Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diode: Type Working Principle Zener Breakdown Invented Pin Configuration and
Uploaded by
priyadarshan sundar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pageszenar diode
Original Title
Zener Diode
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentzenar diode
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views2 pagesDiode: Type Working Principle Zener Breakdown Invented Pin Configuration and
Uploaded by
priyadarshan sundarzenar diode
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
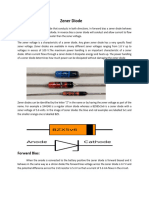
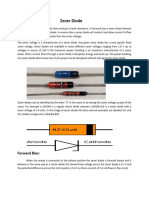
Zener diode
Type Passive
Working principle Zener breakdown
Invented Clarence Melvin Zener
Pin configuration anode and cathode
Electronic symbol
A Zener diode a particular type of diode that, unlike a normal
one, allows current to flow not only from its anode to its cathode,
but also in the reverse direction, when the so-called "Zener
voltage" is reached. Zener diodes have a highly doped p-n
junction. Normal diodes will also break down with a reverse
voltage but the voltage and sharpness of the knee are not as well
defined as for a Zener diode. Also normal diodes are not
designed to operate in the breakdown region, but Zener diodes
can reliably operate in this region.
The device was named after Clarence Melvin Zener, who
discovered the Zener effect. Zener reverse breakdown is due to
electron quantum tunnelling caused by a high-strength electric
field. However, many diodes described as "Zener" diodes rely
instead on avalanche breakdown. Both breakdown types are
used in Zener diodes with the Zener effect predominating
under 5.6 V and avalanche breakdown above.
Zener diodes are widely used in electronic equipment of all kinds
and are one of the basic building blocks of electronic circuits.
They are used to generate low power stabilized supply rails from
a higher voltage and to provide reference voltages for circuits,
especially stabilized power supplies. They are also used to protect
circuits from overvoltage, especially electrostatic
discharge (ESD).
You might also like
- 3.zener DiodeDocument6 pages3.zener DiodethiliniNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument7 pagesZener DiodeMuhammad AsgharNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode ExplanationDocument6 pagesZener Diode ExplanationShubham SwamiNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument13 pagesZener DiodePhenoमिनल IdiotsNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument14 pagesZener DiodePrasanth. SNo ratings yet
- Soumyadip Kalsa, Roll - 33, Sub - BiologyDocument13 pagesSoumyadip Kalsa, Roll - 33, Sub - BiologySMOKER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Topic 1Document36 pagesUnit 1 Topic 1ANDRIL ALAGUSABAINo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument15 pagesZener Diodeumar03029452584No ratings yet
- Diode - Definition, VI Characteristics, and Breakdown in Zener Diode - DiodeDocument8 pagesDiode - Definition, VI Characteristics, and Breakdown in Zener Diode - DiodehavejsnjNo ratings yet
- ZenerDocument3 pagesZenerTajatNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodesDocument12 pagesZener Diodesassodais.mts45No ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument15 pagesZener DiodeEEE M.AASTHIKANo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALANo ratings yet
- Zener Diode ProjectDocument16 pagesZener Diode ProjectJsmBhanot83% (6)
- Zener DDDocument8 pagesZener DDDerren TuscanoNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsDocument3 pagesZener Diode Characteristics and ApplicationsANIL KUMAR YARAMALANo ratings yet
- Zener Diode: Electronic Circuits (18NPC304) Assignment 2 Part - 2Document2 pagesZener Diode: Electronic Circuits (18NPC304) Assignment 2 Part - 2Narendran SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- What Is A DiodeDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Diodedth dthNo ratings yet
- ECE132: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Lab: Experiment 10Document8 pagesECE132: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering Lab: Experiment 10Madhur YadavNo ratings yet
- Zener EeDocument8 pagesZener EeDerren TuscanoNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument3 pagesZener Diodekanak-825262No ratings yet
- Zener Diode: - Nakul Tekade, Shubham RaksheDocument7 pagesZener Diode: - Nakul Tekade, Shubham RaksheMr. NacNo ratings yet
- The Wonderful World of Zener DiodesDocument8 pagesThe Wonderful World of Zener DiodesMITHUN VARMANNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument22 pagesZener DiodeRafath UmaimathNo ratings yet
- University Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation TechnologyDocument6 pagesUniversity Kuala Lumpur Malaysian Institute of Aviation Technologyvishnu ramaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode As Voltage Regulator and Its V-I CharacteristicsDocument13 pagesZener Diode As Voltage Regulator and Its V-I CharacteristicsRUPAM GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument38 pagesPhysics ProjectRitu FalwariaNo ratings yet
- Edu Expansion Presentation (Circuits)Document16 pagesEdu Expansion Presentation (Circuits)nandinigupta613No ratings yet
- ZDDocument29 pagesZDVikram TomerNo ratings yet
- Zenerdiodes 150209070235 Conversion Gate02Document29 pagesZenerdiodes 150209070235 Conversion Gate02Pushkin RathoreNo ratings yet
- 02 Zenerdiodes PPT PRPDocument29 pages02 Zenerdiodes PPT PRPVarsha PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- U-1 (Boe 8-18)Document11 pagesU-1 (Boe 8-18)Tisha SetiaNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode - WikipediaDocument29 pagesZener Diode - WikipediaLupu DanielNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode: Prepared By: Elman John Cabacang Bsece Ii-7Document23 pagesZener Diode: Prepared By: Elman John Cabacang Bsece Ii-7Elman CabacangNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeNeal John VillarmenteNo ratings yet
- Edger ChamiDocument17 pagesEdger ChamilekoringoeNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode 1Document1 pageZener Diode 1umar03029452584No ratings yet
- Zener Diode 1Document1 pageZener Diode 1umar03029452584No ratings yet
- ZenerdiodesDocument12 pagesZenerdiodesImran AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Dioda ZenerDocument2 pagesDioda ZenerGeorge TimpauNo ratings yet
- Zener DiodeDocument19 pagesZener DiodeMD. Abdullah Al NomanNo ratings yet
- Lab # 1O Zener Diode Characteristic: Electronic Devices & Circuits D-19-TE-04Document1 pageLab # 1O Zener Diode Characteristic: Electronic Devices & Circuits D-19-TE-04HarryNo ratings yet
- Soumyadip Kalsa, Roll - 33, Sub - BiologyDocument13 pagesSoumyadip Kalsa, Roll - 33, Sub - BiologySMOKER GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 5369926Document33 pages5369926Syed Uzair ShahNo ratings yet
- Tuquero, Melinyo L Industrialelecslab#2Document7 pagesTuquero, Melinyo L Industrialelecslab#2melenyo tuqueroNo ratings yet
- Prelab ZinerDocument6 pagesPrelab Zinerمحمود القويريNo ratings yet
- Amity School of Engineering & TechnologyDocument50 pagesAmity School of Engineering & TechnologySwathi GudivadaNo ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode? Working Principle of Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode? Working Principle of Zener Diodepawan dhingraNo ratings yet
- Diode Vs Zener Diode Parameters Diode Zener DiodeDocument2 pagesDiode Vs Zener Diode Parameters Diode Zener DiodeSingaravelu VivekanandhanNo ratings yet
- Se - Elec - Simlab - Exp-6 - Roll No-1Document3 pagesSe - Elec - Simlab - Exp-6 - Roll No-1Lester DsouzaNo ratings yet
- 5 Zener DiodeDocument28 pages5 Zener Diodechandan.cj99No ratings yet
- What Is Zener Diode?Document4 pagesWhat Is Zener Diode?Riaz IsraniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document32 pagesChapter 3api-394738731No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics - Ch-2Document29 pagesBasic Electronics - Ch-22203051050594No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document40 pagesChapter 3Ameer Mukhtiar AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Special Purpose DiodesDocument10 pagesSpecial Purpose Diodeskmsriram92No ratings yet
- Physics Master NotesDocument9 pagesPhysics Master NotesGopal kumawatNo ratings yet
- Avalanche BreakdownDocument15 pagesAvalanche BreakdownsNo ratings yet
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Acknowledgement: "Optical Fibres"Document4 pagesAcknowledgement: "Optical Fibres"priyadarshan sundarNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: of Chemistry For Sparing His Precious Time. We Brought in As Raw Data To HimDocument31 pagesAcknowledgement: of Chemistry For Sparing His Precious Time. We Brought in As Raw Data To Himpriyadarshan sundarNo ratings yet
- Optical FiberDocument18 pagesOptical Fiberpriyadarshan sundarNo ratings yet
- Logic GatesDocument24 pagesLogic Gatespriyadarshan sundarNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgement: of Chemistry For Sparing His Precious Time. We Brought in As Raw Data To HimDocument31 pagesAcknowledgement: of Chemistry For Sparing His Precious Time. We Brought in As Raw Data To Himpriyadarshan sundarNo ratings yet
- Supply Installation Commissioning of Worlld Largest MillDocument12 pagesSupply Installation Commissioning of Worlld Largest MillAbe ArdiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Appraising Diagnostic Research StudiesDocument23 pagesLesson 5 Appraising Diagnostic Research StudiesProject MedbooksNo ratings yet
- Design of The Power Control Module of TDDocument9 pagesDesign of The Power Control Module of TDGurbir SinghNo ratings yet
- EEMDocument17 pagesEEMSandaruwan සුජීවNo ratings yet
- DWSIM Training-V02-30dec17Document58 pagesDWSIM Training-V02-30dec17Zanariah HashimNo ratings yet
- Dcs 2019 Questions PaperDocument14 pagesDcs 2019 Questions PaperDASHARATH VISHAWAKARMANo ratings yet
- Ultra Filtration Manual and Line Diagram (Kanin)Document6 pagesUltra Filtration Manual and Line Diagram (Kanin)marksion exchangeNo ratings yet
- INA131 Burr-BrownCorporationDocument10 pagesINA131 Burr-BrownCorporationMartha H.TNo ratings yet
- 01 - Electro Chemistry (Level) Module-6-1Document16 pages01 - Electro Chemistry (Level) Module-6-1Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Sam W Hoke Torch PatentDocument5 pagesSam W Hoke Torch PatentRichard.nlNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid SynthesisDocument28 pagesFatty Acid Synthesishassanainshahi13No ratings yet
- Digital Image ProcessingDocument71 pagesDigital Image ProcessingPratibha SharmaNo ratings yet
- Synchro CheckDocument4 pagesSynchro CheckAdhyartha KerafNo ratings yet
- Biomimetic Dentistry: Basic Principles and Protocols: December 2020Document4 pagesBiomimetic Dentistry: Basic Principles and Protocols: December 2020Bence KlusóczkiNo ratings yet
- BUS 36106 Syllabus Spring 2015Document10 pagesBUS 36106 Syllabus Spring 2015MukundMultaniNo ratings yet
- Fund. Acerinox Horno ArcoDocument8 pagesFund. Acerinox Horno ArcoJavier Mauricio Neira CastrillonNo ratings yet
- Quality Control Tests For Emulsions, Syrups, Tinctures, Elixirs, Ointments and OthersDocument11 pagesQuality Control Tests For Emulsions, Syrups, Tinctures, Elixirs, Ointments and OthersMuhammad Masoom Akhtar100% (2)
- Important QuestionsDocument8 pagesImportant QuestionsdineshbabuNo ratings yet
- Wea Met Aws310 Brochure 210x280 B211290en C Low v2Document4 pagesWea Met Aws310 Brochure 210x280 B211290en C Low v2Anonymous rpSGuQPNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi 4g64 Engine 2 4l Service ManualDocument10 pagesMitsubishi 4g64 Engine 2 4l Service Manualjennifer100% (49)
- Physics SS2 Term 2 Dec 2022Document71 pagesPhysics SS2 Term 2 Dec 2022TahmidNo ratings yet
- Monoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria: Review of FundamentalsDocument38 pagesMonoprotic Acid-Base Equilibria: Review of FundamentalsmakroniNo ratings yet
- Fdot Modifications To LRFD Specifications For Structural Supports For Highway Signs, Luminaires and Traffic Signals (Lrfdlts-1)Document26 pagesFdot Modifications To LRFD Specifications For Structural Supports For Highway Signs, Luminaires and Traffic Signals (Lrfdlts-1)kayshephNo ratings yet
- 16 Kinetics Rigid BodiesDocument30 pages16 Kinetics Rigid BodiesNkoshiEpaphrasShoopalaNo ratings yet
- Third Periodic TestDocument4 pagesThird Periodic TestCrizelda AmarentoNo ratings yet
- Srinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur: Part B Unit IDocument2 pagesSrinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur: Part B Unit IPrabhat SinghNo ratings yet
- Particle Tracing Module Users GuideDocument306 pagesParticle Tracing Module Users GuideAlfonso BarbozaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation - MATH IS FUNDocument8 pagesQuadratic Equation - MATH IS FUNChanchan LebumfacilNo ratings yet
- Hook Height With Drawwork SensorDocument3 pagesHook Height With Drawwork SensorJose PalumboNo ratings yet
- DSC & Ftir 2Document13 pagesDSC & Ftir 2Rashid HussainNo ratings yet