesMy Favorite Number:: John Baez September 19, 2008 The Rankin Lectures Supported by The Glasgow Mathematical Journal TrustNazim ImpulsNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics and Relativity: Immediately Not Accelerating NoDocument65 pagesElectrodynamics and Relativity: Immediately Not Accelerating No張恩睿 CHANG,EN-RUEI C24101147No ratings yet
- Electrical Potential: 1 Partial DerivativesDocument8 pagesElectrical Potential: 1 Partial Derivativesmughees_itcompNo ratings yet
- Application of Laplace Transform - Two Masses On SpringsDocument3 pagesApplication of Laplace Transform - Two Masses On SpringsCharles100% (1)
- The Double Pendulum - Lagrangian Formulation - Diego AssencioDocument8 pagesThe Double Pendulum - Lagrangian Formulation - Diego AssencioAbril jimenezNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Quad4 - ImplementationDocument4 pages0.1 Quad4 - ImplementationDavide QuadrelliNo ratings yet
- Defslt Lec # 04 15-01-21Document5 pagesDefslt Lec # 04 15-01-21AkashNo ratings yet
- Unsteady Flow Over A Wavy Wall: ViscousDocument16 pagesUnsteady Flow Over A Wavy Wall: ViscousSrinivas JangiliNo ratings yet
- E Dxdy + K e Dxdy 2K e Dxdy: 0 0 +y) /2 (2x +y) /2 (2x +y) /2 0 0 0 0Document3 pagesE Dxdy + K e Dxdy 2K e Dxdy: 0 0 +y) /2 (2x +y) /2 (2x +y) /2 0 0 0 0Bhargavi MopuruNo ratings yet
- 0.1 Quad8 (Serendipity) - ImplementationDocument4 pages0.1 Quad8 (Serendipity) - ImplementationDavide QuadrelliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 ExamplesDocument11 pagesChapter 6 ExamplesSurya NarasimanNo ratings yet
- Chap 20Document18 pagesChap 202tlfdlNo ratings yet
- Ij I I I I: 2 Jacob Lewis BourjailyDocument2 pagesIj I I I I: 2 Jacob Lewis BourjailySaul Perez BNo ratings yet
- MIT8 334S14 Lec15Document6 pagesMIT8 334S14 Lec15Luiza mirandaNo ratings yet
- Derivation of Fresnel DiffractionDocument5 pagesDerivation of Fresnel DiffractionWhalsy nNo ratings yet
- Mixed Crack PropagateDocument7 pagesMixed Crack PropagateMohammad Suriyaidulman RianseNo ratings yet
- PHY 5246: Theoretical Dynamics, Fall 2015 September 28, 2015 Midterm Exam # 1Document9 pagesPHY 5246: Theoretical Dynamics, Fall 2015 September 28, 2015 Midterm Exam # 1Jennifer RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Am 53Document11 pagesAm 53Mikael Yuan EstuariwinarnoNo ratings yet
- Ncert Exemplar Math Class 12 Chapter 09 Differential EquationsDocument49 pagesNcert Exemplar Math Class 12 Chapter 09 Differential EquationsAnitaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fluid Mechanics Kundu 4e Solution ManualDocument155 pagesIntroduction To Fluid Mechanics Kundu 4e Solution ManualAyush DeoreNo ratings yet
- Assignment1 SolutionDocument16 pagesAssignment1 Solutiondagani ranisamyukthaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Problem Set 6Document8 pagesSolutions To Problem Set 6IsmaelGalvanPaniaguaNo ratings yet
- Damped and Undamped MotionDocument16 pagesDamped and Undamped MotionWisdom CleverNo ratings yet
- Ideal Fermi Gas: 13.1 Equation of StateDocument14 pagesIdeal Fermi Gas: 13.1 Equation of StateShalltear BloodFallenNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1. Solve The Linearized Governing Equations (Laplace and Bottom Boundary Condition, EquaDocument5 pagesExercise 1. Solve The Linearized Governing Equations (Laplace and Bottom Boundary Condition, EquaSwathi BDNo ratings yet
- Mixed Crack PropagateDocument13 pagesMixed Crack PropagateMohammad Suriyaidulman RianseNo ratings yet
- Zuber CFT LecturesDocument36 pagesZuber CFT LecturesguilleasilvaNo ratings yet
- 2D - Homogeneous Turbulence NotesDocument31 pages2D - Homogeneous Turbulence NotesjjubuchNo ratings yet
- Mit18 02sc Mnotes Cv3Document5 pagesMit18 02sc Mnotes Cv3Tara Chandra PanjiyarNo ratings yet
- Termoproblema 3Document30 pagesTermoproblema 3Joshua WrightNo ratings yet
- Duality A N D Magnetic MonopolesDocument1 pageDuality A N D Magnetic MonopolesEddieNo ratings yet
- Introduction EqDocument1 pageIntroduction EqEddieNo ratings yet
- 14.9 Energy Transport in Wave Guides: D Z D L, Where DL Is An Element of The PathDocument1 page14.9 Energy Transport in Wave Guides: D Z D L, Where DL Is An Element of The PathEddieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21. Duality A N D Magnetic Monopoles: Regularisation The Monopole FieldDocument1 pageChapter 21. Duality A N D Magnetic Monopoles: Regularisation The Monopole FieldEddieNo ratings yet
- AN THE Between Magnetic: Analytic Solution For Force TWO DipolesDocument14 pagesAN THE Between Magnetic: Analytic Solution For Force TWO DipolesEddieNo ratings yet
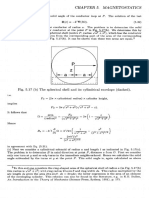
- M, Po (H + M) - H: Macroscopic MagnetostaticsDocument1 pageM, Po (H + M) - H: Macroscopic MagnetostaticsEddieNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic: WavesDocument1 pageElectromagnetic: WavesEddieNo ratings yet
- Themaxwell Equations: LoopDocument1 pageThemaxwell Equations: LoopEddieNo ratings yet
- 250 PDFDocument1 page250 PDFEddieNo ratings yet
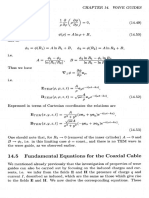
- 14.5 Fundamental Equations The Coaxial Cable: GuidesDocument1 page14.5 Fundamental Equations The Coaxial Cable: GuidesEddieNo ratings yet
- 33 PDFDocument1 page33 PDFEddieNo ratings yet
- The Lihnard-Wiechert Potentials Moving Point Charge: J (R, Ro (T) )Document1 pageThe Lihnard-Wiechert Potentials Moving Point Charge: J (R, Ro (T) )EddieNo ratings yet
- (E - D + H - B) V - (E X H) + J - e .: R, L I RDocument1 page(E - D + H - B) V - (E X H) + J - e .: R, L I REddieNo ratings yet
- 29 PDFDocument1 page29 PDFEddieNo ratings yet
- Magne Tostatics: B (R) - K'V (IR)Document1 pageMagne Tostatics: B (R) - K'V (IR)EddieNo ratings yet
- Examples 177: MD MDDocument1 pageExamples 177: MD MDEddieNo ratings yet
- 88 PDFDocument1 page88 PDFEddieNo ratings yet
- 88 PDFDocument1 page88 PDFEddieNo ratings yet
- Solutions Manual To Irodov General Problems in Physics - Mechanics - Problems From 76 To 100Document30 pagesSolutions Manual To Irodov General Problems in Physics - Mechanics - Problems From 76 To 100EddieNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Presentation of Macroscopic Electrodynamics: FclosedDocument1 page1.2 Presentation of Macroscopic Electrodynamics: FclosedEddieNo ratings yet
- 41 (PLL (P2l - : P12) QL 4 2 P22) QDocument1 page41 (PLL (P2l - : P12) QL 4 2 P22) QEddieNo ratings yet
- UnitsDocument1 pageUnitsEddieNo ratings yet
- Applications Electrostatics: KQ KR KR 8 R 8 R r3 KP-R R r3 r3 4 (R)Document1 pageApplications Electrostatics: KQ KR KR 8 R 8 R r3 KP-R R r3 r3 4 (R)EddieNo ratings yet
- 3.7 Conjugate Functions: Example 3.14: Electrolytic Determination of The CapacityDocument1 page3.7 Conjugate Functions: Example 3.14: Electrolytic Determination of The CapacityEddieNo ratings yet
- E Iey: Be) X Y'BeDocument1 pageE Iey: Be) X Y'BeEddieNo ratings yet