Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
api-3044860520 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
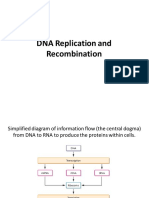
11 views1 pageDNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are joined together by another histone to form supercoiled structures. Telomeres are repetitive base sequences that are found at the ends of chromosomes. DNA replication occurs during S phase and results in two identical DNA molecules through a semi-conservative process where the parental strands serve as templates for new complementary strands to be synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction.
Original Description:
Original Title
chapter 7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are joined together by another histone to form supercoiled structures. Telomeres are repetitive base sequences that are found at the ends of chromosomes. DNA replication occurs during S phase and results in two identical DNA molecules through a semi-conservative process where the parental strands serve as templates for new complementary strands to be synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageChapter 7
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
api-304486052DNA is wrapped around histone proteins to form nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are joined together by another histone to form supercoiled structures. Telomeres are repetitive base sequences that are found at the ends of chromosomes. DNA replication occurs during S phase and results in two identical DNA molecules through a semi-conservative process where the parental strands serve as templates for new complementary strands to be synthesized in the 5' to 3' direction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
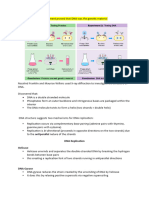
Term Definition
Nucleosome DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins, another histone holds nucleosomes
together for supercoiling
Telomeres Repetitive base sequences at the ends of chromosomes
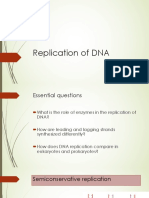
Explain the process of DNA replication
- DNA replication occurs during S phase of interphase in preparation for mitosis
- DNA replication is semi-conservative, with an old strand from parent molecule and a new strand
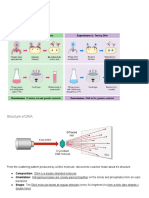
- Helicase unwinds the DNA double helix and separate the two strands by breaking hydrogen
bonds between bases. Each strand of parent DNA is used as template for synthesis
- DNA primes adds NTPs on each template strands to form a short length of RNA primer
- DNA polymerase III binds to RNA primer and adds dNTPs in the 5’ to 3’ direction according to
complementary base pairing. Adenine with Thymine and Guanine with Cytosine
- Two phosphate groups in NTPs and dNTPs are removed to provide energy for forming
phosphodiester bond
- Synthesis is in 5’ to 3’ direction. It is continuous on the leading strand but discontinuous on the
lagging strand, resulting in the formation of Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand
- DNA ligase joins Okazaki fragments together by forming sugar-phosphate bond
You might also like
- Topic: How Cells Work - DNA Replication, Metabolic RegulationDocument3 pagesTopic: How Cells Work - DNA Replication, Metabolic RegulationDeitherNo ratings yet
- Bio Dna Replication - Transcription and TranslationDocument6 pagesBio Dna Replication - Transcription and TranslationXie YuJiaNo ratings yet
- Deoxyribonucleic Acid: Human DNA Is Present in The Nucleus and Mitochonria Carry Genetic InformationDocument17 pagesDeoxyribonucleic Acid: Human DNA Is Present in The Nucleus and Mitochonria Carry Genetic InformationPrashant DhakadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6 - DNA & DNA ReplicationDocument38 pagesChapter 5 & 6 - DNA & DNA ReplicationCate KristineNo ratings yet
- Biochem QuinDocument4 pagesBiochem QuinKingNo ratings yet
- Biochem Group ProjDocument21 pagesBiochem Group ProjYves Christian PineNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and RepairDocument7 pagesDNA Replication and RepairJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- 21 DNA Replication 2023Document59 pages21 DNA Replication 2023Kurstein FerriolNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument28 pagesDNA ReplicationAsim Bin Arshad 58-FBAS/BSBIO/S19100% (1)
- Chapter 5 & 6 - DNA & DNA ReplicationDocument38 pagesChapter 5 & 6 - DNA & DNA ReplicationParsottambhai RathaviNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument5 pagesDNA ReplicationNikki SStarkNo ratings yet
- 7th Cytogenetics Lecture 20121 1Document37 pages7th Cytogenetics Lecture 20121 1RC SILVESTRENo ratings yet
- 4 DnaDocument6 pages4 Dnadr_47839666No ratings yet
- Replikasi DNA Dan Sintesis Protein (Gabungan)Document62 pagesReplikasi DNA Dan Sintesis Protein (Gabungan)adinda tyasprabandariNo ratings yet
- Packaging of DNA Into ChromosomeDocument13 pagesPackaging of DNA Into ChromosomeShashank AppuNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Hybridization. Synthesis. DNA Polymerases Assemble New Strands of DNA From Nucleotides, UsingDocument1 pageDNA Replication: Hybridization. Synthesis. DNA Polymerases Assemble New Strands of DNA From Nucleotides, UsingDominique LopenaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument10 pagesDNA Replication: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaRahul GuptaNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication and Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesDNA Replication and Protein SynthesisFrezelVillaBasiloniaNo ratings yet
- Presentationprint TempDocument27 pagesPresentationprint TempGandepelli SwetchaNo ratings yet
- 14.4 DNA Replication in ProkaryotesDocument3 pages14.4 DNA Replication in ProkaryotesAyushi MauryaNo ratings yet
- Module 8 - Nucleic Acids and Central DogmaDocument52 pagesModule 8 - Nucleic Acids and Central DogmaPauline Grace CadusaleNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Molecular Biology IDocument12 pagesLecture 5 - Molecular Biology IbesillysillyNo ratings yet
- BCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUDocument35 pagesBCH 401 Note 1 - KWASUidriscognitoleadsNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument7 pagesDNA ReplicationMuhammad QayumNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: DNA Replication Is A Biological Process That Occurs in AllDocument11 pagesDNA Replication: DNA Replication Is A Biological Process That Occurs in AllKomal SharmaNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Unit 6 GuideDocument7 pagesAP Biology Unit 6 Guidelolo2212008No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument47 pagesDNA ReplicationYSOBELLATHERESE BILOLONo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: DefinitionDocument6 pagesDNA Replication: DefinitionZEE zeeNo ratings yet
- The Biological Information Flows From DNA To RNA and From There To ProteinsDocument38 pagesThe Biological Information Flows From DNA To RNA and From There To Proteinsfentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 & 6: DNA & DNA ReplicationDocument38 pagesChapter 5 & 6: DNA & DNA ReplicationDiego GarciaNo ratings yet
- 004 DNA Replication EnzymesDocument16 pages004 DNA Replication EnzymesFavio CocaNo ratings yet
- Biology Nucleic A-Level OCR NotesDocument11 pagesBiology Nucleic A-Level OCR Notestbrook2017No ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument21 pagesDNA ReplicationP Santosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument12 pagesNucleic AcidsKelly ZhuNo ratings yet
- Process of Dna ReplicationDocument3 pagesProcess of Dna ReplicationLaiba AsimNo ratings yet
- Biology Gene Expression Article Title: Expression of Biological InformationDocument6 pagesBiology Gene Expression Article Title: Expression of Biological InformationNUR FAQIHAH BINTI FARISH MoeNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument22 pagesDNA Replicationerenyorulmaz143No ratings yet
- Compressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015Document10 pagesCompressed Notes Chapter 6: Expression of Biological Information Sb015SYAZWAN BIN MUSTAFA MoeNo ratings yet
- Zoology DNA ReplicationDocument22 pagesZoology DNA ReplicationbiswassjpNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids + Protein SynthesisNezza WidarkoNo ratings yet
- Study Dna DnaDocument45 pagesStudy Dna DnaKrystel BeltranNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication, The Basis ForDocument23 pagesDNA Replication, The Basis ForDiana M. LlonaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2B - DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesLesson 2B - DNA ReplicationHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet
- Replication Transcription and TranslationDocument16 pagesReplication Transcription and TranslationBalangat Regine L.No ratings yet
- Dna Replication NotesDocument3 pagesDna Replication NotesYash VardhanNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesMolecular Biologyghadeer hassanNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Notes Top Two Things To Address For Next Test!!!Document3 pagesCH 11 Notes Top Two Things To Address For Next Test!!!CJNo ratings yet
- 2 - Molecular Biology and GeneticsDocument14 pages2 - Molecular Biology and Geneticsarahunt253No ratings yet
- Semi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDocument12 pagesSemi-Conservative DNA ReplicationDibyakNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudDocument35 pagesDNA Replication: Desak Made Wihandani Departemen Biokimia FK UnudBagus Arya MahartaNo ratings yet
- 6 Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisDocument49 pages6 Nucleic Acid and Protein SynthesisgyunimNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument2 pagesDNA ReplicationFrancoise AngeliqueNo ratings yet
- DNA ReplicationDocument15 pagesDNA Replicationتوتا عوضNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument62 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationREYNANTE SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 6 BIO462 Chapter 6Document21 pages6 BIO462 Chapter 6Syafiqah SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Dna ReplicationDocument3 pagesDna ReplicationRachel ReneeNo ratings yet
- 6.2: Dna ReplicationDocument43 pages6.2: Dna Replicationa200812No ratings yet
- CH 7 Nucleic AcidsDocument8 pagesCH 7 Nucleic AcidsInes Ait Si SelmiNo ratings yet
- Dna Replication: Sidra HasnainDocument9 pagesDna Replication: Sidra HasnainHusnain AliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document2 pagesChapter 5api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document2 pagesChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document1 pageChapter 10api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet