Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Env68 7 07 03 KC
Uploaded by
api-367296283Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Env68 7 07 03 KC
Uploaded by
api-367296283Copyright:
Available Formats
KEY CONCEPT KEY
CONCEPT
Relative frequency, or experimental probability, is based on the actual results
of an experiment, while theoretical probability is based on calculated results
from the knowledge of the possible outcomes. Experimental probability and
theoretical probability may be close but are rarely exactly the same.
This value changes each
number of times an event occurs
Experimental probability = time an experiment is
total number of times the experiment is carried out
carried out.
The experimental probability tends to get closer to the theoretical
probability of an experiment as more trials are conducted.
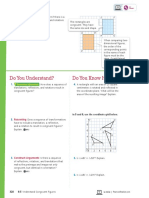
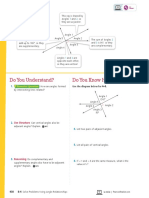
Do You Understand? Do You Know How?
1. Essential Question How is experimental In 4–6, complete each statement.
probability similar to and different from
Kelly flips a coin 20 times. The results are shown in the
theoretical probability?
table, where “H” represents the coin landing heads
up and “T” represents the coin landing tails up.
Flip 1 2 3 4 5
Result H T T H H
Flip 6 7 8 9 10
Result H H T H T
Flip 11 12 13 14 15
Result H T T T H
2. Construct Arguments How can experimental
probability be used to make predictions? MP.3 Flip 16 17 18 19 20
Result T H H T H
4. The theoretical probability that the coin will land
heads up is .
3. Reasoning Is experimental probability always 5. Based on the data, the experimental probability
close to theoretical probability? Explain. MP.2 that the coin will land heads up is .
6. The experimental probability is than the
theoretical probability.
370 7-3
Understand Experimental Probability Go Online | PearsonRealize.com
You might also like
- The Probability of An Event - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityDocument8 pagesThe Probability of An Event - IBDP Mathematics - Applications and Interpretation SL FE2021 - KognityMirjeta ZymeriNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Mathematics ProbabilityDocument57 pagesGrade 11 Mathematics ProbabilityJason TheengNo ratings yet
- S1 Chp7 HypothesisTestingDocument30 pagesS1 Chp7 HypothesisTestingBg BearNo ratings yet
- Objective: Law of Large NumbersDocument8 pagesObjective: Law of Large Numberscrystal evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Seeing TheoryDocument66 pagesSeeing TheoryJohn AvgerinosNo ratings yet
- 4Q. Prob. of SimpleCompound EventDocument6 pages4Q. Prob. of SimpleCompound EventflorinaesposophNo ratings yet
- Jemh 115Document18 pagesJemh 115MoulinaDasNo ratings yet
- Stat230 Chapter01Document5 pagesStat230 Chapter01Maya Abdul HusseinNo ratings yet
- 2-1 Probability - IntroDocument22 pages2-1 Probability - IntrofrsmioNo ratings yet
- PROBABILITYDocument59 pagesPROBABILITYgunjanNo ratings yet
- Basic ProbabilityDocument14 pagesBasic Probabilityzhilmil guptaNo ratings yet
- Coin ProbabilityDocument28 pagesCoin ProbabilityStevecia LukaNo ratings yet
- Probability Concepts ExplainedDocument2 pagesProbability Concepts ExplainedWalter ManliguezNo ratings yet
- 310 InductionDocument13 pages310 InductionMaria JosanaNo ratings yet
- Math: What Is Probability: ? Grade 6Document16 pagesMath: What Is Probability: ? Grade 6Kelly ManganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 LogicDocument42 pagesChapter 1 Logicmastura salmanNo ratings yet
- 10-4 Theoretical ProbabilityDocument2 pages10-4 Theoretical Probabilityapi-2593178567% (3)
- Chap 2Document15 pagesChap 2triangularedgeNo ratings yet
- Math100Part2 ProbabilitySimpleEventsDocument6 pagesMath100Part2 ProbabilitySimpleEvents전실 안No ratings yet
- Probability PacketDocument24 pagesProbability PacketRerxzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13Document18 pagesChapter 13Pawan NayakNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Completed NotesDocument62 pagesWeek 1 Completed NotesColeNo ratings yet
- Logic in Mathematics and ComputingDocument14 pagesLogic in Mathematics and Computingham.karimNo ratings yet
- First Toss Second Toss Third Toss Outcome H T: Uniform DistributionDocument6 pagesFirst Toss Second Toss Third Toss Outcome H T: Uniform DistributionT CNo ratings yet
- Env68 7 07 07 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 07 07 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Goodness of Fit Tests - Fstats - ch5 PDFDocument26 pagesGoodness of Fit Tests - Fstats - ch5 PDFchirpychirpy100% (1)
- Probability and StatisticsDocument15 pagesProbability and StatisticsAshi WaliaNo ratings yet
- Probability - WikipediaDocument18 pagesProbability - Wikipediaهجو مطرNo ratings yet
- CH 4 & CH 5 (Notes)Document25 pagesCH 4 & CH 5 (Notes)Chilombo KelvinNo ratings yet
- Ce 10 Macn 15Document18 pagesCe 10 Macn 15Anant RanjanNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture1 PDFUrahara JefNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Q3 ModuleDocument14 pagesStatistics and Probability Q3 ModuleBenjie DevarrasNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Probability TheoryDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Probability TheoryPrem KumarNo ratings yet
- 1.7 Compound Propositions and Validity of ArgumentsDocument76 pages1.7 Compound Propositions and Validity of ArgumentsMaria Roderene “Dyosa” QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- 3 ProbDocument21 pages3 ProbdiuhuyentrNo ratings yet
- Lectures08-09 Stoch CalchandoutDocument35 pagesLectures08-09 Stoch Calchandoute.mahler1997No ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Probability and Counting RulesDocument49 pagesChapter 4: Probability and Counting RulesKiel John100% (2)
- Math 115Document18 pagesMath 115ShailendraPatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Proofs, Induction and Number Theory: Tannaz R.Damavandi Cal Poly PomonaDocument33 pagesChapter 2: Proofs, Induction and Number Theory: Tannaz R.Damavandi Cal Poly PomonaCLNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of CountingDocument16 pagesFundamental Principles of Countingmichael noveroNo ratings yet
- CH 04Document80 pagesCH 04kir223No ratings yet
- Mathematics 8 4th: of Ways The Event Can Occur (Favorable Outcomes)Document5 pagesMathematics 8 4th: of Ways The Event Can Occur (Favorable Outcomes)jeffNo ratings yet
- Probability: Terms Used in ProbabilityDocument11 pagesProbability: Terms Used in ProbabilityRidge CraftNo ratings yet
- ProbabilityDocument47 pagesProbabilityEntry Management SystemNo ratings yet
- Probability Theory PDFDocument202 pagesProbability Theory PDFSauravNo ratings yet
- Information Retrieval Document from Venkatesh Vinayakarao's Term: Aug – Sep 2019Document57 pagesInformation Retrieval Document from Venkatesh Vinayakarao's Term: Aug – Sep 2019deccancollegeNo ratings yet
- Brief Introduction to Probability and Likelihood in Molecular EvolutionDocument7 pagesBrief Introduction to Probability and Likelihood in Molecular EvolutionPruthvi ArjunNo ratings yet
- 6 Classic Theory of Point Estimation: 6.1 Likelihood Function and MLE: Conceptual DiscussionDocument63 pages6 Classic Theory of Point Estimation: 6.1 Likelihood Function and MLE: Conceptual DiscussionsergioandradNo ratings yet
- Probability and StatisticsDocument35 pagesProbability and StatisticsdeokarsahilNo ratings yet
- Solving Problems Involving Probabilities and Simple EventsDocument7 pagesSolving Problems Involving Probabilities and Simple EventsFlorame Algarme MelanoNo ratings yet
- Probability - Binomial DistributionDocument20 pagesProbability - Binomial DistributionKhishignyam ChuluunbaatarNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Induction by Trockers-1Document74 pagesMathematical Induction by Trockers-1munyahboy playwithmeNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Session 356Document15 pagesTutorial Session 356Beket AbayevNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q4 Mod9Document22 pagesMath8 Q4 Mod9Stephen GelladulaNo ratings yet
- Math8 Q4 Mod9Document23 pagesMath8 Q4 Mod9Aileen Joyce EscasinasNo ratings yet
- Counting and Probability FundamentalsDocument13 pagesCounting and Probability FundamentalsHans ValdeNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Foundations of Information TheoryFrom EverandMathematical Foundations of Information TheoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (9)
- Radically Elementary Probability Theory. (AM-117), Volume 117From EverandRadically Elementary Probability Theory. (AM-117), Volume 117Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Env68 8 08 03 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 08 03 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 02 HSCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 02 HSCapi-326729556No ratings yet
- Env68 8 08 04 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 08 04 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 07 01 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 07 01 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 08 01 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 08 01 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 09 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 09 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 07 02 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 07 02 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 08 02 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 08 02 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 08 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 08 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 07 04 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 07 04 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 10 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 10 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 07 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 07 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 07 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 07 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 07 03 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 07 03 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 05 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 05 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 04 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 04 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 06 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 06 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 08 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 08 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 01 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 01 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 02 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 02 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 02 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 02 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 05 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 05 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 09 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 09 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 8 06 03 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 06 03 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 06 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 06 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 03 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 03 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 07 07 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 07 07 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 07 06 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 07 06 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 04 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 04 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Env68 7 08 01 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 7 08 01 KCapi-367296283No ratings yet
- Study of NanofibresDocument237 pagesStudy of NanofibresGerardo ZambranoNo ratings yet
- ch9 MKT 301 Quiz ReviewDocument4 pagesch9 MKT 301 Quiz ReviewSergio HoffmanNo ratings yet
- Happier at Home by Gretchen Rubin - ExcerptDocument39 pagesHappier at Home by Gretchen Rubin - ExcerptCrown Publishing Group69% (16)
- Concrete Strength Tester Water-Cement RatioDocument50 pagesConcrete Strength Tester Water-Cement RatioBartoFreitasNo ratings yet
- Physical-Science11 Q1 MODULE-1 08082020Document27 pagesPhysical-Science11 Q1 MODULE-1 08082020Cristilyn Briones67% (3)
- Murray NYC Group MeteringDocument5 pagesMurray NYC Group MeteringKannon TamNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Wallace Tree Multiplier With Kogge Stone Adder Using 15-4 CompressorDocument5 pagesPerformance Analysis of Wallace Tree Multiplier With Kogge Stone Adder Using 15-4 Compressoranil kumarNo ratings yet
- 909design of High Efficiency Pelton Turbine For Micro-HydropowerDocument13 pages909design of High Efficiency Pelton Turbine For Micro-HydropowerrachidtuNo ratings yet
- Cultural Dimensions & EthnocentrismDocument38 pagesCultural Dimensions & EthnocentrismKatya Alexis SalitaNo ratings yet
- Handbook Valve Technology 03.04.2020Document132 pagesHandbook Valve Technology 03.04.2020Ramazan YaşarNo ratings yet
- SMD - Metal-Sheet Decking DesignDocument10 pagesSMD - Metal-Sheet Decking DesignAchilles YipNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Evaluation of Anti-Windup PI Controllers: Xin-Lan Li, Jong-Gyu Park, and Hwi-Beom ShinDocument6 pagesComparison and Evaluation of Anti-Windup PI Controllers: Xin-Lan Li, Jong-Gyu Park, and Hwi-Beom ShinsaeedNo ratings yet
- Surveyquestionnaire 1Document6 pagesSurveyquestionnaire 1Almira IbarraNo ratings yet
- Training Catalog Piovan AcademyDocument24 pagesTraining Catalog Piovan AcademyKlein Louse AvelaNo ratings yet
- LP Fuel Gas SystemDocument6 pagesLP Fuel Gas SystemAnonymous QSfDsVxjZNo ratings yet
- Operation and Safety Manual: Ansi As/NzsDocument116 pagesOperation and Safety Manual: Ansi As/NzsMuhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Role of Digital Infrastructure in The Post Pandemic World: Preparing For Civil Services Interview-The Right PerspectiveDocument40 pagesRole of Digital Infrastructure in The Post Pandemic World: Preparing For Civil Services Interview-The Right PerspectiveshekhardfcNo ratings yet
- New TIP Course 4 (DepEd Teacher)Document58 pagesNew TIP Course 4 (DepEd Teacher)Venessa Mulig100% (2)
- Disney's Strategic HRM: Training, Recruitment and HR PlanningDocument9 pagesDisney's Strategic HRM: Training, Recruitment and HR PlanningNgân NgânNo ratings yet
- The Origins Development and Possible Decline of The Modern StateDocument65 pagesThe Origins Development and Possible Decline of The Modern StateJasper Jade MartinNo ratings yet
- Cars and Trucks With Mitsubishi TD04 TurbochargerDocument17 pagesCars and Trucks With Mitsubishi TD04 TurbochargersampapaNo ratings yet
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument13 pagesSolving Systems of Linear Equations in Two VariablesMarie Tamondong50% (2)
- Prince George's County Afro-American Newspaper, January 22, 2011Document16 pagesPrince George's County Afro-American Newspaper, January 22, 2011The AFRO-American NewspapersNo ratings yet
- Toshiba SMMS-7 VRF CatalogueDocument106 pagesToshiba SMMS-7 VRF CatalogueMyo Sein67% (3)
- Fostering Innovation Through Experiential LearningDocument14 pagesFostering Innovation Through Experiential LearningAndrew TranNo ratings yet
- Operation Manual for XMT-808 Digital Temperature ControllerDocument23 pagesOperation Manual for XMT-808 Digital Temperature Controllerjonathan_calixto_4100% (1)
- ReLu Heuristics For Avoiding Local Bad MinimaDocument10 pagesReLu Heuristics For Avoiding Local Bad MinimaShanmuganathan V (RC2113003011029)100% (1)
- (Earth and Space Science (Science Readers) ) Greg Young-Alfred Wegener. Uncovering Plate Tectonics-Shell Education - Teacher Created Materials (2008)Document35 pages(Earth and Space Science (Science Readers) ) Greg Young-Alfred Wegener. Uncovering Plate Tectonics-Shell Education - Teacher Created Materials (2008)Peter GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Technical Card: Information OnlyDocument1 pageTechnical Card: Information OnlyBhuvnesh VermaNo ratings yet
- NSTP Law and ROTC RequirementsDocument47 pagesNSTP Law and ROTC RequirementsJayson Lucena82% (17)