Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calcium Gluconate
Uploaded by
Mae Ann Bueno CastillonCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calcium Gluconate
Uploaded by
Mae Ann Bueno CastillonCopyright:
Available Formats
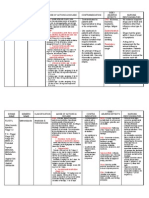
DRUG STUDY
GENERIC NAME: Calcium Gluconate
Brand name: Kalcinate
Drug Classification: fluid and electrolytic and water balance agent; replacement solution
DOSAGE, ROUTE, SIDE EFFECTS and
FREQUENCY (prescribed and INDICATION MECHANISM OF ADVERSE REACTIONS
recommended) ACTION (by system)
Dosage: adult: PO 1–2 g b.i.d. to Calcium Gluconate Injection, Body Whole: Tingling
q.i.d. IV 7 mEq q 1–3d USP is used to treat sensation. With rapid IV,
Route: Intravenous conditions arising from sensations of heat waves
calcium deficiencies such as
(peripheral vasodilation),
hypocalcemic tetany,
fainting.
hypocalcemia related to
GI: PO preparation:
hypoparathyroidism and
hypocalcemia due to rapid Constipation, increased
growth or pregnancy. It is gastric acid secretion.
also used in the treatment of CV: (With rapid infusion)
blackwidow spider bites to hypotension, bradycardia,
relieve muscle cramping and cardiac arrhythmias, cardiac
as an adjunct in the arrest,
treatment of rickets, Skin: Pain and burning at IV
osteomalacia, lead colic and
site, severe venous
magnesium sulfate
thrombosis, necrosis and
overdosage.
sloughing (with
extravasation).
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
CONTRAINDICATION/S (at least 10)
Ventricular fibrillation, metastatic bone Assessment & Drug Effects
disease, injection into myocardium;
administration by SC or IM routes; renal Assess for cutaneous burning sensations and peripheral vasodilation,
calculi, hypercalcemia, predisposition to with moderate fall in BP, during direct IV injection.
hypercalcemia (hyperparathyroidism, Monitor ECG during IV administration to detect evidence of
certain malignancies); pregnancy hypercalcemia: decreased QT interval associated with inverted T wave.
(category B). Observe IV site closely. Extravasation may result in tissue irritation and
Cautious use necrosis.
Digitalized patients, renal or cardiac Monitor for hypocalcemia and hypercalcemia.
insufficiency, sarcoidosis, history of Lab tests: Determine levels of calcium and phosphorus (tend to vary
lithiasis, immobilized patients; lactation. inversely) and magnesium frequently, during sustained therapy.
Deficiencies in other ions, particularly magnesium, frequently coexist
with calcium ion depletion.
Patient & Family Education
Report S&S of hypercalcemia promptly to your care provider.
Milk and milk products are the best sources of calcium (and
phosphorus). Other good sources include dark green vegetables, soy
beans, tofu, and canned fish with bones.
Calcium absorption can be inhibited by zinc-rich foods: nuts, seeds,
sprouts, legumes, soy products (tofu).
Check with physician before self-medicating with a calcium
supplement.
Do not breast feed while taking this drug without consulting physician.
Patient’s Name / Room No.
You might also like
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyKrissy Java79% (14)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyChaepmunk Cy75% (4)
- DRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Calcium GluconateSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyErika ManubayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study Calcium GluconateLarah Mae AndogNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyMichael Baylon DueñasNo ratings yet
- Doxazosin MesylateDocument2 pagesDoxazosin Mesylateapi-3797941No ratings yet
- Folic AcidDocument3 pagesFolic Acidapi-37979410% (1)
- Nifedepine Drug StudyDocument1 pageNifedepine Drug StudyMa. Sheenadel ZamudioNo ratings yet
- MSU-IIT Drug Study: AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesMSU-IIT Drug Study: AcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Warfarin Dosing and Monitoring GuidelinesDocument4 pagesWarfarin Dosing and Monitoring GuidelinesbillyktoubattsNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Antacid GI: Belching, GastricJhon Jade PalagtiwNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic: Systemic Administration AssessmentDocument3 pagesPharmacologic: Systemic Administration Assessmentitsmeaya100% (1)
- Acetazolamide drug studyDocument2 pagesAcetazolamide drug studyjhitch1683% (6)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Drug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineDocument5 pagesDrug Study Ampicillin, CelestamineLLan Kristine Lazarito100% (1)
- Atropine Sulfate Drug STudyDocument2 pagesAtropine Sulfate Drug STudyLiway100% (1)
- CalciumDocument1 pageCalciumRhika Mae Flores ValdezNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Delivery RoomDocument7 pagesDrug Study Delivery RoomkhleeoNo ratings yet
- Phenytoin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesPhenytoin Drug StudyCheezy Bread100% (1)
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonNo ratings yet
- Dopamine HCLDocument1 pageDopamine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (3)
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilJohn Louie EscardaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument7 pagesDrug Study CaseKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- Vii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificDocument1 pageVii. Drug Study Drug Indication Action Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Consideration Date Ordered: Generic Name: SpecificnuraNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument2 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyYanna N. Cuaki100% (2)
- Methyldopa nursing management for hypertensionDocument4 pagesMethyldopa nursing management for hypertensionRico Mae ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Midazolam Drug Study SaclotDocument1 pageMidazolam Drug Study SaclotMaybelle Cababat Saclot100% (1)
- Atropine Sulfate (Drug Study)Document3 pagesAtropine Sulfate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- GlipizideDocument3 pagesGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric NameKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesDrug Study Prednisoloneunnamed personNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: ChlorthalidoneDocument2 pagesDrug Study: ChlorthalidoneLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Drug-Study-Metformin 1Document2 pagesDrug-Study-Metformin 1Caroline Cha100% (1)
- LidocaineDocument2 pagesLidocaineAhprelle Quiring Rodiel100% (1)
- IsoxsuprineDocument1 pageIsoxsuprineAndrean EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyArdrina SappariNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Contraindications: Before:: Diamox, Diamox SequelsDocument3 pagesGeneric Name: Contraindications: Before:: Diamox, Diamox SequelsRomwella May AlgoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Tamiflu, FlagylDocument2 pagesDrug Study - Tamiflu, Flagylmark_gain100% (1)
- Drug Study - Sodium BicarbonateDocument3 pagesDrug Study - Sodium Bicarbonatejepong_paolo0283% (6)
- Potassium Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPotassium Drug StudyNasrah N. Musa100% (2)
- Atropine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesAtropine Drug StudyMaej83% (6)
- Drug Sudy Format MethyldopaDocument3 pagesDrug Sudy Format MethyldopaBianca Marithè RejanoNo ratings yet
- AMINOPHYLLINEDocument2 pagesAMINOPHYLLINEmusiclover017100% (1)
- Vasopressin PDFDocument4 pagesVasopressin PDFAnonymous hF5zAdvwCCNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyGeraldine Gallaron - CasipongNo ratings yet
- Heparin InjectionDocument2 pagesHeparin InjectiongagandipkSNo ratings yet
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonNo ratings yet
- Acetazolamide/diamoxDocument3 pagesAcetazolamide/diamoxjedisay1100% (1)
- Phenobarbital Sodium Antiepileptic Sedative Drug Classification Dosage and Administration Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesPhenobarbital Sodium Antiepileptic Sedative Drug Classification Dosage and Administration Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJeremy_Fabio_5332100% (2)
- Name: Micaela Andrea C. Cielo Date: Year & Section: BS Nursing 2A Drug Study: AlbendazoleDocument2 pagesName: Micaela Andrea C. Cielo Date: Year & Section: BS Nursing 2A Drug Study: AlbendazoleMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Class: Calcium Salts: Agent(s) Common Uses Contraindications Route/Dosage Onset of Action InteractionsDocument8 pagesClass: Calcium Salts: Agent(s) Common Uses Contraindications Route/Dosage Onset of Action InteractionsAlano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- Medications and Nursing Responsibilities for Bone HealthDocument6 pagesMedications and Nursing Responsibilities for Bone HealthDarla JoyceNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Side Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument3 pagesCalcium Gluconate Side Effects and Nursing Considerationsgovind_soni_15No ratings yet
- CefepimeDocument3 pagesCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Vitamin K drug studyDocument2 pagesVitamin K drug studyMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- Verapamil HCLDocument3 pagesVerapamil HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- B Umetani deDocument2 pagesB Umetani deMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Tablets - 100, 200 MG Side Effects: Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTablets - 100, 200 MG Side Effects: Drug StudyMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- D5LRDocument2 pagesD5LRMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (2)
- Biperiden (Drug Study)Document3 pagesBiperiden (Drug Study)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- CefepimeDocument2 pagesCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Amantadine HCLDocument4 pagesAmantadine HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- BuscopanDocument2 pagesBuscopanMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- AbstractDocument1 pageAbstractMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Atropine SulfateDocument2 pagesAtropine SulfateMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- CefepimeDocument2 pagesCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- CefepimeDocument2 pagesCefepimeMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- NCP Situational Low Self EsteemDocument1 pageNCP Situational Low Self EsteemMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (4)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument1 pageReaction PaperMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (4)
- Drug study on Biperiden for ParkinsonismDocument2 pagesDrug study on Biperiden for ParkinsonismMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Albuterol (Salbutamol)Document3 pagesAlbuterol (Salbutamol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsDocument2 pagesDrug Study: Acetadote, Mucomyst MucolyticsMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- BNP (C)Document2 pagesBNP (C)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Undercover by John Bevere Reader's ReflectionDocument8 pagesUndercover by John Bevere Reader's ReflectionMae Ann Bueno Castillon92% (12)
- Amantadine HCLDocument4 pagesAmantadine HCLMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresDocument2 pagesDiagnostic and Laboratory ProceduresMae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Haloperidol)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Haloperidol)Mae Ann Bueno CastillonNo ratings yet
- Personal Development Course for Senior High StudentsDocument7 pagesPersonal Development Course for Senior High StudentsLucelle PalarisNo ratings yet
- Gulayan Project ProposalDocument2 pagesGulayan Project ProposalMarvin LagunillaNo ratings yet
- By Pass System in The Dry ProcessDocument34 pagesBy Pass System in The Dry Processfaheemqc100% (1)
- Slide BP Texas City RefineryDocument20 pagesSlide BP Texas City Refineryamaleena_muniraNo ratings yet
- 01 Itp-380kv Gis - PlanDocument9 pages01 Itp-380kv Gis - PlanYahya SamaraNo ratings yet
- Choosing the Right Career and Job RequirementsDocument2 pagesChoosing the Right Career and Job RequirementsdinnahNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Susceptibility TestDocument5 pagesAntibiotic Susceptibility Testfarhanna8100% (3)
- Practical 5.17 Protein MaterialsDocument2 pagesPractical 5.17 Protein MaterialsdeeyamullaNo ratings yet
- Altivar 71 - ATV71H037M3Document13 pagesAltivar 71 - ATV71H037M3Mite TodorovNo ratings yet
- Nigelaycardo 1Document8 pagesNigelaycardo 1ANGELICA AYCARDO FLORESNo ratings yet
- On of Smart Crab Water Monitoring System Using ArduinoDocument46 pagesOn of Smart Crab Water Monitoring System Using ArduinoLayla GarciaNo ratings yet
- Restraint Prevalence and Perceived Coercion Among Psychiatric Inpatientsfrom South IndiaDocument7 pagesRestraint Prevalence and Perceived Coercion Among Psychiatric Inpatientsfrom South IndiaEdson HilárioNo ratings yet
- Wind Energy 6Document12 pagesWind Energy 6Shanthi RameshNo ratings yet
- Marketing Environment Analysis and Trends Impacting CompaniesDocument27 pagesMarketing Environment Analysis and Trends Impacting CompaniesSamoyed KalraNo ratings yet
- Aminacid MetabolismDocument84 pagesAminacid MetabolismAaronJose100% (1)
- Physical ExaminationDocument7 pagesPhysical ExaminationCha CulveraNo ratings yet
- Cavab - kartı - numune (копия) (копия) (копия) (копия)Document2 pagesCavab - kartı - numune (копия) (копия) (копия) (копия)Javid NovruzovNo ratings yet
- Corporate Governance at HavellsDocument16 pagesCorporate Governance at HavellsVishal Pundir100% (1)
- Eells Chap 5 6Document24 pagesEells Chap 5 6Joaquín OlivaresNo ratings yet
- Lifting Plan ProcedureDocument4 pagesLifting Plan ProcedureNath YauNo ratings yet
- Sika Poxitar FDocument3 pagesSika Poxitar FBudhi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Nichita Stanescu - The Poet of Loneliness and LossDocument28 pagesNichita Stanescu - The Poet of Loneliness and LossEmanuelaCiocanNo ratings yet
- SPE/IADC-189336-MS Pioneering The First Hydraulic Fracturing in Iraq's Complex ReservoirDocument12 pagesSPE/IADC-189336-MS Pioneering The First Hydraulic Fracturing in Iraq's Complex ReservoirKarar AliNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement 1Document4 pagesThesis Statement 1Ieka SyafiqahNo ratings yet
- University of Groningen MagazineDocument14 pagesUniversity of Groningen MagazineKhanh Phuong PhamNo ratings yet
- Cases Digest on Adoption, Guardianship and Related LawsDocument2 pagesCases Digest on Adoption, Guardianship and Related LawsGillian BrionesNo ratings yet
- 4801-Article Text-19217-1-10-20110701Document8 pages4801-Article Text-19217-1-10-20110701David BriggsNo ratings yet
- Quotes by Clarissa Pinkola Estés (Author of Women Who Run With The Wolves)Document1 pageQuotes by Clarissa Pinkola Estés (Author of Women Who Run With The Wolves)Nes GillNo ratings yet
- Create Windows XP boot CD with McAfee Command Line ScannerDocument3 pagesCreate Windows XP boot CD with McAfee Command Line ScannerSudheesh PuthusseryNo ratings yet
- Application Format For Child CustodyDocument2 pagesApplication Format For Child CustodyDHUP CHAND JAISWAL100% (3)