Professional Documents
Culture Documents
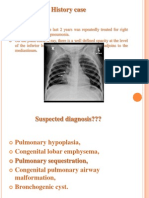
Crawls: Unilateral Hyperlucent Hemithorax
Crawls: Unilateral Hyperlucent Hemithorax
Uploaded by
Vlad Octavian BolocanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Crawls: Unilateral Hyperlucent Hemithorax
Crawls: Unilateral Hyperlucent Hemithorax
Uploaded by
Vlad Octavian BolocanCopyright:
Available Formats
Unilateral hyperlucent hemithorax :
CRAWLS
• C: contralateral lung increased density, e.g. supine pleural effusion
• R: rotation
• A: air, e.g. pneumothorax
• W: wall, e.g. chest wall mass, mastectomy, polio, Poland syndrome, surgical removal of pectoralis major
• L: lungs, e.g. airway obstruction, emphysema, Swyer-James syndrome, unilateral large bullae, large
pulmonary embolus
• S: scoliosis
SAFE POEM
• S: Swyer-James syndrome
• A: agenesis (pulmonary)
• F: fibrosis (mediastinal)
• E: effusion (pleural effusion on the contralateral side)
• P: pneumonectomy/pneumothorax
• O: obstruction
• E: embolus (pulmonary)
• M: mucous plug
ACROSSS
• A: air- pneumothorax
artery - pulmonary aplasia or hypoplasia
• C: chest wall - mastectomy, polio, Poland syndrome
• R: rotated film
• O: obstructive causes - airway obstruction, foreign body, unilateral emphysema, or large embolus
• S: scoliosis
• S: surrounding - increased density in contralateral lung, e.g. pleural effusion in opposite lung in a
recumbent patient
• S: Swyer-James syndrome (Macleod syndrome).
You might also like
- Pulmonary SystemDocument75 pagesPulmonary Systemangeles_robert_71No ratings yet
- 4 - Pulmonary PathophysiologyDocument56 pages4 - Pulmonary PathophysiologyReynandriel100% (1)
- Congenital Lung MalformationsDocument115 pagesCongenital Lung MalformationsAhmad Abu KushNo ratings yet
- Child With Respiratory DysfunctionDocument23 pagesChild With Respiratory DysfunctionmeganNo ratings yet
- 150+ Cases in Chest XrayDocument21 pages150+ Cases in Chest XrayMuntadher KareemNo ratings yet
- Imaging of The Respiratory SystemDocument105 pagesImaging of The Respiratory SystemMizrab Nadeem100% (1)
- Neonatal Chest X Ray 2019Document11 pagesNeonatal Chest X Ray 2019Ahmad ApriansahNo ratings yet
- WSDDocument50 pagesWSDgraceriaaNo ratings yet
- How To Interpret CXRs For OSCEsDocument2 pagesHow To Interpret CXRs For OSCEsPrarthana Thiagarajan100% (9)
- Rest Torace Si PleuraDocument29 pagesRest Torace Si PleuraAndreea RalucaNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument26 pagesAtelectasisArini NurlelaNo ratings yet
- Pleural PathologiesDocument49 pagesPleural PathologiesIsaac ShirimaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract RadiologyDocument106 pagesRespiratory Tract RadiologyKalemNo ratings yet
- Chapter VDocument36 pagesChapter VYoussuf HegazyNo ratings yet
- PleuraDocument51 pagesPleuraattooNo ratings yet
- Lower Resp TraumaDocument62 pagesLower Resp TraumaA Rezki ChairamsyahNo ratings yet
- Pleural PathologiesDocument34 pagesPleural PathologiesAshwani RamawatNo ratings yet
- Chest Injury and Its TypesDocument14 pagesChest Injury and Its TypesKoochi PoojithaNo ratings yet
- MR Radiologi 28 JuniDocument20 pagesMR Radiologi 28 JuninanasafietriNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument15 pagesAtelectasisSuman PoudelNo ratings yet
- AirwayDocument15 pagesAirwayYonathan asnakeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and CardiovascularDocument133 pagesRespiratory and CardiovascularHawraa FadhilNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesRespiratory SystemYoussef ElhamamyNo ratings yet
- X Rays UG ClassDocument64 pagesX Rays UG ClassSwayam AroraNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesThe Respiratory SystemJane Rose SuperadaNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax AmierDocument7 pagesPneumothorax Amieramier90No ratings yet
- Praktikum 1 Patologi ThoraxDocument61 pagesPraktikum 1 Patologi ThoraxFarizky DwitiaNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument81 pagesPneumothoraxAnonymous gYeEkemDNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument13 pagesPleural EffusionAbdirahman Ali YabarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 20 ExaminationDocument41 pagesRespiratory 20 Examinationعلي سرحان عليوي عليبNo ratings yet
- 4th Problem KGD DanielDocument130 pages4th Problem KGD DanielSelly HerliaNo ratings yet
- Examination of Respiratory SystemDocument63 pagesExamination of Respiratory SystemMilliOnuNo ratings yet
- Chest X-Rays: Phillip Smith, BA, RRTDocument29 pagesChest X-Rays: Phillip Smith, BA, RRTAlexandra PopaNo ratings yet
- DR PadmeshDocument25 pagesDR PadmeshNisar ShaikNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Chest: Dr. Jahanzeb Javed Registrar RadiologyDocument37 pagesPediatric Chest: Dr. Jahanzeb Javed Registrar RadiologyJahanzeb JavedNo ratings yet
- Pneumomediastinum & PCDocument19 pagesPneumomediastinum & PCFarra JoeyNo ratings yet
- Chest AssessmentDocument5 pagesChest Assessmentرحاب المريNo ratings yet
- HematothoraxDocument15 pagesHematothoraxmail junkNo ratings yet
- PneumothoraxDocument30 pagesPneumothoraxsanjivdas100% (1)
- To CTTDocument51 pagesTo CTTMaryasi PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- 002 Chest Radiograph Abnormalities-1Document81 pages002 Chest Radiograph Abnormalities-1q77gkyhzs4No ratings yet
- CP4. Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesCP4. Respiratory Systemdafabc50No ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Patients With Pneumothorax: Prepared By: N. WadeDocument33 pagesNursing Care of Patients With Pneumothorax: Prepared By: N. WadeokaciaNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument24 pagesAtelectasisTiara RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- Prenotes C23Document40 pagesPrenotes C23Erika Boots CabalunaNo ratings yet
- Praktikum 2 Patologi ThoraxDocument60 pagesPraktikum 2 Patologi ThoraxTriono AssamsulNo ratings yet
- Development of The Respiratory System: Section of Embryology Department of AnatomyDocument41 pagesDevelopment of The Respiratory System: Section of Embryology Department of AnatomyChristian Pato SidabutarNo ratings yet
- Systemic Disorders of The LungDocument74 pagesSystemic Disorders of The Lungjhay-r reyesNo ratings yet
- AirspaceDocument11 pagesAirspaceChypNo ratings yet
- Chest X-RaysDocument39 pagesChest X-RaysDian Oktaria SafitriNo ratings yet
- What Is Ultrasound?Document15 pagesWhat Is Ultrasound?Al-Mukashfi TahaNo ratings yet
- Chest TraumaDocument21 pagesChest TraumaRussel John MunarNo ratings yet
- k.21 Dry PleurisyDocument14 pagesk.21 Dry PleurisyWinson ChitraNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesDefinition:: Pleural EffusionGetom NgukirNo ratings yet
- AMTEC Revision Resp-ExaminationDocument2 pagesAMTEC Revision Resp-ExaminationjevonyapNo ratings yet
- HemoptysisDocument30 pagesHemoptysisTAUFIK RAMADHAN BIYANo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PDFDocument62 pagesRespiratory System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- AtelectasisDocument30 pagesAtelectasisashoaib0313No ratings yet
- The Compleat Surgeon or, the whole Art of Surgery explain'd in a most familiar MethodFrom EverandThe Compleat Surgeon or, the whole Art of Surgery explain'd in a most familiar MethodNo ratings yet