Professional Documents
Culture Documents
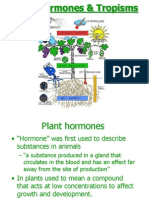
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
Uploaded by
api-304486052Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
Uploaded by
api-304486052Copyright:
Available Formats
Term Definition
Meristems Allow plants to continue to produce more roots, leaves and stems throughout
their life
Photo/Geo tropism
Shoots: Positive phototropism, Negative geotropism
Roots: Negative phototropism, Positive Geotropism
Auxins shift to the darker side (Photo)
Auxins shift towards gravity (Geo)
Explain the role of auxin in phototropism
- Auxin is a plant hormone
- Produced by the shoot tip
- Causes transport of hydrogen ions from cytoplasm wall
- H+ pumping breaks bonds between cell wall fibres
- Makes cell walls flexible
- Auxins make cells grow
- Gene expression also altered by auxin to promote cell growth
- Positive phototropism is growth towards light
- Shoot tip senses direction of brightest light
- Auxin moved to side of stem with least light
- Causes cells on dark side to elongate
Micro propagation
- Specific plant tissue (undifferentiated shoot apex) is selected from a stock plant and sterilised
- Tissue sample is grown on a sterile nutrient agar gel
- Explant is treated with growth hormones to stimulate shoot and root development
- Growing shoots can be continuously divided and separated to form new samples
- Once developed, cloned plant can be transferred to soil
Advantages
- New varieties can be bulked up much more quickly than by previous methods of propagation
- Virus free strains of existing varieties can be produced
- Large numbers of rare plants
You might also like
- Chapter 5 Response in PlantDocument34 pagesChapter 5 Response in Plantintan syaheeraNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument40 pagesPlant HormonesSakina26100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Plant HormonesDocument49 pagesChapter 8 - Plant Hormonessayidah nafisah100% (2)
- Topic 9.3: Growth in PlantsDocument17 pagesTopic 9.3: Growth in Plantssalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- Biology CXC 2022 ReviewDocument46 pagesBiology CXC 2022 ReviewLatoya Scottland100% (2)
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument29 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionJodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- How Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersFrom EverandHow Plants Grow - With Information on the Biology of Plant Cells, Roots, Leaves and FlowersNo ratings yet
- Coordination in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesCoordination in Plants NotesAmna SaleemNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraNo ratings yet
- BIO02 - TropismDocument10 pagesBIO02 - TropismCarlo CondeNo ratings yet
- The Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentDocument29 pagesThe Plant Cell Wall: Growth and DevelopmentbeneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4Document26 pagesChapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4wienna1987No ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Control of Plant Growth and Development Student NoteDocument4 pagesLesson 8 Control of Plant Growth and Development Student NoteallaboutamaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document3 pagesChapter 12Mahir ShahriyarNo ratings yet
- Key Concept OBJECTIVES (Be Able To: - ) Content: Scope and CompetencesDocument8 pagesKey Concept OBJECTIVES (Be Able To: - ) Content: Scope and Competencesnicole mugumbaNo ratings yet
- 06 Plant HormonesDocument4 pages06 Plant HormonessureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Tropic ResponsesDocument4 pagesTropic ResponsesMuhammad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- TropismDocument8 pagesTropismRaazia Arbab - 91028/TCHR/BSSCNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToDocument6 pagesNervous System: Plant Responses To Environmental Changes Are Coordinated by Hormones. Hormones, Also Referred ToJan Alixia BasilioNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 (Chemical Response-Plants)Document7 pagesChapter-12 (Chemical Response-Plants)ToXicNo ratings yet
- Auxin and TropismDocument17 pagesAuxin and TropismmarwaNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 3 - Reproduction & InheritanceDocument18 pagesBiology Unit 3 - Reproduction & Inheritancethisismashael07No ratings yet
- Plant ResponsesDocument24 pagesPlant Responsesk75544863No ratings yet
- Bio T1 ApuntesDocument11 pagesBio T1 ApuntesGuillermo Corbi BallesterNo ratings yet
- Sevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BDocument3 pagesSevilla - Activity 2 - Cassci 1BJoyce SevillaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination in Plants-NotesDocument4 pagesChemical Coordination in Plants-NotesKarishmmNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Gen Bio2 - 3rdQDocument6 pagesReviewer in Gen Bio2 - 3rdQTherese Anne B. FraniNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument6 pagesReproductionzainahNo ratings yet
- Cloze Plant TropismsDocument2 pagesCloze Plant TropismsVirginia MorleyNo ratings yet
- Tropism and Types of Tropism: Class 10 Subject: Biology Chapter: Coordination and ControlDocument11 pagesTropism and Types of Tropism: Class 10 Subject: Biology Chapter: Coordination and ControlAniqa HibbaNo ratings yet
- Biology Auxin PhototropismDocument2 pagesBiology Auxin PhototropismAb BugarinNo ratings yet
- 14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlDocument17 pages14.1 Plant Tropisms and Hormonal ControlRahulKwatraNo ratings yet
- PhytohormonesDocument3 pagesPhytohormonesrustyryan77No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Plants1Document5 pagesChapter 4 Plants1Gabbie CruzNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination in Plants: RadiateDocument14 pagesControl and Coordination in Plants: RadiateTaimoor Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Plant Bio 1Document5 pagesPlant Bio 1Jamaira SamaupanNo ratings yet
- Slide 1: AuxinsDocument8 pagesSlide 1: AuxinsMarawan NoubyNo ratings yet
- Topic 10Document5 pagesTopic 10GdeWawanKurniawanNo ratings yet
- Note PhytohormonesDocument47 pagesNote PhytohormonesAyuni Mokhtar100% (1)
- Auxin: The First Discovered Plant Growth Hormone: Ayushi Mandloi 2019H1290104P M.E. BiotechnologyDocument33 pagesAuxin: The First Discovered Plant Growth Hormone: Ayushi Mandloi 2019H1290104P M.E. BiotechnologyAyushi MandloiNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones & TropismsDocument27 pagesPlant Hormones & TropismsKhadija AliNo ratings yet
- Types of ReproductionDocument36 pagesTypes of ReproductionEdwins MaranduNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFDocument38 pagesKuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFRianNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 Plant MorphologyDocument3 pagesBIO 2 Plant MorphologyMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- To Ti Potency & PlasticityDocument14 pagesTo Ti Potency & PlasticityNasir Hussain FarazNo ratings yet
- The Growth and Development in PlantsDocument59 pagesThe Growth and Development in PlantshildaachfiNo ratings yet
- Bio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Document12 pagesBio 250 (Systems and Maintenance)Amar SafwanNo ratings yet
- Crop - Lecture - Growth HormonesDocument9 pagesCrop - Lecture - Growth HormonesCynel DelaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2 STD 10Document12 pagesCHAPTER-2 STD 10SHRESTH FFNo ratings yet
- c12 BioDocument3 pagesc12 BioNur Anisha Binti Mohd AzmyNo ratings yet
- Nota Biologi UniDocument28 pagesNota Biologi UniMuhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- Biology HSC Notes:: Sexual AsexualDocument26 pagesBiology HSC Notes:: Sexual AsexualGeorge EskandarNo ratings yet
- 16 ReproductionDocument9 pages16 ReproductionEmanuel SafiNo ratings yet
- Bio CH5 F5 StudywithadminDocument5 pagesBio CH5 F5 StudywithadminShamil AdlanNo ratings yet
- The Organism and Its Environment: Integrated Science Theory NotesDocument15 pagesThe Organism and Its Environment: Integrated Science Theory NotesNoah YeboahNo ratings yet
- Bab 6 FITOHORMONEDocument23 pagesBab 6 FITOHORMONEnormaNo ratings yet
- AUXINDocument23 pagesAUXINJose S. Cabato IIINo ratings yet
- Asex UAL Repr Oduc Tion Revie W Shee T: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesAsex UAL Repr Oduc Tion Revie W Shee T: ObjectivesjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- X-Sheet 8 Plant Responses To The Environment: Life Sciences X-SheetsDocument7 pagesX-Sheet 8 Plant Responses To The Environment: Life Sciences X-SheetsThembelani ThempeliNo ratings yet
- O-Level Co-Ordination BIOLOGYDocument21 pagesO-Level Co-Ordination BIOLOGYayikoyoroy10No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document2 pagesChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document1 pageChapter 2api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document2 pagesChapter 5api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document1 pageChapter 4api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document3 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document2 pagesChapter 6api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document1 pageChapter 7api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document1 pageChapter 10api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document2 pagesChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet
- Chapter 9Document1 pageChapter 9api-304486052No ratings yet