Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problems With Consonants For Spanish Speakers
Uploaded by
Laura Pingsdorf0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesPhonetics
Original Title
Priorities Compared
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPhonetics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesProblems With Consonants For Spanish Speakers
Uploaded by
Laura PingsdorfPhonetics
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
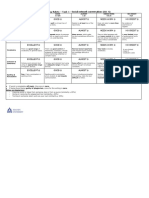
Joanne Kenworthy Peter MacCarthy Collins and Mees
High Priority: vital for intelligibility Category A is for To establish a hierarchy of
Low priority: do not affect intelligibility distinctions between error we must take into
Optional attention: features which contribute to one phoneme of a account the reactions of native
a noticeable foreign accent but do not affect language and another speakers. In general, we can
intelligibility. phoneme of the same rank errors in:
language, giving rise to 1: errors which lead to
HP: The areas of rhythm, word stress, and minimal pairs. No breakdown of intelligibility
sentence stress are high priority areas for all pronunciation of a 2: errors which give rise to
learners. foreign language can irritation or amusement
HP: For content words in stressed position be considered 3: errors which provoke few
should be given high priority but for adequate that doesn’t such reactions and may even
function words ‘the, this, that’ OA is appropriate. satisfactorily distinguish pass unnoticed.
between all its separate
Problems with consonants for Spanish speakers. phonemes. Category 1:
HP: Confusion between andThere is a Category B is for 1. Confusion of crucial
sound in Spanish which is a kind of combination anything in a person’s phonemic contrasts in
of the two sounds, which they tend to substitute way of speaking a vowel system
for the two English consonants. foreign language which (widespread)
HP: may be too close to is judged to be a gross 2. Confusion of fortis/lenis
so the word day sounds like they or marked foreign 3. Consonant clusters
accent. (Spanish)
HP: as in thin is absent in some varieties of Category C is for 4. Crucial consonant
Spanish. Watch out for as in 'fin’ or 'sin' as mispronunciations that contrasts (Spanish)
substitutes. are not particularly 5. Deletion of or
HP: and (sue-zoo) In some varieties these serious in themselves replacement by
sounds do not occur. but might well receive (Spanish)
HP: as in ‘shoe’. This sound does not occur in attention because they 6. Word stress
many varieties. are comparatively easy
LP: and They are unfamiliar sounds and to put right without Category 2:
much expenditure of
learners will either substitute or the sound time.
1. Inappropriate
represented by letter ‘y’ in Spanish. The latter will articulations, strong
Category D covers alveolar trills
sound foreign but still be intelligible.
matters that may be
HP: as in yet. Learners will either use the quite difficult for the
2. Dental fricative problems
(widespread)
Spanish sound ‘y’ or they may substitute foreign learner to get
3. Incorrect allophones of
HP: as in wet. Learners may pronounce this right, even with the
4. Weak and contracted forms
as a or they may insert a before the sound expenditure of some
(widespread)
HP: and Speakers of some South time and trouble, but
5. Inappropriate rhoticism
American varieties may not use sufficient which contribute
6. Strong retroflex setting
aspiration and may tend to delete at the end of notably to authenticity
of pronunciation. Items
a word. HP: as in ‘hold’. Learners will either in this category deserve
Category 3:
delete the sound or pronounce it with a great deal 1. Intonation errors
attention with students
of ‘hissing’ quality. There may also be confusion who are aiming at a
(widespread)
between and , so ‘ham’ may sound like really high overall
2. Lack of syllabic consonants
‘jam’ (widespread)
standard.
3. Compound stress
LP: as in ‘sing’. The learner may pronounce Category E. (widespread
the so the word ends with a consonant cluster. Miscellaneous items of
a phonetic nature that
might be held to
HP: as in ‘sing’. The learner may substitute constitute finer points in
so ‘wing’ may be pronounced as ‘win’ the pronunciation of a
language. University
Consonant clusters and sequences students and teachers
in training will benefit
HP: Two and three element clusters beginning from this.
with (small, slow, scream, school). Learners may
insert a vowel before the so small sounds like
‘a-small’.
LP: Learners will tend to add for noun plurals,
even where is required, so ‘pens’ will sound
like ‘pence’
HP: Speakers may delete in final consonant
clusters (picks, bets)
HP: Final consonant clusters with and are
problematic (test, laughed). Learners may delete
the final or or insert a vowel between the
two consonants
Word Stress
HP: One area of difficulty is the stress of
compound words and adjective + noun
combinations. (blackbird, white house, white
house)
Sentence Stress
HP: Many meanings which are conveyed in
English through sentence stress are conveyed in
Spanish through particular words.
Intonation (Pitch range, final falling pitch
movement, the rise-fall difficulty)
Problems with vowels.
HP: ages-edges confusion. Encourage
lip spreading for
HP: learners may substitute a sound that is
similar to making ‘must’ sound like ‘most’ , or
so it sounds like ‘mast’.
HP: (bit-beat) confusion. Learners will use
the latter for both vowels
HP: confusion (bat-bet) Learners will tend
to use the latter for both vowels
OA: confusion. The former will be used by most
learners for both vowels.
HP: does not occur in Spanish. Learners will
substitute the vowel suggested by the spelling.
HP: There is no variation in length in Spanish
vowels. Learners will tend to make vowels equally
long, which will be too short for the English ear.
You might also like
- Acquisition Homework-Huamaní JacquelineDocument20 pagesAcquisition Homework-Huamaní JacquelineJacqueline HUAMANINo ratings yet
- English Pronunciation 4 BraziliansDocument9 pagesEnglish Pronunciation 4 BraziliansMayaraNo ratings yet
- Comparative Practical Guide to Spanish and Portuguese: A Guide to the Major Pitfalls Between the Two LanguagesFrom EverandComparative Practical Guide to Spanish and Portuguese: A Guide to the Major Pitfalls Between the Two LanguagesNo ratings yet
- TV Show Project Plan FormatDocument4 pagesTV Show Project Plan Formatchoiminki1985No ratings yet
- Ch12 - Weak Forms - Roach 2009Document5 pagesCh12 - Weak Forms - Roach 2009ゲイリー レオンNo ratings yet
- CELTA Assignment 1Document4 pagesCELTA Assignment 1Kerry Wilson100% (7)
- FL2 SG3Document13 pagesFL2 SG3Danica Mendoza0% (1)
- Purposive Communication 101Document11 pagesPurposive Communication 101Cherish Faith TubigNo ratings yet
- Harmer 2015 PronunciationDocument19 pagesHarmer 2015 Pronunciationapi-490111150No ratings yet
- Introduction To Pronunciation HandoutDocument49 pagesIntroduction To Pronunciation HandoutRheeva AnggaNo ratings yet
- Vera Jorge SLA - Session 7: Teaching English Pronunciation, J. Kenworthy, Longman 1987Document2 pagesVera Jorge SLA - Session 7: Teaching English Pronunciation, J. Kenworthy, Longman 1987vamsrorgeNo ratings yet
- Why Do Some People Have An Accent?: The Linguistic Society of America Was FoundedDocument2 pagesWhy Do Some People Have An Accent?: The Linguistic Society of America Was FoundedkdjfkdsjfkdsjdkNo ratings yet
- TEMA 9 Magisterio InglesDocument61 pagesTEMA 9 Magisterio InglesAnonymous J0V441No ratings yet
- Celta Cambridge Assignment 2 Focus On THDocument3 pagesCelta Cambridge Assignment 2 Focus On TH居然No ratings yet
- Language: Stephen Fry: Kinetic Text On LanguageDocument4 pagesLanguage: Stephen Fry: Kinetic Text On LanguageJulia PolleroNo ratings yet
- 8 SpanishDocument7 pages8 Spanish02. ABDUL REHMANNo ratings yet
- English DLP Q1 W3 D2Document4 pagesEnglish DLP Q1 W3 D2imee corroNo ratings yet
- Written Assignment One: Focus On The Learner (Cover Sheet) : Name: Janette Giovanna Nina Rojas Date: 03/07/2016Document13 pagesWritten Assignment One: Focus On The Learner (Cover Sheet) : Name: Janette Giovanna Nina Rojas Date: 03/07/2016Rubi ZimmermanNo ratings yet
- Modulo Clases Practicas. 2020 PDFDocument60 pagesModulo Clases Practicas. 2020 PDFLynn uwuNo ratings yet
- Ahmed Sukhaeri-11190140000111-6DDocument2 pagesAhmed Sukhaeri-11190140000111-6DTracy GrayyNo ratings yet
- Ell Tool - SpanishDocument9 pagesEll Tool - Spanishapi-606458939No ratings yet
- Module-in-Linguistics-1 Rev1Document48 pagesModule-in-Linguistics-1 Rev1Muhhans ArtNo ratings yet
- Speech-Language Concerns 1Document7 pagesSpeech-Language Concerns 1api-291426388No ratings yet
- Kien Mai - An Occasion Not Allow To Use PhoneDocument5 pagesKien Mai - An Occasion Not Allow To Use PhoneniNo ratings yet
- Meeting 1 & 2 - The Nature of LanguageDocument20 pagesMeeting 1 & 2 - The Nature of LanguageNadifah ZahraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 24.02 3Document2 pagesLesson 24.02 3gkjw897hr4No ratings yet
- LCS QE ReviewerDocument35 pagesLCS QE ReviewerRocelle RellamaNo ratings yet
- T02R01 (Cook - 2003 - 40-48103-104)Document7 pagesT02R01 (Cook - 2003 - 40-48103-104)Anna SzollosiNo ratings yet
- EF4e B1 TabcontDocument4 pagesEF4e B1 TabcontsamuelgilNo ratings yet
- Words Often Confused American English TeacherDocument9 pagesWords Often Confused American English TeacherTeacher TatiNo ratings yet
- Varrah Lisun FlanDocument6 pagesVarrah Lisun FlanAdrienne Dave MojicaNo ratings yet
- CLASS 15 VowelsDocument22 pagesCLASS 15 VowelsAndrea Vera BecerraNo ratings yet
- Equipped For Reading SuccessDocument41 pagesEquipped For Reading SuccessRajnee RungtaNo ratings yet
- Bunga Refira - 1830104008 - Phoneme and PhoneticDocument3 pagesBunga Refira - 1830104008 - Phoneme and PhoneticBunga RefiraNo ratings yet
- The Schwa 1 British English StudentDocument3 pagesThe Schwa 1 British English Studentalynasama1975No ratings yet
- Task 4 - Bryan Fabian Mellizo VelasquezDocument11 pagesTask 4 - Bryan Fabian Mellizo VelasquezALEJANDRONo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English (Passive and Active Voice)Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English (Passive and Active Voice)MayaPatliTabiosNo ratings yet
- Lightbown & Spada, Chapter 4: Learner Language Term/Concept Researchers Definition/ExampleDocument3 pagesLightbown & Spada, Chapter 4: Learner Language Term/Concept Researchers Definition/ExampleLindseyScanlonNo ratings yet
- The-Schwa Sound: Student ActivityDocument3 pagesThe-Schwa Sound: Student ActivityAlejandraNo ratings yet
- Wrong Lyrics LessonDocument2 pagesWrong Lyrics LessonЕлизавета БогоявленскаяNo ratings yet
- Learning Languages British English Student BWDocument3 pagesLearning Languages British English Student BWMartin BaintonNo ratings yet
- SD PronunciationDocument10 pagesSD PronunciationElena IzvoreanNo ratings yet
- 5 RW-Lesson-5 - 20240221 - 235944 - 0000Document38 pages5 RW-Lesson-5 - 20240221 - 235944 - 0000reveriehale1210No ratings yet
- English and Spanish DiphthongsDocument4 pagesEnglish and Spanish DiphthongsCandiNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4-IntroductionDocument5 pagesTarea 4-Introductiontulia carabaliNo ratings yet
- SD Phonetics PronunciationDocument7 pagesSD Phonetics PronunciationElena IzvoreanNo ratings yet
- Grade 2 DLL ENGLISH 2 Q4 Week 4Document3 pagesGrade 2 DLL ENGLISH 2 Q4 Week 4nhemsgmNo ratings yet
- PLD Clasa 3 Limba Engleza NouDocument5 pagesPLD Clasa 3 Limba Engleza NouElizavetaCociuNo ratings yet
- Extensive ReadingDocument14 pagesExtensive ReadingMérito SaberNo ratings yet
- A Learning Module in English For Grade 8Document30 pagesA Learning Module in English For Grade 8Maryknoll PonceNo ratings yet
- PDF Celta Assignment 1Document6 pagesPDF Celta Assignment 1Oksana BerezaNo ratings yet
- Analysing Hawaiin Pidgin: Code-Switching Definition: 5 Reasons People Code-Switch - 2023 - MasterclassDocument4 pagesAnalysing Hawaiin Pidgin: Code-Switching Definition: 5 Reasons People Code-Switch - 2023 - MasterclassRAPHAEL RYNE JUNAIDYNo ratings yet
- Quiz W2&3Document1 pageQuiz W2&3SHIELAMAE BELENNo ratings yet
- A World Language: No SmokingDocument6 pagesA World Language: No Smokingsamah gmNo ratings yet
- DLP About Objective No. 3 and 7Document4 pagesDLP About Objective No. 3 and 7Rosalie dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Language: Cambridge English Empower B1+ Academic Skills PlusDocument28 pagesUnit 1 Language: Cambridge English Empower B1+ Academic Skills PlusJuan Pablo Cadena AguilarNo ratings yet
- Traditional Clothing of T' Boli Grade 7 ArtsDocument28 pagesTraditional Clothing of T' Boli Grade 7 Artsmienrado biguerasNo ratings yet
- Subanon Philippines Cerd Jul07 EngDocument25 pagesSubanon Philippines Cerd Jul07 EngdoncathalNo ratings yet
- Kelseys Term 4 - 6 Standards Report TemplateDocument4 pagesKelseys Term 4 - 6 Standards Report Templateapi-448664195No ratings yet
- Honouring Samoan Ways and Understandings Multiple Sites of Healing Kiwi TamaseseDocument9 pagesHonouring Samoan Ways and Understandings Multiple Sites of Healing Kiwi Tamasesesun angelaNo ratings yet
- Perniola - Art and Its ShadowDocument99 pagesPerniola - Art and Its ShadowAndre AlvesNo ratings yet
- Writing Rubric - EIC 5 - Task 1 - Social Network ConversationDocument2 pagesWriting Rubric - EIC 5 - Task 1 - Social Network ConversationAiko NguyênNo ratings yet
- SLNB-2016-06 V.54 JuneDocument98 pagesSLNB-2016-06 V.54 JunePost Your FeedbackNo ratings yet
- Sow English Year 1 2022-2023Document22 pagesSow English Year 1 2022-2023Nizam QusyairiNo ratings yet
- SMRT 206 Katajala-Peltomaa, Toive (Eds.) - Lived Religion and The Long Reformation in Northern Europe C. 1300-1700 PDFDocument334 pagesSMRT 206 Katajala-Peltomaa, Toive (Eds.) - Lived Religion and The Long Reformation in Northern Europe C. 1300-1700 PDFL'uomo della RinascitáNo ratings yet
- Julius Evola 「Zen ー The Religion of the Samurai」 PDFDocument13 pagesJulius Evola 「Zen ー The Religion of the Samurai」 PDFKerberus Barbarossa100% (1)
- FINAL CHAPTER 1 To 3 ROBERT FACTORDocument36 pagesFINAL CHAPTER 1 To 3 ROBERT FACTORRobert FactorNo ratings yet
- Pustakmahal Rapidex Language Learning Coursehindi-Tamil With CDDocument1 pagePustakmahal Rapidex Language Learning Coursehindi-Tamil With CDSatyam sharmaNo ratings yet
- Why Marriage Is Not NecessaryDocument4 pagesWhy Marriage Is Not NecessaryTherese DimapilisNo ratings yet
- Colors in ChristianDocument25 pagesColors in ChristianAdaletNo ratings yet
- People in PanamaDocument28 pagesPeople in PanamaLoly Moreno CastilleroNo ratings yet
- Teachers As TransformersDocument3 pagesTeachers As Transformersapi-249568839No ratings yet
- Magic The Gathering Subculture PDFDocument137 pagesMagic The Gathering Subculture PDFMaximiliano Prieto MoralesNo ratings yet
- Project Danum A PR Advocacy Campaign For The Sapang Bato CommunityDocument3 pagesProject Danum A PR Advocacy Campaign For The Sapang Bato CommunityLucas GantioquiNo ratings yet
- Jerry V Situmorang 2201111825 - English EssayDocument2 pagesJerry V Situmorang 2201111825 - English EssayJerry Vinsensius SitumorangNo ratings yet
- The Enlightenment, Freemasonry, and The Illuminati. by Conrad GoeringerDocument27 pagesThe Enlightenment, Freemasonry, and The Illuminati. by Conrad GoeringerΚοινωνικός Κύκλος100% (1)
- RULE 130, RRC (Full Text of The Law)Document6 pagesRULE 130, RRC (Full Text of The Law)Mendel DimaanoNo ratings yet
- UNIT ACTIVITIES MAP Eng 9Document4 pagesUNIT ACTIVITIES MAP Eng 9mikkaellaNo ratings yet
- Halima-Research-Proposal-Corrected CopieDocument8 pagesHalima-Research-Proposal-Corrected CopieAdelNo ratings yet
- Johara Elichelle V. ItoDocument2 pagesJohara Elichelle V. ItoJohara Elichelle Ito-PandaNo ratings yet
- American StructuralismDocument7 pagesAmerican StructuralismRosa Asr100% (1)
- Immanuel KantDocument3 pagesImmanuel Kantzainab jabinNo ratings yet
- Pishkarbasicsummaryof EnglishnliteratureDocument358 pagesPishkarbasicsummaryof EnglishnliteratureAurélie LYNo ratings yet
- Open For All Ages: One Stop Fashion Learning CenterDocument6 pagesOpen For All Ages: One Stop Fashion Learning CenterseptinanurzenahNo ratings yet
- Comparison 5RU WOS SCO 2004 2013 30july2013 ChartDocument6 pagesComparison 5RU WOS SCO 2004 2013 30july2013 ChartFreedomNo ratings yet
- Finale ResearchDocument71 pagesFinale ResearchZia BellNo ratings yet