Professional Documents
Culture Documents
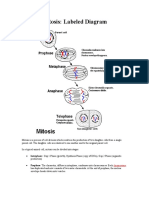
Telophase I: Haploid Chromosomes Sister Chromatids
Telophase I: Haploid Chromosomes Sister Chromatids
Uploaded by
chocoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Telophase I: Haploid Chromosomes Sister Chromatids
Telophase I: Haploid Chromosomes Sister Chromatids
Uploaded by
chocoCopyright:
Available Formats
Telophase I– During this stage, the chromosomes finishing moving to their
opposite poles. When they have all moved, a complete set of chromosomes
is attached to each pole. A membrane forms around each set of
chromosomes, creating nuclei.
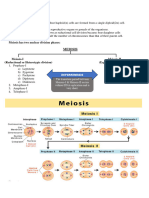
Telophase I and Cytokinesis
At each pole, during this stage, there is a complete haploid set
of chromosomes (but each chromosome still has two sister
In telophase I, the homologs of each bivalent arrive at opposite poles of
chromatids). A cleavage furrow appears, and by the end of this
the cell, and a new nuclear membrane forms around each set of
stage the parent cell has divided into two daughter cells. This
chromosomes. Cytokinesis then divides the cell into two daughter cells.
separation of the cytoplasm is called cytokinesis. In some
Each of the two daughter cells is now haploid (n), with half the number of
organisms nuclear envelopesappear briefly at this point (this
chromosomes per nucleus as in meiosis I. In some species, the nuclear
intermediate stage is called interkinesis). But in others
membrane briefly forms around the chromosomes, while in others it does
the daughter cells begin immediately to prepare for the second
not. The cell now proceeds into meiosis II, with the chromosomes
meiotic division.
remaining condensed.
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN General MCQS, Educational Platform-1Document9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 1st Semester BSN General MCQS, Educational Platform-1Prince Masroor Ali Abro0% (1)
- Biol Activity 5 Word2003Document16 pagesBiol Activity 5 Word2003Faith Jessica ParanNo ratings yet
- Distribution SystemDocument3 pagesDistribution SystemSouvik100% (1)
- Rest Assured Api Testing PDFDocument15 pagesRest Assured Api Testing PDFAutomation TestingNo ratings yet
- Interphase IDocument3 pagesInterphase IJJAMPPONG PSNo ratings yet
- Meiosis StudentDocument33 pagesMeiosis StudentChernaemiller123No ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis Notes (O Level)Document9 pagesBiology Mitosis Notes (O Level)ojilongNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle: Activity 3Document5 pagesThe Cell Cycle: Activity 3Cobe Christian LascunaNo ratings yet
- (W3) Cell CycleDocument6 pages(W3) Cell CycleRednaxela Mejico TarucNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleSTEINER 97No ratings yet
- MEIOSISDocument8 pagesMEIOSISAmelie BalibagonNo ratings yet
- 3.3 ReviewerDocument2 pages3.3 Reviewerstem.patinosamcharrieNo ratings yet
- 14-Cell DivisionDocument9 pages14-Cell DivisionMaku MichaelNo ratings yet
- Agric QuizDocument3 pagesAgric QuizKelsy SalazarNo ratings yet
- Meosis 1Document12 pagesMeosis 1lyraiglesiajaneNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionJeyanthiNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle & Cell Division Comp. NotesDocument18 pagesCell Cycle & Cell Division Comp. Notesmadihashaikh2905No ratings yet
- Mitosis MeiosisDocument8 pagesMitosis MeiosisSyndy Mae Wasing DosogNo ratings yet
- Handout MeiosisDocument4 pagesHandout MeiosisMoira Regina Lugo QuiogueNo ratings yet
- Mehran Niloy: Q:1 How Is Cell Cycle Controlled?Document7 pagesMehran Niloy: Q:1 How Is Cell Cycle Controlled?jenifaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Mitosis and Meiosis Given 2N 6Document29 pagesStages of Mitosis and Meiosis Given 2N 6rnzyrlcasinilloNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024Document2 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division - Short Notes - Arjuna NEET 2024shraddha2572sharmaNo ratings yet
- TEXT READINGS Chapter - 16Document6 pagesTEXT READINGS Chapter - 16tanusehdev17No ratings yet
- Mitosis Meiosis NotesDocument5 pagesMitosis Meiosis NotesnicoleNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument22 pagesMeiosisKOMAL NAVARIYANo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument2 pagesMeiosisMerann NepaNo ratings yet
- Meosis DescriptionDocument3 pagesMeosis DescriptionMarch Jillian Chloe Tan ViñarNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle-INTERPHASE-CELL DIVISIONDocument57 pagesCell Cycle-INTERPHASE-CELL DIVISIONcabilesrobilyn479No ratings yet
- Cell Division Lecture PowerpointDocument40 pagesCell Division Lecture Powerpoint639289117867 JesusmygodNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument8 pagesMeiosisJohn Chiyu Garde-Labite Azuki100% (1)
- Most Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GDocument8 pagesMost Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GfredNo ratings yet
- Mitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (OrganelleDocument7 pagesMitosis: Labeled Diagram: Interphase: Gap 1 Phase (Growth), Synthesis Phase (Copy of DNA), Gap 2 Phase (Organelleazzahra adeliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Document21 pagesLecture 21 of General Biology 2021-2022Mohammad zreadNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionsDocument6 pagesCell DivisionsEuniceNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleRenzdy MejillaNo ratings yet
- What Is Meiosis?Document5 pagesWhat Is Meiosis?James DazNo ratings yet
- I. Binary FissionDocument4 pagesI. Binary FissionMarielle GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Aneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish BetweenDocument2 pagesAneuploidy Cleavage Furrow and Cell Plate Karyotype: Distinguish Betweeneclipse1130No ratings yet
- During Interphase, Cellular Organelles Double: Cytokinesis Is The Final Stage ofDocument1 pageDuring Interphase, Cellular Organelles Double: Cytokinesis Is The Final Stage ofMary Ann Leona SelgaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument2 pagesMitosis and MeiosisFrances Isko FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Meiosis: A. First Meiotic Division (Reductional Division)Document4 pagesMeiosis: A. First Meiotic Division (Reductional Division)Abbas TalibNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionJohanna GultianoNo ratings yet
- Class - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionDocument13 pagesClass - X: Life Science Study Material: Cell DivisionANIRBAN PALNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionCharlotte JalaNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Cell DivisionDocument92 pages1.2 Cell DivisionHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell DivisionLief LifeNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument44 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionKILLER FFNo ratings yet
- CN 6 BioDocument2 pagesCN 6 BioJanna PaduaNo ratings yet
- 7) Mitosis and Meiosis Summary 9744 - 2018Document3 pages7) Mitosis and Meiosis Summary 9744 - 20182022 EMMA WEN XUAN HANSONNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis FactsDocument8 pagesMitosis and Meiosis FactsLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Lab Sheet LUKEDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Lab Sheet LUKElukegaid07951No ratings yet
- 3 ScanDocument5 pages3 ScanAsadNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionGale SatsatinNo ratings yet
- Mitosis, Meiosis I and IIDocument2 pagesMitosis, Meiosis I and IIYEO MING HUI MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle N Cell DivisionDocument3 pagesCell Cycle N Cell DivisionDanish UllahNo ratings yet
- Biology Assessment Task 2Document8 pagesBiology Assessment Task 2akshishree23No ratings yet
- 660a7b133fc74400185b8875 - ## - Cell Cycle and Cell Division Short NotesDocument1 page660a7b133fc74400185b8875 - ## - Cell Cycle and Cell Division Short Notespradhananita848No ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument6 pagesMeiosisAbhijeet KumarNo ratings yet
- Cell BiologyDocument5 pagesCell BiologyLife With Saman khanNo ratings yet
- Meiosis.-Meiosis (del griego μείωσις meíōsis 'disminución')Document6 pagesMeiosis.-Meiosis (del griego μείωσις meíōsis 'disminución')julioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document10 pagesChapter 6missmirachannel1No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument11 pagesCell DivisionDr Nicholas AdeNo ratings yet
- Condominium Space ProgDocument28 pagesCondominium Space ProgBeiya MaeNo ratings yet
- World Trade Center PhysicsDocument16 pagesWorld Trade Center PhysicsmarxshultzNo ratings yet
- Iso 8528 1 2005 en PDFDocument8 pagesIso 8528 1 2005 en PDFhafezasadNo ratings yet
- SPE-5130-PA (October, 1974)Document6 pagesSPE-5130-PA (October, 1974)Lulut Fitra FalaNo ratings yet
- Prac Research 1Document17 pagesPrac Research 1Julius QuilapioNo ratings yet
- Games 2Document136 pagesGames 2bungnabilNo ratings yet
- Witty Royal School ExamsDocument7 pagesWitty Royal School ExamsJovin ComputersNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Over Disney WorldDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Over Disney Worldaflbrpwan100% (1)
- TDS - SnSO4 Regal - (Eng)Document2 pagesTDS - SnSO4 Regal - (Eng)Rana Tahor100% (1)
- Technical: Nasa TNDocument36 pagesTechnical: Nasa TNMatt GrahamNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Problems: Smart/Gitman/Joehnk, Fundamentals of Investing, 12/e Chapter 3Document2 pagesSolutions To Problems: Smart/Gitman/Joehnk, Fundamentals of Investing, 12/e Chapter 3Rio Yow-yow Lansang CastroNo ratings yet
- GC 1999 10 The Siege of HarnaldaDocument5 pagesGC 1999 10 The Siege of HarnaldaErszebeth100% (3)
- DEPEDBATS CID F 009 Pre Obsevation Conference English and FilipinoDocument4 pagesDEPEDBATS CID F 009 Pre Obsevation Conference English and FilipinoAngelo VillafrancaNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing by Ramesh BabuDocument1 pageDigital Signal Processing by Ramesh BabuSubhankar DeyNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Develompent in Cement IndustryDocument9 pagesSustainable Develompent in Cement IndustrylintangnurNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide To Chart PatternsDocument30 pagesThe Essential Guide To Chart PatternsartaveNo ratings yet
- 8437SBTET (C09) DEEE 4th Sem - Ac Machines-I PDFDocument3 pages8437SBTET (C09) DEEE 4th Sem - Ac Machines-I PDFRAJ NAYAAK0% (1)
- Astm D-1349Document1 pageAstm D-1349Светлана ИлларионоваNo ratings yet
- Fashion Basics: SubcultureDocument19 pagesFashion Basics: SubcultureShivamNo ratings yet
- What A Language Student Should Learn?: NeedsDocument8 pagesWhat A Language Student Should Learn?: Needsmonday bluesNo ratings yet
- Komatsu GD655-5 PDFDocument14 pagesKomatsu GD655-5 PDFlesantiago75% (4)
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory SystemayuNo ratings yet
- Garbage Receipt: Category of The Garbage Amount of GarbageDocument2 pagesGarbage Receipt: Category of The Garbage Amount of Garbagealex kingNo ratings yet
- Pp2 Schemes of Work EnvironmentDocument9 pagesPp2 Schemes of Work Environmentvincent mugendiNo ratings yet
- Rig Pass Site Visit Form - Rev5Document10 pagesRig Pass Site Visit Form - Rev5omargarzajrNo ratings yet
- How To Setup A Simple Scenario With SAP Records Management 2323Document22 pagesHow To Setup A Simple Scenario With SAP Records Management 2323JORGENo ratings yet
- P3 Integration FormulaDocument6 pagesP3 Integration FormulaRahyan AshrafNo ratings yet