Professional Documents
Culture Documents
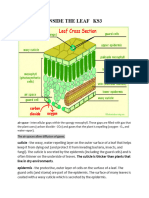
Cuticle Upper Epidermis Palisade Mesophyll Spongy Mesophyll Lower Epidermis Vascular Bundle Xylem Phloem
Uploaded by
MinsiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cuticle Upper Epidermis Palisade Mesophyll Spongy Mesophyll Lower Epidermis Vascular Bundle Xylem Phloem
Uploaded by
MinsiCopyright:
Available Formats
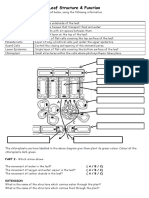
*ACTIVITY 21 : LEAF STRUCTURE
1. Give the different layers found in the leaf give the function of each. Identify the type of
tissue found in each layer
Internal Leaf Structure
a) Cuticle: Waxy layer water proofing upper leaves.
b) Upper epidermis: Upper layer of cells. No chloroplasts. Protection.
c) Palisade Mesophyll: Tightly packed upper layer of chloroplast containing cells.
d) Spongy Mesophyll: Lower layer of chloroplast containing cells. Air spaces around them.
e) Lower Epidermis: Lower external layer of cells in leaf.
f) Vascular Bundle: Bundle of many vessels (xylem and phloem) for transport.
g) Xylem: Living vascular system carrying water & minerals throughout plant.
h) Phloem: Living vascular system carrying dissolved sugars and organic compounds
throughout plant.
i) Guard Cells: 2 cells surrounding stomata that control rate of gas & water exchange.
j) Stomata: Opening between guard cells for gas & water exchange.
2. give and describe the external parts of the leaf (tabulated)
Leaf Blade: Wide flattened area of leaf for concentrating sunlight on photosynthetic cells.
Petiole: Short stem that attaches leaf to main stem or branch.
Veins: Vascular bundles within leaf for transort.
Node: Growth region of stem where leaves or new branches arise.
Axillary bud: Baby leaf or stem (next years growth)
3. give the functions of the leaf
Function of Leaves:
a. Increase surface area for Photosynthesis.
b. Gas exchange (CO2 in, O2 out).
c. Site of transpiration, evaporation of water that helps pull water up from roots.
You might also like
- Exercise 7 Leaf MorphologyDocument6 pagesExercise 7 Leaf MorphologyVanessaOlgaJ.DagondonNo ratings yet
- Leaf Anatomy LabDocument4 pagesLeaf Anatomy LabSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Importance of PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesImportance of PhotosynthesisSuhaan HussainNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument11 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneDocument6 pagesChapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneApostolos KoutsaftisNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2A - Plant AnatomyDocument48 pagesUNIT 2A - Plant AnatomyMyreal Venice CrudaNo ratings yet
- Report SheetDocument6 pagesReport SheetMikhail LandichoNo ratings yet
- Plant Organs Is A Collection of Plant Tissues That Have Specific Functions. Kinds of Plant Organs Are Root, Stem, Leaf and FlowerDocument15 pagesPlant Organs Is A Collection of Plant Tissues That Have Specific Functions. Kinds of Plant Organs Are Root, Stem, Leaf and FlowerkuwukNo ratings yet
- Semester One Exam Notes OfficialDocument23 pagesSemester One Exam Notes OfficialNethumleeNo ratings yet
- ST Joseph's Institution (Senior School) IBDP1 HL Biology PracticalDocument5 pagesST Joseph's Institution (Senior School) IBDP1 HL Biology PracticalSean NgNo ratings yet
- Leaf Structure Worksheet Low Ability Exit TicketDocument1 pageLeaf Structure Worksheet Low Ability Exit Ticketozman100% (1)
- Lab 16Document5 pagesLab 16bridgettNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Plant PhysiologyDocument27 pagesAnatomy & Plant Physiologyshree devNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plant Notes Apr13 - 1Document18 pagesTransport in Plant Notes Apr13 - 1Danes WaranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Young Dicot RootDocument3 pagesAnatomy of A Young Dicot RootVanessa Leuterio0% (2)
- (Pic On Pg. 131 in Our Manual Is More Descriptive) : Internal Anatomy of The LeafDocument2 pages(Pic On Pg. 131 in Our Manual Is More Descriptive) : Internal Anatomy of The LeafIvana BrijlallNo ratings yet
- Biology SS1 2ND Term E-NotesDocument51 pagesBiology SS1 2ND Term E-NotesINIOLUWA AKEJU100% (3)
- Science 9 Q1melc 5 Plant Structure For PhotosynthesisDocument41 pagesScience 9 Q1melc 5 Plant Structure For PhotosynthesisMenchie YabaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Gr.11 Lesson 21 Photosynthesis IntroductionDocument22 pagesLife Sciences Gr.11 Lesson 21 Photosynthesis Introductiontmalatji106No ratings yet
- Biology 11: Kingdom Plantae: Unit TopicsDocument18 pagesBiology 11: Kingdom Plantae: Unit TopicsMariel AnaNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Document42 pagesForm 5 Biology Chapter 1 Transport (D)Marcus LeeNo ratings yet
- Leaf Structure WorksheetDocument1 pageLeaf Structure Worksheetapi-309893409100% (1)
- Dokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyDocument11 pagesDokumen - Tips Lab 3 Report Plant AnatomyAin SufizaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Plant PhysiologyDocument5 pagesLab Report Plant Physiologysarahyahaya100% (1)
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesAnatomy of Flowering PlantsSadik FsNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues and Organs LabDocument8 pagesPlant Tissues and Organs LabKayleigh SullivanNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & LeavesDocument38 pagesPhotosynthesis & LeavesSanthoshNo ratings yet
- Reinforcement Plant Growth: Beaconhouse School System Unit: Class: VIIDocument8 pagesReinforcement Plant Growth: Beaconhouse School System Unit: Class: VIIAleena Zahra Naqvi/TCHR/BMBNo ratings yet
- Sample Exam Answers: Mark TwainDocument8 pagesSample Exam Answers: Mark TwainThiagoPereiraNo ratings yet
- 9.12 Plant TissuesDocument3 pages9.12 Plant TissuesGodfrey ObingoNo ratings yet
- Plant AnatomyDocument8 pagesPlant Anatomyharshith0100No ratings yet
- G-10 Biology, 4.1 The LeafDocument2 pagesG-10 Biology, 4.1 The Leafjohn nigussieNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Class 11Document6 pagesModule 2 Class 11ishikamalik470No ratings yet
- CAPE PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesCAPE PhotosynthesisIsheba Warren100% (24)
- Plants Biology 2Document11 pagesPlants Biology 2Hiral KatyalNo ratings yet
- 30.4C: Leaf Structure, Function, and Adaptation: Key PointsDocument3 pages30.4C: Leaf Structure, Function, and Adaptation: Key PointsTresha CosmeñoNo ratings yet
- Bio LabDocument13 pagesBio Labapi-3730385100% (9)
- CC CC: Cva A A AaaDocument5 pagesCC CC: Cva A A AaaPaul Alfred Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Inside The Leaf KS3Document2 pagesInside The Leaf KS3Ziya JiwaniNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument3 pagesPlantsAby LimNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Plant - LeavesDocument9 pagesParts of A Plant - Leavesmizah87No ratings yet
- Esensial Chapter 4 Grade 7-1Document28 pagesEsensial Chapter 4 Grade 7-1Cleona EinarNo ratings yet
- Campbell Biology 12th Edition SummaryDocument6 pagesCampbell Biology 12th Edition Summaryprincesje05No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper-04 (Solved)Document14 pagesCBSE Class 11 Biology Sample Paper-04 (Solved)cbsesamplepaper0% (1)
- Alido, Charlito VDocument5 pagesAlido, Charlito VCharlito AlidoNo ratings yet
- Plant's Metabolic ProcessesDocument19 pagesPlant's Metabolic Processesniquitafayediaz8No ratings yet
- Biozone 2 PG 342Document3 pagesBiozone 2 PG 342Ji-Soo KimNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2.2-2.3Document15 pagesChapter 2.2-2.3Gerard Bio100% (2)
- 9.1 Plant Structure and Growth: Topic 9: Plant Science (HL)Document6 pages9.1 Plant Structure and Growth: Topic 9: Plant Science (HL)Morgan LockeNo ratings yet
- Plant StructureDocument33 pagesPlant Structurevioleotero850No ratings yet
- B4, Part 2 Plant OrganisationDocument11 pagesB4, Part 2 Plant Organisationshayaanzaman0No ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument62 pagesTransport in Plantsminahils100% (1)
- Leaf Structure and Function - Worksheet 2Document1 pageLeaf Structure and Function - Worksheet 2Hasmira Nor100% (3)
- Lab #2 - Leaf Internal StructureDocument1 pageLab #2 - Leaf Internal StructureTishonna DouglasNo ratings yet
- Plant Test Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesPlant Test Multiple Choice QuestionsnamratanimiNo ratings yet
- Cell Organisation in PlantsDocument21 pagesCell Organisation in PlantsRajananthini PushpanathanNo ratings yet
- TransportinplantsDocument62 pagesTransportinplantsHaniyyah SaudNo ratings yet
- Crop Physiology Exercise-2Document7 pagesCrop Physiology Exercise-2Ravikant MishraNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet