100% found this document useful (1 vote)
645 views20 pagesSap Interview Questions
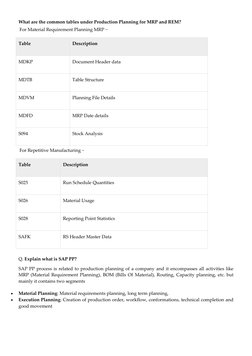
SAP Production Planning (PP) is an ERP module that handles planning processes like capacity and material planning. It executes production orders, bills of material, and goods movement. SAP PP handles master data for BOMs, work centers, and routings. Key elements include discrete and repetitive production, the production order lifecycle, organizational structure, and integration with other SAP modules like SD, MM, FI/CO, and QM. Master data includes BOMs, materials, work centers, and routings. Planning strategies include make-to-stock and make-to-order. Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is used to meet demand through production and procurement based on parameters like processing key and scheduling.
Uploaded by
Nagarjuna ReddyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
645 views20 pagesSap Interview Questions
SAP Production Planning (PP) is an ERP module that handles planning processes like capacity and material planning. It executes production orders, bills of material, and goods movement. SAP PP handles master data for BOMs, work centers, and routings. Key elements include discrete and repetitive production, the production order lifecycle, organizational structure, and integration with other SAP modules like SD, MM, FI/CO, and QM. Master data includes BOMs, materials, work centers, and routings. Planning strategies include make-to-stock and make-to-order. Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is used to meet demand through production and procurement based on parameters like processing key and scheduling.
Uploaded by
Nagarjuna ReddyCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd