Professional Documents
Culture Documents
53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - Input, Output Modules PDF
53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - Input, Output Modules PDF
Uploaded by
Arjun Goud0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views64 pagesOriginal Title
53_36765_ME593_2014_1__1_1_input, output modules.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views64 pages53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - Input, Output Modules PDF
53 - 36765 - ME593 - 2014 - 1 - 1 - 1 - Input, Output Modules PDF
Uploaded by
Arjun GoudCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 64
INPUT / OUTPUT MODULES
PLC Block Diagram
Types of I/O Modules
• Discrete input and output
• Analog input and output
• Specialty I/O modules
• Communication modules
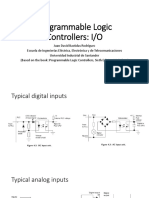
Discrete Versus Analog Inputs
• Discrete or digital input signals are two-state
signals:
– Input ON or OFF, 1 or 0
• Analog input signals are values:
– 0 to 10 volts DC
– -10 to +10 volts DC
– 4 to 20 milliamps
Module Features
• Identifier as to type of module:
– Input
– Output
– Combination input or output
• Status indicators
• Screw terminals for connecting field devices
• Removable terminal blocks
SLC 500 Combination I/O Module
(1 of 2)
Image courtesy of Allen-Bradley, a Rockwell Automation business
SLC 500 Combination
I/O Module (2 of 2)
• Each screw terminal will have a unique
identifier called an address.
• Each field device input screw terminal will
correlate to a status indicator.
• Status indicator will be on when the input
point sees an input signal.
• Status indicator will have same address
identifier as input screw terminal.
Typical Wiring of Input Signals
16-Point Input Module
with 8 Points Per Common
Binary Data Representation
• We communicate to others using groups of
letters arranged into words.
• The PLC uses groups of bits called words.
• Different bit patterns represent different
information.
Bits
• Unlike English, computers have only two
characters available 1 or 0.
• Each 1 or 0 is called a binary digit or bit.
• Binary is base or radix 2.
• A single bit is the smallest unit of computer
data.
PLC Words
• One measure of a computer’s capabilities is
the length of the data words on which it can
operate.
• Current PLCs use 16-bit words.
• Newer PLCs use 32-bit words.
• SLC 500 family PLCs are 16-bit computers.
Information Represented
as Combinations of Bits
Parts of a 16-Bit Word
Bytes, Nibbles, and Bits
16-Point Module’s
I/O Points Represented in a Word
Physical Input Conditions and the
Corresponding Input Data Word
8-Point Input Module
Represented in a Word
24-Point I/O Module
Represented in Two Words
Two Words Representing
Inputs for a 32-Bit Module
Data Table Format
• Words are 16 bits.
– Bits 0 through bit 15
• First word or bit is always 0.
• SLC 500 data tables can contain up to 256
words (0 to 255).
Words Arranged in a Data Table
Input Data File (1 of 2)
• Each input screw terminal has one memory
location to store on or off status.
• Input data is stored in the input data file.
– Also called the input status file
• Input status file holds input status
information, which is used to solve ladder
program.
Input Data File (2 of 2)
• Identified as an I-type data file
• Only one input status file allowed per project
• Only has words created for actual modules in
system
Discrete Input
Status Table Word
• 16-point discrete input modules are assigned
one word in the input status table.
• A 16-point discrete input module residing in
slot 3 would be addressed as I:3.0, bits 0
through 15.
Input Status Table
Discrete I/O Module With 32 Points
• Because input status word is 16 bits wide,
there are 16 bits available for up to 16 I/O
screw terminals.
• A 32-point I/O module will require two 16-bit
words to accommodate all I/O points.
• For a 32-point input module in slot 3, two
words, I:3.0 and I:3.1 will be created as part of
the I/O configuration.
32-Point Input Module
Input Addressing for Upper 16 Bits
• Screw terminal 16 address would be I:3.1/0.
• Screw terminal 17 address would be I:3.1/1.
• Screw terminal 18 address would be I:3.1/2.
• Screw terminal 31 address would be I:3.1/15.
– Can be entered on ladder as I:3/31, will display as
set up in properties
I/O Address Format for
SLC 500 Family of PLCs
RSLogix 500 Software
Input Status Table Screen View
RSLogix 500 Software
Output Status Table Screen View
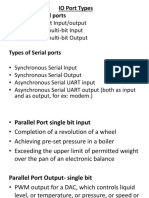
Analog Inputs
• Typical analog signals come from temperature,
pressure, position, and motor speed.
• Analog input modules convert analog signals
to digital words.
• Analog input signals are current or voltage.
Typical Analog Inputs
• Analog input signals
– 0 to 10 volts DC
– -10 to +10 volts DC
– 0 to 5 or 1 to 5 volts DC
– 4 to 20 milliamps
– 0 to 20 milliamps
– -20 to +20 milliamps
Analog Module Configurations
• Analog input information comes in as an input
channel.
• Analog modules are
– All inputs
– All outputs
– Combination of input and output channels
Analog Input Signals
Represent Values
• A potentiometer supplying a 0- to 10-V DC
input signal to an analog input module could
send a converted signal of 0 to 32767 into PLC
memory.
• Analog data format is determined by module
and module configuration.
Local Versus Remote I/O
• Local analog modules in a SLC 500 system
automatically send the converted signal into
the input status table.
• Remote I/O analog signals require block
transfers.
Analog Input Modules and
the Input Status Table
• Each analog channel will be represented by a
entire word in the input status table.
• A two-channel analog input module will have
two words in the input status table to
represent the binary representation of the
analog voltage or current.
Analog Data Is Represented
as Whole Word Data
• Analog signals are not digital signals
represented as 1s and 0s.
• Analog information is represented as a
16-bit signed integer in the data table.
• Each channel will require one word.
• Data table will reserve one word for each
channel.
• This is part of the I/O configuration process.
Input Word Assignment
• 1746-NI8 is an 8-channel analog input
module.
• Eight words will be assigned to the input
status table as part of the I/O configuration.
• Module in slot 4 will have words I:4.0 through
I:4.7, one for each channel.
1746-NI8
Input Status Table Words
PLC Output Section
• The output section of a PLC system is the
physical connection between the processor
and the outside world.
Output Classifications
• Output modules fall into three classifications.
– Discrete
– Analog
– Specialty
Discrete Outputs
• Motor starter coils • Control relays
• Pilot lights • Start pushbuttons
• Solenoids • Stop pushbuttons
• Alarms • Horns
• Valves • Start / stop signals to
• Fans variable speed drives
Operating Characteristics (1 of 2)
• Discrete output modules are simply switching
devices that carry out commands from the
processor.
• They receive their operating power from the
PLC’s power supply.
• Power output point switches to control field
devices are provided by the user.
Operating Characteristics (2 of 2)
• Each output point contains a switching device,
which is located inside the module.
• The switching device is turned on or off
according to the bit value residing in that
particular output module’s status table
address.
Three Basic Types
of Output Modules
• Solid-state (triac) switching for AC loads
• MOSFET for DC loads
• Mechanical relay
Basic Wiring for a 120 VAC
Relay Output Module Variations
• Combination input and relay output module
• Isolated relay outputs
• 8 or 16 outputs with shared commons
Combination 120 VAC Input
and Relay Output Module
8-Point Relay Output Module
AC Isolated Output Module
Interposing Relays
• Most output modules switch between one-
half and four amps.
• To switch higher current loads, a mechanical
relay called an interposing relay is placed
between the output point and the load.
• Output module switches the relay.
• Relay switches the load.
Interposing Relay Switches Load That
Exceeds Module Capability
Analog Output Modules
• They accept a 16-bit output status word,
which the module converts to an analog value
through a digital-to-analog converter.
• Analog output modules send out a varying
current or voltage signal.
Typical Analog Field Devices
• Temperature
• Pressure
• Position
• Valves
• Variable frequency drives
• Meters
Typical Analog Outputs
• Analog output signals
– 0 to 10 volts DC
– -10 to +10 volts DC
– 0 to 5 or 1 to 5 volts DC
– 4 to 20 milliamps
– 0 to 20 milliamps
– -20 to +20 milliamps
Analog Module Configurations
• Analog output information is sent to the field
device by way of an output channel.
• Analog modules are
– All inputs
– All outputs
– Combination of input and output channels
Analog Output Signals
Represent Values
• A binary output signal from 0 to 32767 from
the output status table could be converted to
a 0 to 10 V DC output signal to control an
analog field device.
• Analog data format is determined by module
and module configuration.
Local Versus Remote I/O
• Local analog modules in an SLC 500 system
automatically receive the binary value from
the output status table.
• Remote I/O analog signals require block
transfers.
Analog Input Modules and the Output
Status Table
• Each analog channel will be represented by an
entire word in the output status table.
• A two-channel analog output module will
have two words in the output status table to
represent the binary representation of the
analog voltage or current.
Analog Data Is Represented
as Whole Word Data
• Analog signals are not digital signals
represented as 1s and 0s.
• Analog information is represented as a
16-bit signed integer in the data table.
• Each channel will require one word.
• Data table will reserve one word for each
channel.
• This is part of the I/O configuration process.
Output Word Assignment
• 1746-NO4V is a four-channel analog voltage
output module.
• Four words will be assigned to the output
status table as part of the I/O configuration.
• Module in slot 4 will have words O:4.0
through O:4.3, one for each channel.
1746-NO4V Input
Status Table Words
You might also like
- Advance PLC Programming Course V2019 PDFDocument54 pagesAdvance PLC Programming Course V2019 PDFRomel Agan100% (1)
- LTE MO CommandsDocument41 pagesLTE MO CommandsRohit Singh Tomar78% (9)
- PLC Hardware ComponentsDocument62 pagesPLC Hardware ComponentsibraheemNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controllers: Topic 2 - 2Document45 pagesProgrammable Logic Controllers: Topic 2 - 2Vedant .ChavanNo ratings yet
- PLC Hardware ComponentsDocument30 pagesPLC Hardware ComponentsJosephNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Io InterfaceDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Io InterfaceSafa MNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis 2Document65 pagesFinite Element Analysis 2Theerkka TharisananNo ratings yet
- Dasar Dasar PLCDocument65 pagesDasar Dasar PLCAgie FernandezNo ratings yet
- PLCDocument39 pagesPLCHari PrasadNo ratings yet
- Programmable Peripheral InterfaceDocument34 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interfacekshirsagar_anNo ratings yet
- PLC Basics - En.idDocument68 pagesPLC Basics - En.idBambang Hadi KusumaNo ratings yet
- PLC (Programmable Logic Control)Document57 pagesPLC (Programmable Logic Control)sunilNo ratings yet
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC)Document47 pagesProgrammable Logic Controllers (PLC)denramrNo ratings yet
- Jdbastir - 9 - PLC 3 - IODocument33 pagesJdbastir - 9 - PLC 3 - IOJean Paul Suárez PadillaNo ratings yet
- MEL - 334: Low Cost Automation: Programmable Logic ControllerDocument65 pagesMEL - 334: Low Cost Automation: Programmable Logic ControllerSoufyan DexterNo ratings yet
- PLC m4Document17 pagesPLC m4Goutham KNo ratings yet
- MY MPS Lecture-9 UART, ADC, DAC TIMERSDocument45 pagesMY MPS Lecture-9 UART, ADC, DAC TIMERSZaraNo ratings yet
- Materi PLC Ke 5Document27 pagesMateri PLC Ke 5Dido WidyatamaNo ratings yet
- Interfacing LectureDocument136 pagesInterfacing LectureTewodrosNo ratings yet
- Iotuni 2Document45 pagesIotuni 2Ashwin BenkeNo ratings yet
- Experiment No 04 Ladder Diagram Development For Different Types of Logic GatesDocument7 pagesExperiment No 04 Ladder Diagram Development For Different Types of Logic GatesRavindra0% (1)
- PLC Entradas y Salidas Itv-M2Document22 pagesPLC Entradas y Salidas Itv-M2robertozapatarNo ratings yet
- 8255 Programmable Peripheral InterfaceDocument27 pages8255 Programmable Peripheral InterfaceumramanNo ratings yet
- Programmable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIDocument27 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIISantosh KumarNo ratings yet
- 8255Document26 pages8255Balakrishnan PaNo ratings yet
- PLC ScadaDocument43 pagesPLC ScadaabhijeetNo ratings yet
- C - 2 - PLC Hardware ComponantsDocument69 pagesC - 2 - PLC Hardware ComponantsShreesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Lect 2Document31 pagesLect 2rawan.waelmuNo ratings yet
- Unit - 6Document52 pagesUnit - 6s.rezina96No ratings yet
- 10) Encoder Prac 10Document8 pages10) Encoder Prac 10Anb BajwaNo ratings yet
- Programmable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIDocument27 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIHariTejNo ratings yet
- Basics of Programmable Logic ControllerDocument79 pagesBasics of Programmable Logic Controllersam_al_gino375No ratings yet
- Lion Specification enDocument16 pagesLion Specification enShaka ZuluNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design Combinational LogicDocument29 pagesDigital Logic Design Combinational LogicsfdNo ratings yet
- Final ManualDocument98 pagesFinal ManualbhuvaneshNo ratings yet
- Unit II Special Purpose Programmable Peripherals and Their InterfacingDocument10 pagesUnit II Special Purpose Programmable Peripherals and Their InterfacingPraveen RathnamNo ratings yet
- Programmable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIDocument27 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIDushyanth Reddy KusupatiNo ratings yet
- I/A Series Hardware: ® Product SpecificationsDocument20 pagesI/A Series Hardware: ® Product Specificationsrasim_m1146No ratings yet
- ch19 - 1 PLC PDFDocument39 pagesch19 - 1 PLC PDFMASOUDNo ratings yet
- Interfacing ICs - 8255Document48 pagesInterfacing ICs - 8255Adarsh AnandNo ratings yet
- Io Ports - CommunicationDocument42 pagesIo Ports - CommunicationRajesh KoneNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument430 pagesIlovepdf MergedYuvraj ChhabraNo ratings yet
- Programmable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIDocument27 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIMahesh Raje KolheNo ratings yet
- PLC & ScadaDocument43 pagesPLC & ScadaRama Kant Sahu90% (21)
- 2 Module - 1 - 2 - Part 3 Peripheral Interfacing ICsDocument31 pages2 Module - 1 - 2 - Part 3 Peripheral Interfacing ICsChristy PollyNo ratings yet
- Module 4Document104 pagesModule 4Sudeeksha GanguliNo ratings yet
- Programmable Peripheral InterfaceDocument25 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interfacejaga_desh86No ratings yet
- Programmable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIDocument27 pagesProgrammable Peripheral Interface: Interfacing Part IIIJolly SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- 8255 Programmable Peripheral InterfaceDocument27 pages8255 Programmable Peripheral InterfaceSivaprakasam KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Adc Dac KRDocument34 pagesAdc Dac KRwohaja9323No ratings yet
- 8051 Vs Motorola 68HC11Document19 pages8051 Vs Motorola 68HC11zuanne83No ratings yet
- STM Logic 1.8 GPIO ApplicationsDocument73 pagesSTM Logic 1.8 GPIO Applicationsc121No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Digital/Analog I/O SystemDocument82 pagesChapter 5: Digital/Analog I/O SystemNguyễn Tuấn HòaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-3 (Microprocessors and Microcontrollers)Document31 pagesLecture-3 (Microprocessors and Microcontrollers)KhuleedShaikhNo ratings yet
- IO Interface PDFDocument55 pagesIO Interface PDFrajesh5500No ratings yet
- 8085 Instruction Addressing Modes ImppDocument87 pages8085 Instruction Addressing Modes ImppRohan VaidyaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Chapter 4-7@networking ModelsDocument94 pagesChapter 4-7@networking ModelsSilabat AshagrieNo ratings yet
- Quad Operational Amplifiers LM324: FeaturesDocument4 pagesQuad Operational Amplifiers LM324: FeaturessebastianNo ratings yet
- 3 s2.0 B9780323919234000185 MainDocument16 pages3 s2.0 B9780323919234000185 MainWasyehun TamratNo ratings yet
- FMGaDocument7 pagesFMGaWilson Roberto Sanchez SolanoNo ratings yet
- Bigip Update Upgrade GuideDocument85 pagesBigip Update Upgrade Guidealways_redNo ratings yet
- Sigma: Amplitude Modulation/ Demodulation System Trainer Model - Com101Document29 pagesSigma: Amplitude Modulation/ Demodulation System Trainer Model - Com101Vương Thành ĐôNo ratings yet
- PythonDocument191 pagesPythonRajasekhar Reddy100% (1)
- Computer Applications Icse10th Ans MDocument371 pagesComputer Applications Icse10th Ans Mgroup projectNo ratings yet
- Gcfi6e Im Ch05Document17 pagesGcfi6e Im Ch05cebos dlaminiNo ratings yet
- ELET 211 Lab Manual 2022Document125 pagesELET 211 Lab Manual 2022Ahmad ManaNo ratings yet
- SP DM413 A.003Document18 pagesSP DM413 A.003astral projectNo ratings yet
- DSCI 5350 - Lecture 2 PDFDocument54 pagesDSCI 5350 - Lecture 2 PDFPrazNo ratings yet
- Bytesense - Forms - Nda Unilateral Signing LogDocument2 pagesBytesense - Forms - Nda Unilateral Signing LogJannatul ferdousNo ratings yet
- Item Code Lot Number MPN Component Type Class SMD/THT Class Make Distributor/ManufactureruomDocument58 pagesItem Code Lot Number MPN Component Type Class SMD/THT Class Make Distributor/ManufactureruomBalu KamathNo ratings yet
- 4-Channel Analog Input RTD/TC Intrinsically Safe: A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G HDocument2 pages4-Channel Analog Input RTD/TC Intrinsically Safe: A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G HIsaac FernándezNo ratings yet
- AN3481Document16 pagesAN3481rosarioantonyNo ratings yet
- Fault Codes - P0087/49 (Also P0190/49, P0192/49, P0193/49) - Fuel Pressure Too LowDocument6 pagesFault Codes - P0087/49 (Also P0190/49, P0192/49, P0193/49) - Fuel Pressure Too LowJonn Sim-OneNo ratings yet
- SAT Collection CS 11Document55 pagesSAT Collection CS 11Эльжан БалгаринаNo ratings yet
- Lab A, Securing Administrative Access Using AAA and RADIUS: TopologyDocument13 pagesLab A, Securing Administrative Access Using AAA and RADIUS: TopologyGary Giovanni Cabezas GutierrezNo ratings yet
- E-Business Suite 11iDocument50 pagesE-Business Suite 11iashi_25145591099No ratings yet
- JSP by Example TutorialDocument42 pagesJSP by Example Tutorialapi-3818400No ratings yet
- GL200 User Manual V1.01Document14 pagesGL200 User Manual V1.01mirobaresicNo ratings yet
- GDPR SmartThings File Description en US v113 210731 164502Document28 pagesGDPR SmartThings File Description en US v113 210731 164502Syede shizrah ShizrahNo ratings yet
- Upgrade Instructions: Valid For Sinumerik 840D Software Version 07.04.36.00Document15 pagesUpgrade Instructions: Valid For Sinumerik 840D Software Version 07.04.36.00Sam eagle goodNo ratings yet
- Features Description: LTC1046 "Inductorless" 5V To - 5V ConverterDocument14 pagesFeatures Description: LTC1046 "Inductorless" 5V To - 5V ConverterΚΩΝΣΤΑΝΤΙΝΟΣ ΚΟΝΤΟΜΙΣΙΟΣNo ratings yet
- Phase 2 p&ID - Google SearchDocument4 pagesPhase 2 p&ID - Google SearchAhmed Essam El-DinNo ratings yet
- Cyberratings Enterprise Firewall Test Report 2021Document15 pagesCyberratings Enterprise Firewall Test Report 2021JorilNo ratings yet
- PeopleSoft Internet Architecture (PIA)Document11 pagesPeopleSoft Internet Architecture (PIA)Anbudan Chandru100% (3)