Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Essay Question Nucleic Acid Technology and Applications
Uploaded by
InactiveAccount100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
991 views1 pageRecombinant DNA is made by using the same restriction enzyme on a strand of DNA and the plasmid (vector) the sticky ends are joined together and by using DNA ligase are made to hold. Other technologies nucleic acid technology includes southern blotting, DNA microarray assays, DNA finger printing and many more.
Original Description:
Original Title
Essay Question Nucleic acid technology and applications
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRecombinant DNA is made by using the same restriction enzyme on a strand of DNA and the plasmid (vector) the sticky ends are joined together and by using DNA ligase are made to hold. Other technologies nucleic acid technology includes southern blotting, DNA microarray assays, DNA finger printing and many more.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
991 views1 pageEssay Question Nucleic Acid Technology and Applications
Uploaded by
InactiveAccountRecombinant DNA is made by using the same restriction enzyme on a strand of DNA and the plasmid (vector) the sticky ends are joined together and by using DNA ligase are made to hold. Other technologies nucleic acid technology includes southern blotting, DNA microarray assays, DNA finger printing and many more.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Nucleic acid technology and applications
I. What are some current recombination technologies described in your textbook?
A. Basically, most of the recombination technology revolves around the use of restriction enzymes,
RFLPs (restriction fragment length polymorphisms), and recombinant DNA vectors. Recombinant
DNA is made by using the same restriction enzyme on a strand of DNA and the plasmid (vector)
although plasmids are not the only means of creating recombinant DNA. The restriction enzyme cuts
the DNA into many pieces and once the gene of interest is found, they insert it into the plasmid which
is cut by the same restriction fragment. The sticky ends are joined together and by using DNA ligase
are made to hold. The plasmid is then inserted into a bacterial cell to replicate along with cell, thus
creating many copies of the gene of interest. Besides just replicating a gene of interest, other
recombination technologies involve creating transgenic animal (chimeras) and plants. Other
technologies nucleic acid technology includes southern blotting, DNA microarray assays, DNA finger
printing and many more.
II. What are some practical applications of nucleic acid technology?
A. First, there is DNA fingerprinting, which uses RFLPs and gel electrophoresis. Basically, in gel
electrophoresis the RFLPs create bands across the gel according to their size. The smaller the RFLPs
are the faster and further they move across the gel. This is called a DNA fingerprint because it is very
unlikely that someone will have the same banding pattern as another person unless they are identical
twins. It is mainly used in forensics, but can also be used for paternity testing. Other applications of
nucleic acid technology include genetic maps, the human genome project which of coarse is trying to
map the entire human genome, DNA microarray assay which can detect and measure the expression of
thousands of genes at one time in order to see which genes are functioning and which are not. Also,
this technology has been used to created transgenic plants that are resistant to weed killers and other
chemicals. It is also being applied to create transgenic animals like cattle that will grow faster or
produce more milk. Last, but no least, there is gene therapy which, in the future, will enable scientist
to replace defective genes with fully functional ones and hopefully will be able to prevent the passing
on of these genes to future generations.
III. What legal and ethical problems may arise from these applications?
A. There are many problems and concerns that arise from these applications. One is the possibility that
recombinant DNA technology might create hazardous new pathogens. Other concerns involve the
safety of genetically modified organisms such as plants and animals. One of the main concerns,
however, involves the human genome project. Some of the questions posed for this were: Who should
have the right to examine some else’s genes? How should that information be used? Should that
information be used in determining whether a person is suitable for a certain job or insurance? No
knows the answers to these questions yet, and it because of these questions that the research and results
are slowing down for the applications of DNA technology. The only thing that scientists can do for
now is proceed with humility and caution.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
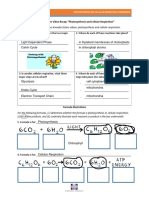
- Amoeba Sister Video CR and Photosynthesis QuestionsDocument2 pagesAmoeba Sister Video CR and Photosynthesis QuestionsKajal VaghasiaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Observation - MutationDocument19 pagesDLL - Observation - Mutationleny santos100% (1)
- Pre TestDocument4 pagesPre TestInactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Terminology Notebook-Ch. 22-24: Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Understanding Words p830 Andr-Contra - CrurDocument15 pagesTerminology Notebook-Ch. 22-24: Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Understanding Words p830 Andr-Contra - CrurInactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Terminology Notebook-Ch. 19-21: Chapter 19 Respiratory System Understanding Words p735Document10 pagesTerminology Notebook-Ch. 19-21: Chapter 19 Respiratory System Understanding Words p735InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Vocab1 4Document14 pagesVocab1 4InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- TN1Document13 pagesTN1InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 9-12Document7 pagesStudy Guide 9-12InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Soci1306 Exam 2Document15 pagesSoci1306 Exam 2InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document9 pagesLab 1InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document15 pagesLab 5InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Lab 7Document6 pagesLab 7InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Exam 1Document11 pagesExam 1InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- MYCAA Spouse Education and Training PlanDocument3 pagesMYCAA Spouse Education and Training PlanInactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Lab 6Document9 pagesLab 6InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Forum 1Document3 pagesForum 1InactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Assignment Four: MidlifeDocument3 pagesAssignment Four: MidlifeInactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- 3 Out of 3 PointsDocument10 pages3 Out of 3 PointsInactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Shakers: at Their Height in The 1830s, Attracted Some 6000 Followers. The Shakers Traced TheirDocument5 pagesShakers: at Their Height in The 1830s, Attracted Some 6000 Followers. The Shakers Traced TheirInactiveAccountNo ratings yet
- Chenqi Liu - 11 - DNA Vs RNA and Protein Synthesis - Amoeba Sisters - SHODocument2 pagesChenqi Liu - 11 - DNA Vs RNA and Protein Synthesis - Amoeba Sisters - SHOthomasmarteauhNo ratings yet
- Alexander Et Al-2011-British Journal of PharmacologyDocument326 pagesAlexander Et Al-2011-British Journal of PharmacologyDNav14No ratings yet
- Mekanisme Vitamin C Menurunkan Stres Oksidatif Setelah Aktivitas FisikDocument7 pagesMekanisme Vitamin C Menurunkan Stres Oksidatif Setelah Aktivitas Fisikpurity sabilaNo ratings yet
- Study Guide-Axon Guidance 1Document2 pagesStudy Guide-Axon Guidance 1joeyNo ratings yet
- Ap Bio Semester 1 Final ReviewDocument4 pagesAp Bio Semester 1 Final ReviewLynnie ShieNo ratings yet
- M 6 LabDocument2 pagesM 6 LabBal33% (3)
- LOP-Oktober2019 ENGDocument91 pagesLOP-Oktober2019 ENGlidya kurniawanNo ratings yet
- Villate Bejarano OlatzDocument122 pagesVillate Bejarano OlatzOstwald CartucheNo ratings yet
- 1 Original ManuscriptDocument70 pages1 Original ManuscriptLuis RamosNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication 2014Document15 pagesDNA Replication 2014SATYANARAYANA RAO100% (1)
- Plant Hormone ReceptorsDocument12 pagesPlant Hormone ReceptorsJitendra MishraNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Microbial Dark MatterDocument16 pagesPeriodontal Microbial Dark MatterAndrés Nicolás Beltrán SeguraNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Tirosin Kinase 4Document13 pagesJurnal Tirosin Kinase 4Maya SariNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDinkey AlegadoNo ratings yet
- Genetic Testing For Autism, Explained: Spectrum - Autism Research NewsDocument3 pagesGenetic Testing For Autism, Explained: Spectrum - Autism Research NewsTimothyNo ratings yet
- Minechem ChemicalsDocument4 pagesMinechem ChemicalsMilos LaptosevicNo ratings yet
- Application of Aromatic Compounds: Student Name: Student Number: Student Level: Course Name: Course CodeDocument12 pagesApplication of Aromatic Compounds: Student Name: Student Number: Student Level: Course Name: Course Code1828298 1828298No ratings yet
- Enantiomers Evaluation CetirizineDocument4 pagesEnantiomers Evaluation Cetirizinebebel555No ratings yet
- ImmunoglobulinDocument39 pagesImmunoglobulinReguird AllaeinniNo ratings yet
- MHCDocument22 pagesMHCJanani JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Campbell Biology 10Th Edition by Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky and Jackson Isbn 0321775651 9780321775658 Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesSolution Manual For Campbell Biology 10Th Edition by Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky and Jackson Isbn 0321775651 9780321775658 Full Chapter PDFsusan.hall408100% (12)
- Biochem Midterm ReviewerDocument19 pagesBiochem Midterm ReviewerERIKA ROSE ALEJONo ratings yet
- Simon and Daniel 2009Document12 pagesSimon and Daniel 2009PaulaSaPereiraNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Stomatal MovementDocument19 pagesMechanism of Stomatal MovementMaham AjmalNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellscalustre2016No ratings yet
- Acs Bioconjchem 1c00326 PDFDocument12 pagesAcs Bioconjchem 1c00326 PDFHunny SharmaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument40 pagesBiochemistry 8Th Edition Campbell Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFciaramilcahbrpe100% (13)
- DNA Computing and Molecular Programming: Satoshi Murata Satoshi KobayashiDocument169 pagesDNA Computing and Molecular Programming: Satoshi Murata Satoshi Kobayashimehdi1902No ratings yet