Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Diuretics MOA Notes Indications Side Effects Drugs
Uploaded by
monica leeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Diuretics MOA Notes Indications Side Effects Drugs
Uploaded by
monica leeCopyright:
Available Formats
Diuretics MOA Notes Indications Side effects Drugs
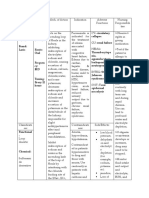
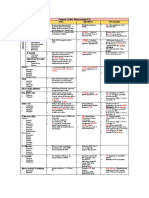
1. Mannitol Inhibits water Increases urine Dec IOP in glaucoma- Acute hypovolemia Mannitol
reabsorption throughout volume promotes drainage of
the tubule aqueous chamber
Dec ICP
Olguric states
(rhadomyolysis)
2. Carbonic Carbonic Anhydrase Decrease formation of Glaucoma Bicarbnaturia Acetazolamide
Anhydrase inhibitor inhibition in PCT and H+ inside PCT Acute mountain sickness Metabolic acidosis Dorzolamide
Principal cells of CD Dec Na/H antiport (prophylaxis prior to Hypokalemia
Increase Na and HCO3 climb; acidosis is Hyperchloremia
excretion protective) Paresthesias (inhibits CA in
Increase diuresis Tx: Metabolic alkalosis CNS)
Alkalinizes urine and Renal stones (alkaline urine
causes rapid increases risk for PO4 stones)
metabolic acidosis
Contraindicated in sulfa
allergy
3. Loop diuretics Inhibits NaK2Cl Short half-life (not For high-volume diuresis Hypokalemia Furosemide
- enter through cotransporter in TAL of used in treatment of such as Pulmonary Metabalic alkalosis Torsemide
glomerulus / via loop of Henle; significant hypertension) edema or to decrease Hypomagnesemia Ethacrynic acid
secretion by OAT Natriuresis fluid overload in heart Hypocalcemia
(uric acid transport failure Ototoxicity (endolymph has
site) NaK2Cl cotransporter,
Used for treatment of blockage prevents normal
NaK2Cl cotransporter hypercalcemia due to it’s electrolyte balance)
creates an AP, calcium-wasting effect
opening paracellular (“Loops lose calcium”) Contraindicated in sulfa
spaces for allergy
reabsorption of Ca,
Mg and loss of this (+) EXCEPT Ethacrynic acid
potential decreases
reabsorption of Ca
and Mg
4. Thiazide diuretics Inhibits NaCl Long lasting but cause For treatment of Metabolic alkalosis (due to Hydrochlorothiazide
-enter through cotransporter at DCT, less diuresis (less hypertension because increased Na delivery to CD Chlorthalidone
glomerulus / via leading to natriuresis potent) than Loops rapid diuresis is not and inc gene expression of Indapamide
secretion by OAT and diminished necessary aldosterone; inc reabsorption
(uric acid transport intravascular blood Increase Ca resorption of Na in intercalated cells, inc
site) volume dec BP due to opening of Prevent stone formation H+ excretion in principal cells)
voltage-gated Ca in those with Hypokalemia
channel, leading to hypercacliuria and at risk Hyperuricemia (pharmacologic
decreased calcium for Ca Oxaloacetate inhibition, actively secreted by
excretion in urine OAT)
Nephrogenic diabetis Hypertriglyceridemia
insipidus (paradox: give Hypercalcemia
diuretic so that patient
will urinate less) Contraindicated in sulfa
allergy
5. Potassium- Sparing Amiloride- blocks Amiloride: heart failure Hyperkalemia Amioride and
Diuretics sodium channels in when hypokalemia is a Spironolactone- blocks Triamterene
Principal cells of CD concern testosterone receptor
causing natriuresis. (androgen antagonism, like Spironolactone and
Normally this sodium Spironolactone: heart gynecomastia) eplerenone
channels reclaims failure as well as
sodium at the expense aldoseterone-secreting Eplerone- aldosterone
of potassium tumors before surgical antagonist with NO
correction antiandrogen effects
Spironolactone- causes
blockage of aldosterone
receptor, preventing
upregulation of principal
cells and leading to
decreased sodium
reclamation
Note:
Sodium reabsorption:
PCT >60%; TAL > 25%; DCT <10%; CD <5%
You might also like
- Super SquatsDocument104 pagesSuper SquatsIt's Just Me100% (3)
- 12lec Cardiac InfectionsDocument93 pages12lec Cardiac Infectionsmonica leeNo ratings yet
- Flat Belly Diet Plan For WomenDocument7 pagesFlat Belly Diet Plan For WomenMaria Isaura Lopez100% (3)
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyCrisha Ann Billones BacutaNo ratings yet
- CVS: Diuretics GuideDocument2 pagesCVS: Diuretics GuideCatNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary Syndrome Risk Factors and ManagementDocument54 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome Risk Factors and Managementxiaou123100% (1)
- Functional Foods: Presented To: Ms Rabia Presented By: Amna AdilDocument10 pagesFunctional Foods: Presented To: Ms Rabia Presented By: Amna AdilAMNA ADILNo ratings yet
- Ring Dip Progression Template For CR PDFDocument18 pagesRing Dip Progression Template For CR PDFAnaLiza PinlacNo ratings yet
- Fat Burning Lasers For Surgical Body SculptingDocument5 pagesFat Burning Lasers For Surgical Body SculptingsrimatsimhasaneshwarNo ratings yet
- A.A AntagonismDocument19 pagesA.A Antagonismjraj030_2k6No ratings yet
- Hyponatremia: ElectrolytesDocument5 pagesHyponatremia: ElectrolytesCyreen Jill Aliling100% (1)
- Pro-Anorexia Content On Social MediaDocument25 pagesPro-Anorexia Content On Social MediaLINo ratings yet
- Gram Positive Bacteria: Sporeforming Nonsporeforming Anaerobe AerobeDocument1 pageGram Positive Bacteria: Sporeforming Nonsporeforming Anaerobe Aerobemonica leeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Stomach.Document4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Stomach.Miza HayaniNo ratings yet
- Global Ingredient and Out of Home Dining Trends Aug 2016Document31 pagesGlobal Ingredient and Out of Home Dining Trends Aug 2016cufi007No ratings yet
- Renal PharmacologyDocument7 pagesRenal PharmacologywanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- W2 PHARMACOLOGY OF DIURETICS Short Notes 2017Document6 pagesW2 PHARMACOLOGY OF DIURETICS Short Notes 2017Syximsh FPNo ratings yet
- ELECTROLYTES EditedDocument6 pagesELECTROLYTES EditedKrystel Bea DinqueNo ratings yet
- Dr. Padmanabha T S Dept of Pharmacology Aims, B.G.NagarDocument19 pagesDr. Padmanabha T S Dept of Pharmacology Aims, B.G.NagarPadmanabha GowdaNo ratings yet
- Water Follows Sodium (Via OsmoticDocument3 pagesWater Follows Sodium (Via OsmoticMark Vincent SahagunNo ratings yet
- Diuretics and Renal Hormones - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewDocument4 pagesDiuretics and Renal Hormones - McMaster Pathophysiology ReviewSandra MedinaNo ratings yet
- ADH & Potassium Sparing Diuretics BDSDocument18 pagesADH & Potassium Sparing Diuretics BDSDr.U.P.Rathnakar.MD.DIH.PGDHMNo ratings yet
- Thiazide: MOA: Na & CL Symport From Lumen Into Early DCT OedemaDocument3 pagesThiazide: MOA: Na & CL Symport From Lumen Into Early DCT OedemaAzizan HannyNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics NephrologyDocument25 pagesPediatrics NephrologyNujhat TabassumNo ratings yet
- Ph'cology of Diuretics (RZH)Document48 pagesPh'cology of Diuretics (RZH)beby febyola siagianNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Drugs For Nursing PharmacologyDocument1 pageDiuretic Drugs For Nursing Pharmacologylhayes1234100% (7)
- Kidney & NephronDocument3 pagesKidney & NephronrodtanchoNo ratings yet
- DIURETICS LECTURE ZebDocument52 pagesDIURETICS LECTURE ZebPROF DR SHAHMURAD100% (2)
- Diuretic Drugs: Thiazides Sites of ActionDocument52 pagesDiuretic Drugs: Thiazides Sites of Actionuzzal ahmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture+24 +25+diureticsDocument69 pagesLecture+24 +25+diureticsGhina RizwanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Alkalosis: Devin Eckstein and Howard E. CoreyDocument4 pagesMetabolic Alkalosis: Devin Eckstein and Howard E. CoreySamantha JiménezNo ratings yet
- The Heart and Circulatory System and The Kidney 2Document28 pagesThe Heart and Circulatory System and The Kidney 2Izzuddin AhmadNo ratings yet
- K (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisDocument4 pagesK (Anion Gap 12) (Anion Gap 12) Acute Asthma Hypovolemia: - Vomit - Pyloric StenosisAhmad Asyraf AzmanNo ratings yet
- Hypokalemia 2Document32 pagesHypokalemia 2aqilasafikaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: Na/K/Cl Co-Transporter (NKCC2)Document3 pagesDiuretics: Na/K/Cl Co-Transporter (NKCC2)Safiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Diuretics TableDocument5 pagesDiuretics TableLaylee ClareNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Disorders: Clinical Significance of Hyponatremia, Hypernatremia, Hypokalemia & HyperkalemiaDocument6 pagesElectrolyte Disorders: Clinical Significance of Hyponatremia, Hypernatremia, Hypokalemia & HyperkalemiaKim Mae ComendadorNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Symptoms, Causes, ECG Changes, Diagnostics and ManagementDocument3 pagesElectrolyte Imbalances: Symptoms, Causes, ECG Changes, Diagnostics and ManagementDeanne Morris-DeveauxNo ratings yet
- Diuretics TableDocument6 pagesDiuretics TableVie TNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 Fluid and Electrolytes: Hyperkalemia or Potassium ExcessDocument2 pagesNCM 112 Fluid and Electrolytes: Hyperkalemia or Potassium ExcessAngeline NavarroNo ratings yet
- Diuretics Class Examples Indication M.O.A Side Effects: PhysiologyDocument3 pagesDiuretics Class Examples Indication M.O.A Side Effects: PhysiologyThulasi tootsieNo ratings yet
- Effects and mechanisms of diuretics in the kidneyDocument34 pagesEffects and mechanisms of diuretics in the kidneyJosephine SNo ratings yet
- EDICTO Acute Metabolic Alkalosis (FINAL)Document1 pageEDICTO Acute Metabolic Alkalosis (FINAL)GLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBANo ratings yet
- Hypertension Drugs and Their Mechanisms of ActionDocument55 pagesHypertension Drugs and Their Mechanisms of ActionNurul PertiwiNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument3 pagesPharmacologyDuy LuuNo ratings yet
- Quick Facts For Electrolyte AnalysisDocument3 pagesQuick Facts For Electrolyte AnalysiscrystalsheNo ratings yet
- A - GM - B C A: Rings Ru Uts S With Ig Ands - ND Tarts AkingDocument3 pagesA - GM - B C A: Rings Ru Uts S With Ig Ands - ND Tarts AkingtiaraNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Acidosis - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional EditionDocument2 pagesMetabolic Acidosis - Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders - Merck Manuals Professional Editionmaulidanabilah5No ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte Balance: Control Mechanisms and ImbalancesDocument7 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Balance: Control Mechanisms and ImbalancesDavid DvoskineNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument43 pagesElectrolyte ImbalanceJoshua JoNo ratings yet
- Diuretics part-1: Types, mechanisms, uses, interactions and adverse effectsDocument19 pagesDiuretics part-1: Types, mechanisms, uses, interactions and adverse effectsmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics MergedDocument727 pagesDiuretics MergedRinkiNo ratings yet
- Vidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014Document51 pagesVidconf Diuretic Antidiuretic 2014naltrisilvianNo ratings yet
- Renal Tubular Defects.Document20 pagesRenal Tubular Defects.HeforSheNo ratings yet
- c15 Diuretic AgentsDocument13 pagesc15 Diuretic AgentsmohammadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 CVS & RenalDocument116 pagesChapter 3 CVS & RenalKIDUS YAREDNo ratings yet
- Potassium Disorders: Syeda Shaheera ZaidiDocument60 pagesPotassium Disorders: Syeda Shaheera ZaidiMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- Diuretic DrugsDocument2 pagesDiuretic DrugsEngku ElisaNo ratings yet
- Diuretics: BY-DR. Saurabh Kansal Dept. of Pharmacology Msy Medical College MeerutDocument33 pagesDiuretics: BY-DR. Saurabh Kansal Dept. of Pharmacology Msy Medical College MeerutPrakhar GoelNo ratings yet
- Diuretic DrugsDocument62 pagesDiuretic DrugsAbdul WahabNo ratings yet
- Dr. Hendrata - CLINICAL POTASSIUM IMBALANCE (Slide PERNEFRI Jakarta (24-27 Nop 2011)Document45 pagesDr. Hendrata - CLINICAL POTASSIUM IMBALANCE (Slide PERNEFRI Jakarta (24-27 Nop 2011)Patricia WenNo ratings yet
- Sodium, Chloride, Potassium, Calcium Lab Values ExplainedDocument6 pagesSodium, Chloride, Potassium, Calcium Lab Values Explainedchubbygunny_29776413No ratings yet
- RenalElectrolytecharts 220906 101323 2Document7 pagesRenalElectrolytecharts 220906 101323 2Saheed jaladeNo ratings yet
- Diuretic Theraphy and Drugs For Renal FailureDocument2 pagesDiuretic Theraphy and Drugs For Renal Failurerenz bartolomeNo ratings yet
- PHS CVSDocument25 pagesPHS CVStewogbadeomobuwajo005No ratings yet
- Primary Changes and Compensations in Simple Acid-Base DisordersDocument4 pagesPrimary Changes and Compensations in Simple Acid-Base DisordersKimberly Trezona PlonkaNo ratings yet
- CVS - DiureticsDocument8 pagesCVS - Diureticshlouis8No ratings yet
- Water & Electrolyte BalanceDocument27 pagesWater & Electrolyte Balanceanisa rachmitaNo ratings yet
- DR Yosra Diuretics 2023Document46 pagesDR Yosra Diuretics 2023gntawfeqNo ratings yet
- Diuretics 140628134114 Phpapp02Document45 pagesDiuretics 140628134114 Phpapp02P merugu100% (1)
- Guide to Calcium, Phosphate, and Parathyroid Hormone DisordersDocument7 pagesGuide to Calcium, Phosphate, and Parathyroid Hormone DisordersGregNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E NotesDocument1 pageAntiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E Notesmonica leeNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics and Epidemiology: Types of Research Study Evaluation of Diagnositc TestsDocument2 pagesBiostatistics and Epidemiology: Types of Research Study Evaluation of Diagnositc Testsmonica leeNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E NotesDocument1 pageAntiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVT Drugs MOA Indication S/E Notesmonica leeNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVTDocument1 pageAntiarrhytmics Treatable Antiarrhytmics: Atrial Fibrillation, Atrial Flutter, Vtach and PSVTmonica leeNo ratings yet
- Spartan DietDocument2 pagesSpartan DietdadoNo ratings yet
- Dzexams Bac Anglais Sci 20201 1675771Document6 pagesDzexams Bac Anglais Sci 20201 1675771narimen lamis rezkiNo ratings yet
- Veg Diet Plan PDFDocument3 pagesVeg Diet Plan PDFplus100yearsNo ratings yet
- Describe Yourself in Simple Terms: A) Describe Yourself (Step 1) : Give Basic Information About YourselfDocument10 pagesDescribe Yourself in Simple Terms: A) Describe Yourself (Step 1) : Give Basic Information About YourselfMariaIsabelAlcazarCedeñoNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) PDFDocument2 pagesCongestive Heart Failure (CHF) PDFZazulizer Are BackNo ratings yet
- Mcdonalds Diet ActivityDocument2 pagesMcdonalds Diet Activityapi-246304404No ratings yet
- Icd 9 N 10 BEDAHDocument11 pagesIcd 9 N 10 BEDAHAida FaridhaNo ratings yet
- Natural Life Testimonial at AduthuraiDocument5 pagesNatural Life Testimonial at AduthurairasikaaNo ratings yet
- NHM Letter World Diabetes DayDocument9 pagesNHM Letter World Diabetes DayAnonymous RCDcVGlFpzNo ratings yet
- 11 Thesis PlanDocument33 pages11 Thesis PlanNavpreet SinghNo ratings yet
- BenzimidazolDocument145 pagesBenzimidazolMartinez Fuentes PaulinaNo ratings yet
- Practice 5-QUESTIONSDocument7 pagesPractice 5-QUESTIONSLatifah AlsahaleyNo ratings yet
- Asupan Zat Gizi Makro Status Gizi Dan STDocument7 pagesAsupan Zat Gizi Makro Status Gizi Dan STamelia cholisohNo ratings yet
- Beyond General Resistance Training. Hypertrophy Versus Muscular Endurance Training As Therapeutic Interventions in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisDocument35 pagesBeyond General Resistance Training. Hypertrophy Versus Muscular Endurance Training As Therapeutic Interventions in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus - A Systematic Review and Meta-AnalysisMarcos Túlio de SáNo ratings yet
- User ManualDocument31 pagesUser ManualHadiseh AbdyNo ratings yet
- 10 Intriguing Facts About Ancient EgyptDocument5 pages10 Intriguing Facts About Ancient EgyptDiana LarisaNo ratings yet
- Pumpkin Seeds Mixture Ameliorates Diabetic NephropathyDocument6 pagesPumpkin Seeds Mixture Ameliorates Diabetic NephropathymplennaNo ratings yet
- The Obesity FixDocument82 pagesThe Obesity Fixjbennet065No ratings yet
- MetaboTrim PH PIPDocument2 pagesMetaboTrim PH PIPYeth FolloscoNo ratings yet
- Emotional Influences On Food Choice Sensory, Physiological andDocument9 pagesEmotional Influences On Food Choice Sensory, Physiological andpanda_pandita22No ratings yet