0% found this document useful (0 votes)
174 views4 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation Overview
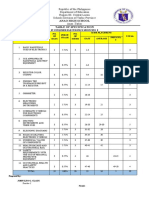
The document contains a question bank for the subject "Measurements & Instrumentation" for the second year, fourth semester B.E. degree examinations in Electrical and Electronics Engineering. It includes questions divided into 5 units - Introduction, Electrical and Electronics Instruments, Comparison Methods of Measurements, Storage and Display Devices, and Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems. The questions assess various concepts related to instruments, measurements, transducers, and data acquisition on different cognitive levels like understanding, application, and analysis.
Uploaded by
Vel MuruganCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
174 views4 pagesMeasurements and Instrumentation Overview
The document contains a question bank for the subject "Measurements & Instrumentation" for the second year, fourth semester B.E. degree examinations in Electrical and Electronics Engineering. It includes questions divided into 5 units - Introduction, Electrical and Electronics Instruments, Comparison Methods of Measurements, Storage and Display Devices, and Transducers and Data Acquisition Systems. The questions assess various concepts related to instruments, measurements, transducers, and data acquisition on different cognitive levels like understanding, application, and analysis.
Uploaded by
Vel MuruganCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd