Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intoduction: Turbochargers
Intoduction: Turbochargers
Uploaded by
ahmed2000Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intoduction: Turbochargers
Intoduction: Turbochargers
Uploaded by
ahmed2000Copyright:
Available Formats
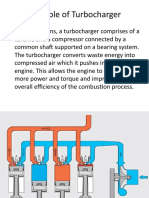
TURBOCHARGERS
1. INTODUCTION
A naturally-aspirated engine is one common type reciprocating piston I.C
engine that depends solely on atmospheric pressure to counter the partial vacuum in the
induction tract to draw in combustion air. In a naturally aspirated engine; air for combustion
or an air/fuel mixture is drawn into the engines cylinders by atmospheric pressure acting
against a partial vacuum that occurs as the piston travels downwards toward bottom dead
centre during the induction stroke. Due to restriction at intake track, a small pressure drop
occurs as air is drawn in, resulting in a volumetric efficiency of less than 100 percent - and a
less than complete air charge in the cylinder.
A supercharger is an air compressor used for forced induction of an internal combustion
engine . The greater mass flow-rate provides more oxygen to support combustion than would
be available in a naturally-aspirated engine, which allows more fuel to be provided and more
work to be done per cycle, increasing the power output of the engine. A supercharger can be
powered mechanically by a belt, gear, shaft, or chain connected to the engine's crankshaft. It
can also be powered by an exhaust gas turbine. A turbine-driven supercharger is known as a
turbocharger.
Figure 1: General setup of supercharger is shown.
A turbocharger is a small radial fan pump driven by the energy of the exhaust gases of an
engine. A turbocharger consists of a turbine and a compressor on a shared shaft. The turbine
DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING Page 1
You might also like
- Turbo Charger LectureDocument6 pagesTurbo Charger LectureAbdelrhman Essam AttiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SuperchargingDocument16 pagesChapter 3 Superchargingmustafa1011100% (1)
- 03 Principle of TurbochargerDocument19 pages03 Principle of TurbochargerSky RNo ratings yet
- Turbo Charger - ProjectDocument36 pagesTurbo Charger - ProjectSam Sams100% (2)
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesFrom EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocument65 pagesTurbocharger and Superchargerzia malikNo ratings yet
- 4 Stroke Petrol EngineDocument11 pages4 Stroke Petrol EngineAnkit Joshi50% (4)
- Description: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocument16 pagesDescription: Necessity of Turbocharger and SuperchargerNazrul Aizat ZunaidiNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger PresentationDocument18 pagesTurbocharger PresentationShrwan Gyawali100% (3)
- TurbochargerDocument17 pagesTurbochargerAravindhRaj100% (1)
- Instruction Manual and Spare Parts Catalog: Junior Ii-B Junior Ii-E Junior Ii-WDocument54 pagesInstruction Manual and Spare Parts Catalog: Junior Ii-B Junior Ii-E Junior Ii-WAung MyatNo ratings yet
- SuperchargerDocument24 pagesSuperchargerpravat dalai100% (1)
- What Is Forced Induction?Document15 pagesWhat Is Forced Induction?Fugaru Paul - AlexandruNo ratings yet
- Super ChargingDocument23 pagesSuper Charginghirenbabaji100% (2)
- Turbochargers, Final Report of The SeminarDocument19 pagesTurbochargers, Final Report of The SeminarMuddukrishna C Shetty91% (22)
- A Naturally Aspirated EngineDocument1 pageA Naturally Aspirated EngineRobert HolemsNo ratings yet
- Supercharger VS TurbochargerDocument25 pagesSupercharger VS TurbochargerAllen CastorNo ratings yet
- P1.4 - Supercharger & TurbochargerDocument19 pagesP1.4 - Supercharger & TurbochargerAlaye AkpanaNo ratings yet
- Turbochargers: BY: Muddukrishna C Shetty USN:4AL08ME023Document25 pagesTurbochargers: BY: Muddukrishna C Shetty USN:4AL08ME023Vinod SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Ch-12 - Turbocharger & Super MecDocument29 pagesCh-12 - Turbocharger & Super Mecahmed jemalNo ratings yet
- Super Charging: By: Macalintal, Lawrence BDocument10 pagesSuper Charging: By: Macalintal, Lawrence BAdrian Kim MagsinoNo ratings yet
- BCMEDocument9 pagesBCMEVenkateshwaran VenkyNo ratings yet
- Internal Combustion Engines & Gas Turbines: TopicDocument11 pagesInternal Combustion Engines & Gas Turbines: TopicSahil SinghhNo ratings yet
- Supercharger and TurbochargerDocument11 pagesSupercharger and Turbocharger20bme094No ratings yet
- Supercharging and TurbochargingDocument8 pagesSupercharging and TurbochargingMudassir Hussain100% (1)
- Final Turbohargr ReportDocument32 pagesFinal Turbohargr ReportPooja BanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Supercharging TurbochargingDocument33 pagesChapter 12 Supercharging Turbochargingdesie yalewNo ratings yet
- Turbo ChargerDocument13 pagesTurbo ChargerSwaraj TodankarNo ratings yet
- Super ChargingDocument24 pagesSuper ChargingGagan KaushikNo ratings yet
- Turbocharging: Shubham Patel 130040119085 6 Mech-M2Document15 pagesTurbocharging: Shubham Patel 130040119085 6 Mech-M2Mohammad Al QadomeNo ratings yet
- 8 1turbochargerDocument24 pages8 1turbochargerkedir67No ratings yet
- Turbo NotesDocument18 pagesTurbo NotescleousNo ratings yet
- TURBOCHARGERDocument5 pagesTURBOCHARGERAnand Raju100% (1)
- Supercharging System Chap 4 Fall 2019 PDFDocument10 pagesSupercharging System Chap 4 Fall 2019 PDFSergen SerinNo ratings yet
- Induction SystemDocument6 pagesInduction SystemDaniel MkandawireNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Turbo Charger in Two WheelerDocument2 pagesFabrication of Turbo Charger in Two WheelerNavas AzeezNo ratings yet
- Unit II - Turbo Super ChargerDocument14 pagesUnit II - Turbo Super ChargerdrkbalaNo ratings yet
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargersachin yadavNo ratings yet
- 17ME655-Module 4 PDFDocument40 pages17ME655-Module 4 PDFVinayakNo ratings yet
- Sources of Pressurized AirDocument7 pagesSources of Pressurized AirHNo ratings yet
- Operating PrincipleDocument6 pagesOperating PrincipleGedan CristianNo ratings yet
- Automotive Superchargers and Turbochargers: U.S. Air Force, Colorado Springs, Colorado, U.S.ADocument48 pagesAutomotive Superchargers and Turbochargers: U.S. Air Force, Colorado Springs, Colorado, U.S.APatricia LozerNo ratings yet
- 01 Study of CarburetorDocument13 pages01 Study of CarburetorSAMRUDDHI SARDARNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar On: "SuperchargersDocument17 pagesTechnical Seminar On: "SuperchargersSiddarth NNo ratings yet
- Basic's of Aircraft EnginesDocument5 pagesBasic's of Aircraft Enginesvenu991No ratings yet
- Turbocharger: Presented byDocument26 pagesTurbocharger: Presented byYasewn KALAWANTNo ratings yet
- Turbocharger and SuperchargerDocument16 pagesTurbocharger and SuperchargerPrajwal ZinjadeNo ratings yet
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargerAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargerrishirajtomar100% (8)
- Why A SuperchargerDocument16 pagesWhy A SuperchargerMohamad MousaNo ratings yet
- TurbochargingDocument7 pagesTurbochargingTsihatesfaNo ratings yet
- 001 Turbo ChargerDocument26 pages001 Turbo ChargerfrankNo ratings yet
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargerveer1992No ratings yet
- Performance and Power Augmentationupdated PrinoutDocument19 pagesPerformance and Power Augmentationupdated PrinoutSamarth SNo ratings yet
- Turbo ChargerDocument19 pagesTurbo ChargerHamimi AkmalNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Gas Turbine EngineDocument16 pagesAircraft Gas Turbine EngineAnupNo ratings yet
- SuperchargerDocument20 pagesSuperchargerSunil ChowdaryNo ratings yet
- 2.16.1 Principles of Forced InductionDocument8 pages2.16.1 Principles of Forced Inductionstefanovicana1No ratings yet
- The Petrol Engine: A Text-book dealing with the Principles of Design and Construction, with a Special Chapter on the Two-stroke EngineFrom EverandThe Petrol Engine: A Text-book dealing with the Principles of Design and Construction, with a Special Chapter on the Two-stroke EngineNo ratings yet
- Automatic Transmission (AT) : Transmission With Ravigneaux Planetary-Gear SetDocument1 pageAutomatic Transmission (AT) : Transmission With Ravigneaux Planetary-Gear Setahmed2000No ratings yet
- Preliminary Information 1. General Remarks: 1.6 Troubleshooting (Faults, Causes and Remedies) 7Document1 pagePreliminary Information 1. General Remarks: 1.6 Troubleshooting (Faults, Causes and Remedies) 7ahmed2000No ratings yet
- TECHDocument1 pageTECHahmed2000No ratings yet
- Lube Oil System 3R721: Figure 5.4.1 Typical Main Lube Oil Filter Assembly Element ReplacementDocument1 pageLube Oil System 3R721: Figure 5.4.1 Typical Main Lube Oil Filter Assembly Element Replacementahmed2000No ratings yet