Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Coordination in Plants
Uploaded by
Zah SchlafmützeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical Coordination in Plants
Uploaded by
Zah SchlafmützeCopyright:
Available Formats
Chemical coordination in plants
Responses shown by plants are known as tropisms.
There are two main types of tropisms:
positive tropisms – the plant grows towards the stimulus
negative tropisms – the plant grows away from the stimulus
Phototropism is a response where the stimulus is light, whereas geotropism (also called gravitropism) is
a response where the stimulus is gravity.
The five commonly recognized groups of plant hormones (growth substances) are auxins,
gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene.
Uses of plant hormones in crop production (agriculture)
Selective weedkillers (herbicide) – some plants will absorb the growth substances more. They will
grow too quicky and die. Effective in getting rid of weeds around crops.
Example - dandelions without killing the grass, or getting rid of thistles without killing the wheat
plants.
Rooting powder – encourages quick root growth in stem cuttings. Useful in asexual reproduction.
Fruit ripening – hormones can be used to speed up or slow down ripening. Useful when fruits
need to be transported far or fruits are needed any time of the year.
Seedless fruits can be produced by spraying plant hormones on the flowers.
Dormancy – seed germinating can be stopped until ideal conditions are available. Germination
can also be triggered using hormones.
You might also like
- 06 Plant HormonesDocument4 pages06 Plant HormonessureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Coordination in Plants NotesDocument5 pagesCoordination in Plants NotesAmna SaleemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4Document26 pagesChapter 3 Coordination and Response Part 4wienna1987No ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument19 pagesPlant HormonesWu YiruiNo ratings yet
- What Are The Health Benefits of Soy?Document4 pagesWhat Are The Health Benefits of Soy?Irfan SuliansyahNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL COORDINATION IN PLANTS - NotesDocument6 pagesCHEMICAL COORDINATION IN PLANTS - NotesMinal Shahbaz saeedNo ratings yet
- Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesGrowth Regulatorsirfan shahNo ratings yet
- Cropsci2 ReportDocument33 pagesCropsci2 Reportj.cortez.525157No ratings yet
- Planthormones 141025004114 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument75 pagesPlanthormones 141025004114 Conversion Gate02 PDFSaiTimmarao100% (1)
- Plant Hormone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument7 pagesPlant Hormone - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaCristie SumbillaNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination in Plants: RadiateDocument14 pagesControl and Coordination in Plants: RadiateTaimoor Hassan KhanNo ratings yet
- Bio CH5 F5 StudywithadminDocument5 pagesBio CH5 F5 StudywithadminShamil AdlanNo ratings yet
- Organic Growing Plant Growth HormonesDocument1 pageOrganic Growing Plant Growth Hormonessam winchesterNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth and Development-An IntroductionDocument6 pagesPlant Growth and Development-An IntroductionSenthilkumar PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth Regulators in Agriculture: Department of Agronomy Bahauddin Zakariya University MultanDocument32 pagesPlant Growth Regulators in Agriculture: Department of Agronomy Bahauddin Zakariya University MultanIrfan SuliansyahNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument29 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionJodd Ardee TorresNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument28 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsFaishol MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth Regulators (2014)Document34 pagesPlant Growth Regulators (2014)matthewNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFDocument38 pagesKuliah 11 - 12. Respon Tan THDP Stimulus PDFRianNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones and Plant ReproductionDocument30 pagesPlant Hormones and Plant ReproductionTeguh SaputraNo ratings yet
- BIO 2 Plant MorphologyDocument3 pagesBIO 2 Plant MorphologyMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Horticulture Science Understanding Plant Growth Regulators: Lesson 13Document23 pagesHorticulture Science Understanding Plant Growth Regulators: Lesson 13deepak_rc731757No ratings yet
- PP19. Responding To The Environment PlantsDocument50 pagesPP19. Responding To The Environment Plantstinyikomaluleka00No ratings yet
- GLUCOSIDEDocument3 pagesGLUCOSIDEAngel Ellene MarcialNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument40 pagesPlant HormonesSakina26100% (1)
- BIO02 - TropismDocument10 pagesBIO02 - TropismCarlo CondeNo ratings yet
- LR Berg - Introductory Botany (2008) c11Document19 pagesLR Berg - Introductory Botany (2008) c11Kate Jewel CullamatNo ratings yet
- Outline The Application of Plant Growth Regulators (Synthetic Auxin, Synthetic Gibberellins, Synthetic Ethylene) in AgricultureDocument3 pagesOutline The Application of Plant Growth Regulators (Synthetic Auxin, Synthetic Gibberellins, Synthetic Ethylene) in AgricultureArichandranMuniandyNo ratings yet
- Growth and DevelopmentDocument18 pagesGrowth and Developmentpriaj46No ratings yet
- Plant Response To StimuliDocument38 pagesPlant Response To Stimulideepak_rc731757No ratings yet
- 10 3 Tropic Response ppt2Document37 pages10 3 Tropic Response ppt2api-309893409No ratings yet
- Bio Written Report Ancheta and IñaDocument4 pagesBio Written Report Ancheta and IñaFerdinand RyanNo ratings yet
- 9.plant HarmonesDocument6 pages9.plant HarmonesRAVINDRA PRASADNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Classes of Hormones Self CheckDocument7 pagesLesson 1: Classes of Hormones Self CheckRenz Jian B. MacasiebNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument9 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsDestia Ayu100% (1)
- Plant Growth RegulatorsDocument5 pagesPlant Growth RegulatorsRockyNo ratings yet
- Co-Ordination in PlantsDocument8 pagesCo-Ordination in PlantsSephoraNo ratings yet
- What is plant production method The plant production system encompasses the basic genetic and physiological regulations on plant growth, the impact on growth of soil, water, nutrients, disease and pests and the infDocument40 pagesWhat is plant production method The plant production system encompasses the basic genetic and physiological regulations on plant growth, the impact on growth of soil, water, nutrients, disease and pests and the infjohnabeth jamonNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To JoinDocument18 pagesPlant Hormone Csir Net Notes Merit Life Sciences 85560092620 To Joinmerit tutorials com NET JRF JAM TUTORIALSNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormone - WikipediaDocument13 pagesPlant Hormone - WikipediaNageso FitoNo ratings yet
- PendahuluanDocument11 pagesPendahuluansekarNo ratings yet
- Growth and Development of CropsDocument17 pagesGrowth and Development of CropsSUSHMA PRIYANo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument3 pagesPlant HormonesAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- CropSci101 Module 4Document24 pagesCropSci101 Module 4Jetro Neil GapasinNo ratings yet
- Plant HormonesDocument14 pagesPlant HormonesMahamud Hasan PrinceNo ratings yet
- Herbicides SelectivityDocument6 pagesHerbicides SelectivitySahely KanthalNo ratings yet
- G2 Unit 2 Variation Standardization of Natural Products Quality Control Origins of Secondary MetaboliteDocument69 pagesG2 Unit 2 Variation Standardization of Natural Products Quality Control Origins of Secondary MetaboliteMa Jessica Allequer LlanoNo ratings yet
- F5 Chapter 5 Response in PlantsDocument26 pagesF5 Chapter 5 Response in PlantsNur Atikah AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Phytohormone: Growth in AnimalsDocument7 pagesPhytohormone: Growth in AnimalsAnonymous rq5C3bZkMNo ratings yet
- E529 Herbicides How They Work and The Symptoms They Cause 1Document12 pagesE529 Herbicides How They Work and The Symptoms They Cause 1marvitaNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 5 KaisyahDocument36 pagesBiology Chapter 5 KaisyahKaisyah Rizqiin Mohamed KamaludeenNo ratings yet
- How Plants SurviveDocument5 pagesHow Plants SurviveChrisNo ratings yet
- Tropisms in Plants: LO Be Able To Explain How Phototropism and Gravitropism Help Plants To GrowDocument7 pagesTropisms in Plants: LO Be Able To Explain How Phototropism and Gravitropism Help Plants To GrowHarriet TurnbullNo ratings yet
- Plant Responding To Environmental ChangeDocument10 pagesPlant Responding To Environmental ChangeArellano Ian Kenneth PNo ratings yet
- CV HYDRO List of SpraysDocument3 pagesCV HYDRO List of Sprayssameer lalNo ratings yet
- Control and CoordinationDocument7 pagesControl and CoordinationKanish AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones NXPowerLiteDocument25 pagesPlant Hormones NXPowerLiteZionne TanafrancaNo ratings yet
- How Pesticide WorkDocument10 pagesHow Pesticide WorkOdilo TarigasaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Coordination in PlantsDocument3 pagesChemical Coordination in Plantsrkjoseph1410No ratings yet
- Shakespeare Literature RevisionDocument1 pageShakespeare Literature RevisionZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Literature Picture RevisionDocument2 pagesLiterature Picture RevisionZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Comprehension Task - 1 Hour: Read The Extract From A Little Princess Below, and Answer The QuestionsDocument4 pagesComprehension Task - 1 Hour: Read The Extract From A Little Princess Below, and Answer The QuestionsZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Confirmatory Analysis Based On A Grounded Theory ModelDocument3 pagesConfirmatory Analysis Based On A Grounded Theory ModelZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Coordination - Human Bio HB10Document5 pagesCoordination - Human Bio HB10Zah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Zaid Write S For Sentence or Q For QuestionDocument6 pagesZaid Write S For Sentence or Q For QuestionZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
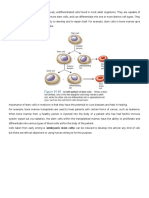
- Stem Cells Are Populations of Relatively Undifferentiated Cells Found in Most Adult Organisms. They Are Capable ofDocument2 pagesStem Cells Are Populations of Relatively Undifferentiated Cells Found in Most Adult Organisms. They Are Capable ofZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Blood and Circulation NotesDocument6 pagesBlood and Circulation NotesZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell and Leaf Structure: Structures Found Only in Plant CellsDocument1 pagePlant Cell and Leaf Structure: Structures Found Only in Plant CellsZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
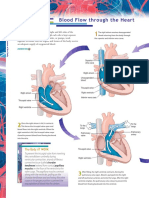
- Blood Flow Through The HeartDocument2 pagesBlood Flow Through The HeartZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Water PrincessDocument22 pagesWater PrincessZah Schlafmütze75% (8)
- Digestive System NotesDocument6 pagesDigestive System NotesZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Print Word Activities 3Document4 pagesPrint Word Activities 3Zah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Phonics 1Document3 pagesPhonics 1Zah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Brer Annansy and The Crocodile EggsDocument2 pagesBrer Annansy and The Crocodile EggsZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Ain 1. R - 2. M - 3. P - 4. TR - 5. BR - 6. GR - 7. Ag - 8. CHDocument3 pagesAin 1. R - 2. M - 3. P - 4. TR - 5. BR - 6. GR - 7. Ag - 8. CHZah SchlafmützeNo ratings yet
- Qaurter 2 Module 6Document32 pagesQaurter 2 Module 6Roden GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Doubled Haploid Production in Capsicum Annuum L. Using Anther Culture: A ReviewDocument6 pagesDoubled Haploid Production in Capsicum Annuum L. Using Anther Culture: A ReviewCarlos Rodríguez MartínNo ratings yet
- DLP 3 (Agri-Fishery Arts in Senior High.)Document7 pagesDLP 3 (Agri-Fishery Arts in Senior High.)Jamie Angela B. Salvador100% (2)
- First Evidence of Seed Predation by Arthropods From Gondwana and Its Early Paleozoic HistoryDocument10 pagesFirst Evidence of Seed Predation by Arthropods From Gondwana and Its Early Paleozoic HistoryThamiris BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Micro Propagation of Banana Musa SP CV Agnishwar by in Vitro Shoot Tip CultureDocument6 pagesMicro Propagation of Banana Musa SP CV Agnishwar by in Vitro Shoot Tip Cultureadididi33No ratings yet
- Forest EcologyDocument25 pagesForest Ecologyyusninda nadilliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 7-Diversity in Living Organisms - Class Ix - ScienceDocument32 pagesChapter - 7-Diversity in Living Organisms - Class Ix - ScienceMadhav DayareNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Document8 pagesEarth and Life Science Perpetuation of Life 1Sayno, Samantha Jade C.No ratings yet
- Selecting Blueberries For Residential Production in TennesseeDocument6 pagesSelecting Blueberries For Residential Production in TennesseeBobNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles and Protocol in Plant Tissue CultureDocument17 pagesBasic Principles and Protocol in Plant Tissue CultureHelenChungNo ratings yet
- Indigenous Plants of South GippslandDocument1 pageIndigenous Plants of South GippslandKateNo ratings yet
- Ascomycetes: Phylum AscomycotaDocument28 pagesAscomycetes: Phylum AscomycotaTayyaba QamarNo ratings yet
- It Took One Seed To Make A Diff'rence, It Took One Seed To Grow Up Tall It Took One Seed To Have The Courage, One Seed That's All!Document1 pageIt Took One Seed To Make A Diff'rence, It Took One Seed To Grow Up Tall It Took One Seed To Have The Courage, One Seed That's All!premabunNo ratings yet
- 6 - Sporebearing WorksheetDocument3 pages6 - Sporebearing WorksheetRaniey Mayol100% (1)
- Grade 6 Science Q3 Quiz2Document3 pagesGrade 6 Science Q3 Quiz2Adrian CorpinNo ratings yet
- Rootstack PistachioDocument7 pagesRootstack Pistachiobig johnNo ratings yet
- Biology Infographics by SlidesgoDocument7 pagesBiology Infographics by SlidesgoSoni SherpaNo ratings yet
- Final Agriculture 6 Module 5 Week 5Document19 pagesFinal Agriculture 6 Module 5 Week 5Merly abetsuelaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Urea On Plants GrowthDocument20 pagesEffect of Urea On Plants GrowthPallavi RajNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Land Preparation and Seed SelectionDocument6 pagesGroup 2 Land Preparation and Seed SelectionJAY MARIE PRESBITERONo ratings yet
- Agriculture 6 - W4Document17 pagesAgriculture 6 - W4Mhae_DarksnowNo ratings yet
- Merrill (1903) - Dictionary of Plant NamesDocument210 pagesMerrill (1903) - Dictionary of Plant Namesknightcloud50% (2)
- Biology M7 Plant Parts & FunctionsDocument22 pagesBiology M7 Plant Parts & FunctionsSheila Pardines100% (4)
- AngiospermDocument5 pagesAngiospermAbdul BasitNo ratings yet
- GR 10 Assign 2Document8 pagesGR 10 Assign 2KhensaniNo ratings yet
- TeaDocument51 pagesTeaBhart BhardwajNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET Mark The Letter ADocument9 pagesWORKSHEET Mark The Letter ADu Nguyễn TrọngNo ratings yet
- Pai Sho: Move 3 Move 4 Move 5 Move 5 Move 3 Move 4Document1 pagePai Sho: Move 3 Move 4 Move 5 Move 5 Move 3 Move 4nickNo ratings yet
- IB 5.3 Student NotesDocument16 pagesIB 5.3 Student Notescamila hartmannNo ratings yet
- The Amazing World of PlantsDocument4 pagesThe Amazing World of PlantsFabrizio MVNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- Return of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseFrom EverandReturn of the God Hypothesis: Three Scientific Discoveries That Reveal the Mind Behind the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (52)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (393)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (110)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (411)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Darwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignFrom EverandDarwin's Doubt: The Explosive Origin of Animal Life and the Case for Intelligent DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (39)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (597)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)