Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assam Poster
Uploaded by
Anonymous WDIx7WC6Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assam Poster
Uploaded by
Anonymous WDIx7WC6Copyright:
Available Formats
Abstract ID : 247
INVENTORY OF RUBBER PLANTATIONS AND IDENTIFICATION OF POTENTIAL AREAS
FOR ITS CULTIVATION IN ASSAM USING HIGH RESOLUTION IRS DATA
Pradeep B and James Jacob
Rubber Research Institute of India (RRII), Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Govt. of India
Rubber Board P.O, Kottayam- 686 009, Kerala, India
Correspondence: pradeep@rubberboard.org.in
INTRODUCTION Satellite- based acreage estimation of wastelands
suitable for rubber cultivation in Assam was about
Natural rubber (Hevea brasiliensis) is one of the most 24783 ha
important commercial plantation crops in India.
Area under wastelands suitable for rubber was
In India, about 7.4 lakh ha is under rubber cultivation, highest in Karimghanj district followed by Karbi
in which 70% of its area lies in Kerala and
Ground truth & field Anglong, Kamrup, Goalpara and Dima Hasao
data collection
Kanyakumari district of Tamil Nadu (IRS, 2013). districts.
Climate, topography and soil of North-eastern states Table 2. Satellite-derived acreage of rubber and
of India are fully or marginally favourable for rubber wastelands suitable for its cultivation in Assam
cultivation but its exact geo-spatial locations are not Figure 3. Sl Districts Rubber Wastelands % of % of total
estimated yet. Methodology of no area suitable for total wastelands
delineation of (ha) rubber rubber suitable for
Identification of existing rubber holdings and cultivation rubber
rubber and (ha)
potential areas for its cultivation in North-east India is wastelands 1 Goalpara 3388 2988 20.1 12.1
attempted using high resolution satellite remote suitable for its 2 Kamrup 1063 4525 6.3 18.3
sensing data cultivation 3 Karimganj 3453 6969 20.5 28.1
4 Cachar 167 128 1.0 0.5
OBJECTIVES 5 Dima Hasao 732 1010 4.3 4.1
RESULTS & DISCUSSION (N.C. Hills)
Rubber trees have a typical unique deep red tone during 6 Hailakandi 293 619 1.7 2.5
March-April seasons. Rubber holdings were identified 7 Karbi Angong 3872 6052 22.9 24.4
To map spatial extent of existing rubber cultivation
using spectral signature, phenology etc. Wastelands 8 Golaghat 500 98 3.0 0.4
in Assam 9 Nagaon 166 39 1.0 0.2
suitable for rubber were estimated and finalized from
10 Morigaon 70 39 0.4 0.2
Carto merged L-4 data using terrain conditions, land cover
11 Darrang 588 208 3.5 0.8
To estimate spatial extent of cultivable wastelands types etc. 12 Bongaigaon 688 195 4.1 0.8
suitable for rubber cultivation in Assam without 13 Dhubri 540 837 3.2 3.4
interfering with forests, food crops and major 14 Kokrajhar 419 178 2.5 0.7
vegetations. 15 Barpeta 19 7 0.1 0.0
16 Nalabari 7 14 0.0 0.1
17 Sonitpur 93 19 0.6 0.1
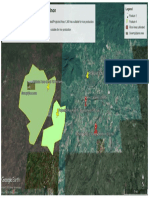
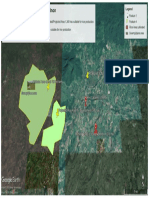
STUDY AREA: Assam state in India 18 Jorhat 564 561 3.3 2.3
19 Lakhimpur 19 0 0.1 0.0
20 Sivasagar 188 157 1.1 0.6
East longitudes 89o31'02.34"E to 96o03'41.23"E 21 Dhemaji 13 30 0.1 0.1
North latitudes 24o01'32.25"N to 28o02'03.37"N 22 Dibrugarh 0 2 0 0
Geographical area: 78470.2 Sq.km 23 Tinsukia 30 108 0.2 0.4
Total area 16872 24783
CONCLUSIONS
Figure 4. Comparison of NDVI values of dominant The study highlighted the utility of high resolution IRS
vegetations present in Assam with rubber during March- data to estimate rubber plantations and cultivable
April season. wastelands suitable for its cultivation in Assam.
The total estimate of spatial extent of rubber We have estimated about 16872 ha of area under rubber
plantations three years old and above in Assam for the and 24783 ha of cultivable wastelands suitable for its
year 2011- 2012 was 16872 ha cultivation in Assam.
Figure 1.
Area under rubber cultivation was the highest in Karbi Estimated wastelands can be further prioritized based
METHODOLOGY Anglong district. on soil fertility, climate etc for determining the extent of
suitability for rubber cultivation.
Temporal and multi-resolution satellite data (IRS, Goalpara, Kamrup, Karimkhanj and Karbi Anglong are
Cartosat merged LISS IV) was used for major rubber growing districts which accounted 69.8% The study would be a geo-spatial decision support
platform for policy makers and planners to promote
identification and estimation of spatial extent of of total rubber cultivation in Assam
rubber cultivation in a sustainable way by protecting
rubber plantations and cultivable wastelands food crops, forests, major vegetations and biodiversity
suitable for its cultivation. in Assam.
Mapping of wastelands suitable for rubber
cultivation was carried out without interfering food Acknowledgement
crops, protected areas, major vegetation, steep
valleys etc. Authors express sincere thanks to Dr. Dhurjati Chowdhury
(Retd. Project Co-ordinator, NE) and Mr. Mrinal Chowdhury
(former Scientist) of Rubber Boards Regional Research Station,
Table 1. Details of satellite data used in the study Guwahati, Assam for their help during field visit and ground truth
collection from the study area.
References
IRS., 2013. Indian Rubber Statistics. Statistics and Planning
(mapping accuracy of rubber: 95.2 %) Department. The Rubber Board, Kerala, Ministry of Commerce
Ground truth points collected from rubber & Industry, Govt. of India, 36, pp. 2-20.
growing districts in Assam
Figure 5. Geo-spatial distribution of rubber plantations
and wastelands suitable for its cultivation in Assam Ray, D., Behera, M. D., and Jacob, J., 2014. Indian
Rubber trees are deciduous in nature a) b) c)
Defoliation: Dec- January Brahmaputra valley offers significant potential for cultivation of
Refoliation: Feb- March rubber trees under changed climate. Current Science, 107 (3),
pp. 461-469.
RRSC and RRII., 2012. Geospatial technology for acreage
mature rubber holding estimation of natural rubber and identification of potential areas
for its cultivation in Tripura state. Collaborative project report of
RRSC, ISRO, Bengaluru and RRII, Rubber Board, Kottayam,
pp. 17- 42.
1074 points d) e) f) The 38th Asian Conference on Remote Sensing on
(GPS Garmin oregon 550) Figure 6. Spectral signature characteristics of rubber plantations in Space Applications: Touching Human Lives
satellite images of a) LISS III b) LISS IV) and c) LISS IV merged October 23-27, 2017
Cartosat. Figure d-f shows different types of wastelands suitable for NR
Figure 2. cultivation in Assam as seen in Carto merged LISS IV. New Delhi (India)
You might also like
- Kuhipath 2nd EditionDocument77 pagesKuhipath 2nd EditionSatyakam Dutta87% (38)
- Karbala Cement Factory-Report PDFDocument33 pagesKarbala Cement Factory-Report PDFAnonymous nQ9Rqm100% (2)
- Mapping and Characterization of Rubber Plantations Using Resourcesat DataDocument1 pageMapping and Characterization of Rubber Plantations Using Resourcesat DatapradeepNo ratings yet
- Distribution Natural Rubber CultivationDocument11 pagesDistribution Natural Rubber CultivationRahul JaganNo ratings yet
- Rock Resources of UAE PosterDocument1 pageRock Resources of UAE PostericiarNo ratings yet
- Mining Plan of River Sand Quarry Area - 4.0ha. (On Parbati River), Village - Berad, Tehsil-Biaora, District - Rajgarh (M.P.)Document29 pagesMining Plan of River Sand Quarry Area - 4.0ha. (On Parbati River), Village - Berad, Tehsil-Biaora, District - Rajgarh (M.P.)NAVEEN ROYNo ratings yet
- Subgrade Strengthening of Roads On Black Cotton Soil Using Quarry DustDocument3 pagesSubgrade Strengthening of Roads On Black Cotton Soil Using Quarry DustVENKATESH POONDRUNo ratings yet
- CET IMMM Report - Reshma 1.3.2020Document8 pagesCET IMMM Report - Reshma 1.3.2020Reshma ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilisation Using Lime, Flyash and Shredded Rubber: Presented by Guided byDocument72 pagesSoil Stabilisation Using Lime, Flyash and Shredded Rubber: Presented by Guided byTEMY PETERNo ratings yet
- State: Karnataka Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: DAVANAGEREDocument31 pagesState: Karnataka Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: DAVANAGEREKavya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Andhra PradeshDocument16 pagesAndhra Pradeshjohn powerNo ratings yet
- Dominorog Projected Rice AreaDocument1 pageDominorog Projected Rice AreaWarly BarcumaNo ratings yet
- Dominorog Projected Rice AreaDocument1 pageDominorog Projected Rice AreaWarly BarcumaNo ratings yet
- 75 Ramsar Sites in India Now!Document8 pages75 Ramsar Sites in India Now!Abhi SinghNo ratings yet
- Chikmagalur 2012Document29 pagesChikmagalur 2012maheshanischithaNo ratings yet
- Major Soil Type of KarnatakDocument4 pagesMajor Soil Type of KarnatakchikkannaswamyNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1achinthaakalanka1001No ratings yet
- 14.1 Summary of Coal Industry: Ole of Oal in NdiaDocument10 pages14.1 Summary of Coal Industry: Ole of Oal in Ndiaficky_iitdNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Soil by Using Rice Husk Ash: MR - Vishal Ghutke, Ms. Pranita Bhandari, Mr. Vikash AgrawalDocument4 pagesStabilization of Soil by Using Rice Husk Ash: MR - Vishal Ghutke, Ms. Pranita Bhandari, Mr. Vikash AgrawalRajveer SaeNo ratings yet
- RSPO Peat Inventory Template Amended (14 September 22)Document64 pagesRSPO Peat Inventory Template Amended (14 September 22)namasayanazlyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Mines and GeologyDocument15 pagesDepartment of Mines and GeologyStarNo ratings yet
- State: Chhattisgarh Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: Bastar 1.0 District Agriculture Profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological ZoneDocument41 pagesState: Chhattisgarh Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: Bastar 1.0 District Agriculture Profile 1.1 Agro-Climatic/Ecological ZoneRavi S. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Mining Method and Mine Design in Dighipara Coal Field, Dinajpur, BangladeshDocument9 pagesSelection of Mining Method and Mine Design in Dighipara Coal Field, Dinajpur, BangladeshAndryan FebriadiNo ratings yet
- 21 Sep 2018 120728550P4WRIDMQAnnexureIIIBriefSummaryDocument4 pages21 Sep 2018 120728550P4WRIDMQAnnexureIIIBriefSummary730-002 Arun kumarNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of Expansive Soil Using Bagasse Ash & LimeDocument6 pagesStabilization of Expansive Soil Using Bagasse Ash & LimeRajveer SaeNo ratings yet
- Dune Sand-Aggregate Mixes and Dune Sand-Sulfur Mixes For Asphalt Concrete PavementsDocument8 pagesDune Sand-Aggregate Mixes and Dune Sand-Sulfur Mixes For Asphalt Concrete PavementsHACCP Food CodeNo ratings yet
- FECL3 ON SubgradeDocument8 pagesFECL3 ON SubgradeAbbas AyadNo ratings yet
- WestBengal 1-Bankura-31.12.2011 - 0Document38 pagesWestBengal 1-Bankura-31.12.2011 - 0Subhajit BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- ENVIS Centre On Wildlife & Protected Areas: Tiger ReservesDocument8 pagesENVIS Centre On Wildlife & Protected Areas: Tiger ReservesGopi AkellaNo ratings yet
- ENVIS Centre On Wildlife & Protected Areas: Tiger ReservesDocument8 pagesENVIS Centre On Wildlife & Protected Areas: Tiger ReservesGopi AkellaNo ratings yet
- Ground Improvement of Problematic Soft Soils Using Shredded Waste TyreDocument5 pagesGround Improvement of Problematic Soft Soils Using Shredded Waste TyreAidaFarzanaNanaNo ratings yet
- Map India 2003Document4 pagesMap India 2003Saurabh SumanNo ratings yet
- Kumar 2020Document8 pagesKumar 2020Kuntal Ghosh 20PCE046No ratings yet
- Tecnical Note (Tarea 3)Document7 pagesTecnical Note (Tarea 3)Jannet FariasNo ratings yet
- Orissa 15 - Boudh 31.05.2011Document40 pagesOrissa 15 - Boudh 31.05.2011Chandra sekher PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Stabilization of CL and CI Soil Using Sugarcane Bagasse Ash and Quarry DustDocument5 pagesStabilization of CL and CI Soil Using Sugarcane Bagasse Ash and Quarry DustInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Soil Stabilization by Using Wheat Husk Ash: March 2018Document6 pagesSoil Stabilization by Using Wheat Husk Ash: March 2018Arham SheikhNo ratings yet
- Comparing The Standards of Coarse Aggregate in Bidar With Morth SpecificationDocument6 pagesComparing The Standards of Coarse Aggregate in Bidar With Morth SpecificationumashankaryaligarNo ratings yet
- Application of Geonatural Spoils in Sub Base For Road ConstructionDocument4 pagesApplication of Geonatural Spoils in Sub Base For Road ConstructionVenkatesh ThumatiNo ratings yet
- Indian Jute at A GlanceDocument1 pageIndian Jute at A GlanceAshfaq MohdNo ratings yet
- 07092014124633imyb - 2012 - 11 - 27 UttarakhandDocument6 pages07092014124633imyb - 2012 - 11 - 27 UttarakhandHitesh AswaniNo ratings yet
- State: Jharkhand Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: BokaroDocument35 pagesState: Jharkhand Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: BokarosunilkumarchaudharyNo ratings yet
- Madarchod Arvind Sharma Ka ProofDocument5 pagesMadarchod Arvind Sharma Ka ProofPriyanka NarwalNo ratings yet
- 644296ee86310talwa G-4 For Iron-Manganese ProposalDocument25 pages644296ee86310talwa G-4 For Iron-Manganese Proposalamit kumar guptaNo ratings yet
- Barwani District: Ministry of Water ResourcesDocument14 pagesBarwani District: Ministry of Water ResourcesDinesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Mineral Occurrence Reserves Uses No. of Mining Leases Granted LimestoneDocument3 pagesMineral Occurrence Reserves Uses No. of Mining Leases Granted LimestoneHilal LoneNo ratings yet
- Wardha Valley 2016Document41 pagesWardha Valley 2016Pushpendra ChouhanNo ratings yet
- 1.0 District Agriculture Profile: State: GUJARAT Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: BANASKANTHADocument34 pages1.0 District Agriculture Profile: State: GUJARAT Agriculture Contingency Plan For District: BANASKANTHAastuteNo ratings yet
- Diya Stone Quarry - Rajesh PatelDocument40 pagesDiya Stone Quarry - Rajesh PatelVIKAS PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Efecto de Las Mezclas de Cenizas y Cemento de Subida en La Resistencia A La Compresión No Confinada Del Suelo CohesivoDocument5 pagesEfecto de Las Mezclas de Cenizas y Cemento de Subida en La Resistencia A La Compresión No Confinada Del Suelo CohesivoHeiner Requejo RamosNo ratings yet
- UP27 AzamgarhDocument30 pagesUP27 Azamgarhanilkumarak9532No ratings yet
- Effect of Gradation and Plasticity On Compaction Characteristics PDFDocument3 pagesEffect of Gradation and Plasticity On Compaction Characteristics PDFJawad AbidiNo ratings yet
- Conservation and Management of Mangroves in India, With Special Reference To The State of Goa and The Middle Andaman IslandsDocument7 pagesConservation and Management of Mangroves in India, With Special Reference To The State of Goa and The Middle Andaman IslandsLingaraj DashNo ratings yet
- Geology of Madurai DistrictDocument45 pagesGeology of Madurai DistrictEdison Chandraseelan100% (2)
- Butt2016 Article StrengthBehaviorOfClayeySoilSt PDFDocument9 pagesButt2016 Article StrengthBehaviorOfClayeySoilSt PDFsalmanNo ratings yet
- Use of Gold Mill Tailings in Making Bricks: A Feasibility StudyDocument8 pagesUse of Gold Mill Tailings in Making Bricks: A Feasibility StudyArdian Kris BramantyoNo ratings yet
- Utilisation of Waste Derived Out of Mining: V.D. RajagopalDocument37 pagesUtilisation of Waste Derived Out of Mining: V.D. RajagopalSanjay MurthyNo ratings yet
- AR9-Papumpare-01 07 2015Document36 pagesAR9-Papumpare-01 07 2015BakeNo ratings yet
- Jeas 0318 6835Document8 pagesJeas 0318 6835Ram Chandra MeenaNo ratings yet
- Assamese PDFDocument2 pagesAssamese PDFTips in AssameseNo ratings yet
- Arihant Class 12 Term 2 English Core 2022 @cbsebookshubDocument193 pagesArihant Class 12 Term 2 English Core 2022 @cbsebookshubgxsdgsdfg100% (4)
- Assam 04092012Document53 pagesAssam 04092012Sahu PraveenNo ratings yet
- 22-09-2014579V2-E1-013 Small Tea PlantationsDocument7 pages22-09-2014579V2-E1-013 Small Tea PlantationsTamash MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Country Map: MyanmarDocument1 pageCountry Map: MyanmarMOC e-GovNo ratings yet
- Review - The Braided River - A Journey Along The Brahmaputra by Samrat Choudhury - Telegraph IndiaDocument5 pagesReview - The Braided River - A Journey Along The Brahmaputra by Samrat Choudhury - Telegraph IndiaPriyank PatelNo ratings yet
- Cpgee23 Notification ResultsDocument286 pagesCpgee23 Notification Resultsmanashchetia9435No ratings yet
- 1647025635897polity of AssamDocument31 pages1647025635897polity of AssamIsmail AliNo ratings yet
- Assignment ADTUDocument5 pagesAssignment ADTUAkash PayunNo ratings yet
- Kalita (Caste) - WikipediaDocument3 pagesKalita (Caste) - WikipediaMarthaNo ratings yet
- 29 BibliographyDocument7 pages29 BibliographynazmulNo ratings yet
- Natural Resources of AssamDocument2 pagesNatural Resources of AssamRipunjay GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Cement ResumeDocument2 pagesCement Resumeadhikarikingshuk100% (1)
- Social Scientist Volume 2 Issue 6-7 1974 (Doi 10.2307/3516480) Hiren Gohain - Origins of The Assamese Middle Class - Reply To CommentDocument6 pagesSocial Scientist Volume 2 Issue 6-7 1974 (Doi 10.2307/3516480) Hiren Gohain - Origins of The Assamese Middle Class - Reply To CommentRonnie ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Notification Assam PSC AE JEDocument7 pagesNotification Assam PSC AE JEMonu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Historical Geography of Medieval Assam: Nitrananda GogojDocument639 pagesHistorical Geography of Medieval Assam: Nitrananda GogojRatna Pritam BarmanNo ratings yet
- STATE SYMBOLS OF ASSAM PDF Study InsightDocument10 pagesSTATE SYMBOLS OF ASSAM PDF Study InsightBikashNo ratings yet
- Colonialism in Northeast India: An Environmental History of Forest Conflict in The Frontier of Lushai Hills 1850-1900Document9 pagesColonialism in Northeast India: An Environmental History of Forest Conflict in The Frontier of Lushai Hills 1850-1900inventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- Writing The History of Northeast India PDFDocument354 pagesWriting The History of Northeast India PDFAnamika Vats100% (1)
- New Media and Assamese Literature An IntroductionDocument3 pagesNew Media and Assamese Literature An IntroductionEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- The Problem Called LanguageDocument23 pagesThe Problem Called LanguagemampiyNo ratings yet
- Tea of AssamDocument4 pagesTea of AssamKangkan SharmaNo ratings yet
- State Level Eligibility Test Commission, Assam (N.E. Region) Gopinath Bordoloi Nagar 781014 Test, 2012 Correct Answer SubjectDocument45 pagesState Level Eligibility Test Commission, Assam (N.E. Region) Gopinath Bordoloi Nagar 781014 Test, 2012 Correct Answer SubjectMP CSIR NET PHYSICSNo ratings yet
- The Tourism Sector of AssamDocument6 pagesThe Tourism Sector of AssamRimpa DeyNo ratings yet
- Case Study of AssamDocument34 pagesCase Study of AssamRaj KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Assam Times - Chandraprabha Saikiani - The Legendary CrusaderDocument3 pagesAssam Times - Chandraprabha Saikiani - The Legendary Crusadergogoi_pranNo ratings yet
- Social Science 6 - A 1202 1206 Full PaperDocument5 pagesSocial Science 6 - A 1202 1206 Full Paperinspector bcwNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of Special LibrariesDocument31 pagesGrowth and Development of Special Librariessantoshguptaa100% (1)
- Paik SystemDocument2 pagesPaik Systemrockyburlung100% (2)