Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter V
Uploaded by
Youssuf Hegazy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views36 pagesThe document provides an overview of medical terminology related to the respiratory and cardiovascular systems presented by Dr. Basma El Awady, including definitions of terms describing structures, functions, and diseases of the lungs, trachea, bronchi, pleura, and related areas as well as example medical procedures. Key areas covered include the anatomy and functions of lungs, types of breathing patterns, lung diseases, and common respiratory tests and procedures.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides an overview of medical terminology related to the respiratory and cardiovascular systems presented by Dr. Basma El Awady, including definitions of terms describing structures, functions, and diseases of the lungs, trachea, bronchi, pleura, and related areas as well as example medical procedures. Key areas covered include the anatomy and functions of lungs, types of breathing patterns, lung diseases, and common respiratory tests and procedures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views36 pagesChapter V
Uploaded by
Youssuf HegazyThe document provides an overview of medical terminology related to the respiratory and cardiovascular systems presented by Dr. Basma El Awady, including definitions of terms describing structures, functions, and diseases of the lungs, trachea, bronchi, pleura, and related areas as well as example medical procedures. Key areas covered include the anatomy and functions of lungs, types of breathing patterns, lung diseases, and common respiratory tests and procedures.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 36
Medical Terminology
Respiratory Tract System
Cardiovascular System
Dr. Basma El Awady
Lecturer in Kasr Al Ainy, Faculty of Medicine
Cairo University
• Eu/pnea: normal breathing
• A/pnea: Absence of breathing
• Dys/pnea: Difficult breathing
• Tachy/pnea: Increased rate and depth of breathing
• Brady/pnea: Slow breathing
• Ortho/pnea: Able to breathe only when sitting or standing
• Pneumon/ectomy: Excision of part or all of a lung
Pneumon/o/tomy: Incision of a lung
• Pneumon/o/pathy: Any disease of the lungs
• Pneumon/o/rrhagia: Hemorrhage of a lung
• Pneumon/ia: Acute inflammation of the lungs caused by
a variety of organisms and viruses
• Pneumon/itis: Inflammation of the lungs
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Atel/ectasis is the imperfect expansion of the
lungs. Collapsed lung. (collapsed alveoli)
• Pneumon/o/melan/osis: A lung disease in which
lung tissue becomes black due to breathing black
dust, soot, or black smoke
• Pneumon/o/myc/osis: disease of the lungs
caused by a fungus.
• Pharyng/o/myc/osis: Fungal disease (condition)
of the pharynx (throat).
• Rhin/o/myc/osis: Fungal disease (condition) of
the nose.
• Dermat/o/myc/osis: fungal disease of the skin
• Myc/o/dermat/itis: Inflammation of the skin
caused by a fungus Dr. Basma El Awady
• Pneum/o = Air
• Pneumon = Lung
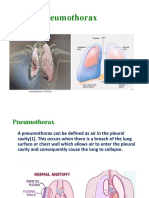
• Pneum/o/thorax: Collection of air in the chest
cavity (thoracic cavity) that causes lung collapse –
Pneum/o/thorac/ic (adj.)
• Pneum/o/therapy: Treatment with compressed
air
• Pneum/o/hem/o/thorax: Collection of air and
blood in the chest cavity
• Pneum/o/py/o/thorax: Collection of air and pus
in the chest cavity
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Pulmon/o = Lung
• Pulmon/ary: Pertaining to lungs
• Pulmon/ary valve is the heart valve through which
blood travels to the lungs. Blood flows from the heart
to the lungs via the pulmon/ary artery.
• Pulmonary embolus: Blockage in an artery of the
lungs caused by a mass of undissolved matter (such as
a blood clot, tissue, air bubbles, and bacteria)
• Orth/o = straight
• Orth/o/pnea is difficulty breathing if laying straight in
a horizontal position. Emphysema sufferers often find
it easier to breathe when sitting or standing erect
(orthopnea).
• Hem/o/ptysis is a condition of bloody sputum.
Hem/o/pty/sis: Expectoration (coughing up) blood
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Hyper/ventil/ation: Excessive movement of air in and out
of lungs.
• Hyp/oxia: Low oxygen in organs and tissues.
• Cyan/osis: Bluish color due to hypoxia.
• Alveol/o – Alveoli
• The lungs covered by the pleura – Pleur/o
• Mentum = Chin
• Nas/o/ment/al: Pertaining to the nasal cavity and chin
• Nas/o/antr/itis: Inflammation of the antrum (maxillary
sinus) and the nasal cavity
• Nas/o/pharyng/itis: Inflammation of nose and pharynx
• Nas/o/lacrim/al: Pertaining to the nose &lacrimal duct
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Epi/staxis: Epi- = upon. Staxis = dripping or oozing
Epi/staxis: nosebleed. Hemorrhage from the
nose.
• Pharyng/o = Pharynx, Throat
• Pharyng/o/lith: Calculus in the wall of the
pharynx
• Pharyng/o/myc/osis: A fungus disease of the
pharynx
• Pharyng/itis: Inflammation of the pharynx
• Pharyng/o/cele: Herniation of the pharynx
• Pharyng/o/tomy: Throat Incision of the pharynx
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Pharyng/o/pathy: Disease of the pharynx
• Pharyng/o/plasty: Surgical repair of the pharynx
• Pharyng/o/scope: Instrument to examine the pharynx
• Laryng/o = Larynx, Larynx contains the vocal cord
• Laryng/itis: Inflammation of the larynx
• Laryng/algia: Pain in the larynx
• Stridor: abnormal sound caused by spasms or swelling
of larynx
• Laryng/o/stomy: Creating a new opening in larynx
• Laryng/o/tomy: Incision into the larynx to create a
temporary opening
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Laryng/o/cele: Herniation of the larynx
• Laryng/o/pathy : Any disease of the larynx
• Laryng/o/scope: Instrument used to examine
the larynx.
• Laryng/o/spasm: Spasm of the larynx
• Trache/o = Trachea
• Trache/o/py/osis: A condition of the trachea
with pus formation
• Trache/o/rrhagia: Hemorrhage from the
trachea
Dr. Basma El Awady
Laryngoscope
Tracheostomy tube Broncholith
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Trache/algia: Pain in the trachea
• Trache/o/tomy: Incision into the trachea
• Trache/o/cele: Herniation of the trachea
• Trache/o/scopy: Examination of the trachea
• Trache/al: Pertaining to the trachea
• Trache/o/laryng/o/tomy: Incision of trachea
and larynx
• Trache/ostomy: Surgical creation of a new
opening in the trachea
• Endo/trache/al: Within the trachea
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Bronch/o = Bronchi
• Bronch/itis: Inflammation of the bronchi
• Bronch/o/scope: An instrument to examine the
bronchi
• Bronch/o/scopy: Examination of a bronchus with
instrument
• Bronch/o/lith: calculus in a bronchus
• Bronch/o/stomy: Formation of a new opening
into a bronchus
• Bronch/o/rrhagia: Bronchial hemorrhage
• Bronch/o/spasm: Spasm of a bronchus
• Bronch/o/rrhaphy: Suturing of a bronchus
Dr. Basma El Awady
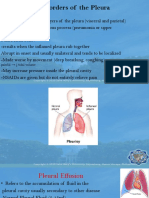
• Pleur/o, (a) = Pleura
• Pleur/al: Pertaining to the pleura (membrane
around the lungs) – Plural of pleura is pleurae
• Pleural Effusions: Any abnormal fluid in the pleural
cavity, the space between the visceral and parietal
pleura,
• Pleur/itis, Pleur/isy: Inflammation of the pleura
• Pleur/algia, Pleur/o/dynia: Pain in the pleura
• Pleur/o/centesis: Surgical puncturing of the pleura
• Viscer/o/pleural: Pertaining to the membrane
attached to the lung
• Pleur/o/lith: calculus in the pleura
• Pleur/ectomy: Excision of part of the pleura
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Phren/o – Muscle that assists with inhalation and
exhalation= the diaphragm =
• Phrenic nerve controls the diaphragm.
• Phren/o/plegia: Paralysis of the diaphragm
• Phren/ectomy: Removal of a portion of the phrenic
nerve
• an/osmia: without (the sense of ) smell
• an-: without, not
• aphonia: inability to speak through disease of or
damage to the larynx or mouth.
• dys/phonia: bad (impaired) voice quality
• dys-: bad; painful; difficult Dr. Basma El Awady
• Sinistr/o/cardi/a: Displacement of the heart to the left
• Sinistr/o/cerebr/al: Pertaining to the left half of the
cerebrum
• Sinistr/o/man/ual: Left-handed
• Sinistr/o/ped/al: Left-footed
• Dextr/o/card/ia: Displacement of the heart to the right
• Dextr/o/gastr/ia: Displacement of the stomach to the
right.
• Dextr/o/man/ual: Right-handed
• Dextr/o/ped/al: Right-footed
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Acidosis: Excessive acidity of body fluids
• A/sphyxia: Condition caused by insufficient intake
of oxygen
• Coryza: inflammation of the mucous membrane in
the nose, caused especially by a cold.
• Pleurisy: Inflammation of the pleural membrane
characterized by a stabbing pain that is intensified
by coughing or deep breathing; also called pleuritis
• Syncope: partial or complete loss of consciousness
with interruption of awareness of oneself and ones
surroundings (fainting).
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
includes respiratory disorders that produce:
a chronic partial obstruction of the air passages.
The patient finds it difficult to breath (dyspnea)
especially upon exertion and usually exhibits a
chronic cough.
• The three major disorders included in COPD are
asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema.
• COPD is caused by long-term cigarette smoking. But
there are likely other factors at play in the
development of COPD, such as a genetic
susceptibility to the disease, exposure to dust,
smoke or fumes. Dr. Basma El Awady
• Emphysema is a condition in which the alveoli at
the end of the smallest air passages (bronchioles)
of the lungs are destroyed as a result of damaging
exposure to cigarette smoke and other irritating
gases and particulate matter.
Dr. Basma El Awady
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Chronic bronchitis is inflammation of the lining
of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and
from the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. It's
characterized by daily cough and mucus
(sputum) production.
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Consolidation: loss of sponginess of lungs due to
engorgement (distention of a body part or organ
with blood or other fluids).
• Pulmonary edema: Accumulation of extravascular
fluid in lung tissues and alveoli, caused most
commonly by heart failure.
• Empyema: pus in the pleural cavity
empyema Dr. Basma El Awady consolidation
• Arterial blood gas (ABG): Test that measures
partial pressure of oxygen (Po2), carbon
dioxide (Pco2), pH (acidity or alkalinity), and
bicarbonate level of an arterial blood.
• Pulmonary function tests: Multiple tests used
to evaluate the ability of the lungs to take in
and expel air as well as perform gas exchange
across the alveolocapillary membrane
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Pleurectomy: Excision of part of the pleura,
usually parietal
• Pneumonectomy/ Pulmon/ectomy : excision of
a lung
• Rhinoplasty: reconstructive surgery of the nose
to correct deformities or for cosmetic purposes.
• Septoplasty: Surgical repair of a deviated nasal
septum usually performed when the septum is
encroaching on the breathing passages or nasal
structures
• Thoracentesis: Surgical puncture and drainage of
the pleural cavity; also called pleurocentesis or
thoracocentesis Dr. Basma El Awady
Drugs Used to Treat Respiratory
Disorders
• Antihistamines: Block histamines from binding
with histamine receptor sites in tissues.
Histamines cause sneezing, runny nose,
itchiness, and rashes.
• Antitussives: Relieve or suppress coughing by
blocking the cough reflex in the medulla of the
brain. Antitussives alleviate nonproductive dry
coughs and should not be used with productive
coughs.
Dr. Basma El Awady
Drugs Used to Treat Respiratory Disorders
• Bronchodilators: Stimulate bronchial muscles to relax,
thereby expanding air passages, resulting in increased air
flow
• Corticosteroids: Act on the immune system by blocking
production of substances that trigger allergic and
inflammatory actions
• Decongestants: Constrict blood vessels of nasal passages
and limit blood flow, which causes swollen tissues to shrink
so that air can pass more freely through the passageways
• Expectorants: Liquify respiratory secretions so that they
are more easily dislodged during coughing episodes.
Expectorants are prescribed for productive coughs.
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Aneurysm: Localized abnormal dilation of a vessel, usually
an artery; widened blood vessel
• Aneurysm/o/rrhaphy: suture of an aneurysm
• Angi/o/graphy: visual examination of blood vessel.
• Angi/o/plasty: surgical repair of vessel
• Aorta: the main artery of the body, supplying oxygenated
blood to the circulatory system.
• Aort/o/stenosis : narrowing of aorta
• Coarctation: narrowing of a vessel, especially the aorta.
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Vascul/itis: inflammation of (blood) vessels.
• Arteri/o/rrhexis: rupture of an artery.
• Cardi/o/megaly : enlargement of the heart.
• Embol/ectomy : removal of an embolus.
• Hemangi/oma: tumor of blood vessels
• My/o/cardi/al: pertaining to heart muscle.
• Phleb/ectasis: expansion of a vein
• Ven/o/stasis: standing still of (blood in a) vein;
also called phlebostasis
• Arteri/o/scler/osis: hardening of the artery
• Sclera (white of eye)
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Ventricul/ar: pertaining to a ventricle (chamber of
the heart or brain).
• Arteri/o/gram: record of an artery
• electr/o/cardi/o/graph: instrument for recording
electrical (activity) of the heart
• A/sphyxia: without a pulse, also called suffocation
• endo/vascul/ar: relating to (the area) within a
vessel
• Extra/vascul/ar: relating to the (area) outside a
vessel.
• Peri/cardi/al: pertaining to (the area) around the
heart
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Tachy/cardia: rapid heart (beat) <100
• Brady/cardia: slow heart (beat) >55
• Varicose veins: are enlarged, twisted, superficial veins.
They develop when the valves of the veins do not function
properly (incompetent) and fail to prevent the backflow of
blood.
• Cardiac arrest: Loss of effective cardiac function, which
results in cessation of circulation
• Cardi/o/my/o/pathy: Any disease or weakening of heart
muscle that diminishes cardiac function
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): Blood clot that
forms in the deep veins of the body, especially
those in the legs or thighs.
• Heart failure (HF): Failure of the heart to supply
an adequate amount of blood to tissues and
organs.
• Fibrillation: spontaneous muscle contractions,
especially of the heart.
• Hemostasis: arrest of bleeding or circulation.
• Hyper/lipid/emia: Excessive amounts of lipids
(cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides) in
the blood
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Hypertension (HTN): Elevated blood pressure persistently
exceeding 140 mm Hg systolic or 90 mm Hg diastolic
• Angina: severe chest pain often also spreading to the
shoulders, arms, and neck, owing to an inadequate blood
supply to the heart.
• Infarct: Area of tissue that undergoes necrosis following
cessation of blood supply
• Ischemia: Local and temporary deficiency of blood supply
due to circulatory obstruction
• Palpitation: Sensation that the heart is not beating
normally.
• Palpation:To examine or explore by touching (an organ or
area of the body).
• Arrhythmia: irregular heartbeat Dr. Basma El Awady
• Electrocardiogram: graphic line recording that
shows the spread of electrical excitation to
different parts of the heart.
• Cardiac enzyme studies: cardiac enzymes are
released into the bloodstream from damaged
heart muscle tissue. Their presence in a blood
specimen is consistent with myocardial damage.
• Coronary: arteries that supply blood to the heart
• Echocardiography: ultrasound to visualize internal
cardiac structures and produce images of the
heart
Dr. Basma El Awady
• Ather/oma: tumor of fatty plaque; the fatty material which
forms deposits in the arteries. Plaque is made up of fat,
cholesterol, calcium, and other substances found in the
blood. Over time, plaque hardens and narrows your
arteries and leads to Ather/o/sclerosis
• Ather/ectomy: Removal of material from an occluded
vessel
• Catheter: Thin, flexible, hollow plastic tube that is small
enough to be threaded through a vein, artery, or tubular
structure
Dr. Basma El Awady
Dr. Basma El Awady Atherectomy
• Valvotomy: Incision of a valve to increase the size of
the opening; used in treating mitral stenosis
• Venipuncture: Puncture of a vein by a needle
attached to a syringe or catheter to withdraw a
specimen of blood; also called phlebotomy.
• Stent: device used to hold open vessels, tubes, or
obstructed arteries
Venipuncture Dr. Basma El Awady Stent
• Diuretics: act on kidneys to increase excretion of water and
sodium.
• Nitrates Dilate blood vessels of the heart, causing an
increase in the amount of oxygen delivered to the
myocardium,
• Statins: lower cholesterol in the blood and reduce its
production in the liver by blocking the enzyme that
produces it.
• Peripheral vasodilators: Peripheral vasodilators treat
peripheral vascular diseases, diabetic peripheral vascular
insufficiency.
• Antiarrhythmics: correct cardiac arrhythmias
• beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers hypertension and
arrhythmias. Dr. Basma El Awady
Vegetations: small masses of inflammatory material found
on the leaflets of valves
Bruit: soft, blowing sound heard on auscultation; murmur
generated by turbulent flow of blood in an artery.
Dr. Basma El Awady
Thank You
Dr. Basma El Awady
You might also like
- Pleurisy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandPleurisy, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesRespiratory SystemYoussef ElhamamyNo ratings yet
- Atelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesFrom EverandAtelectasis, (Lung Collapse) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related DiseasesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System PDFDocument62 pagesRespiratory System PDFGayathri SNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27Document6 pagesChapter 27monster40lbsNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology: Unit 13 Respiratory System and PulmonologyDocument43 pagesMedical Terminology: Unit 13 Respiratory System and PulmonologyRizzy UgayNo ratings yet
- 4 RSDocument16 pages4 RSzabdullahstud1No ratings yet
- BiologyDocument36 pagesBiologymaleeha shahzadNo ratings yet
- Approach To Cough and HemoptysisDocument24 pagesApproach To Cough and Hemoptysisbansaleliza26No ratings yet
- Respiratory System PDFDocument49 pagesRespiratory System PDFMaria Jemimah NievesNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATORY-SYSTEM pptx1137Document32 pagesRESPIRATORY-SYSTEM pptx1137Jerick Sevilla SearesNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: Done By: Daniella DhanesarDocument25 pagesRespiratory System: Done By: Daniella DhanesarDaniellaNo ratings yet
- Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument40 pagesBreathing and Exchange of GasesPranesh ShandilyaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: TH NDDocument22 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: TH NDSuhaila Naif NasserNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary SystemDocument75 pagesPulmonary Systemangeles_robert_71No ratings yet
- Kardiorespirasi 5Document83 pagesKardiorespirasi 5Naufal MubarakNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DeasesDocument12 pagesRespiratory DeasesheniNo ratings yet
- 4 - Pulmonary PathophysiologyDocument56 pages4 - Pulmonary PathophysiologyReynandriel100% (1)
- Chap07 RespiratoryDocument44 pagesChap07 RespiratoryShere AlmansuoriNo ratings yet
- Patholpgic Change in EmphysemiaDocument16 pagesPatholpgic Change in Emphysemiafenil1194No ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument35 pagesRespiratory SystemPatricia Mae SalazarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 20 ExaminationDocument41 pagesRespiratory 20 Examinationعلي سرحان عليوي عليبNo ratings yet
- Investigations - Respiratory System: Vd. Santhosh BDocument33 pagesInvestigations - Respiratory System: Vd. Santhosh Bsantosh S BNo ratings yet
- BronchiectasisDocument14 pagesBronchiectasisNipul MondolNo ratings yet
- Approach To Child With WheezingpediatricsDocument25 pagesApproach To Child With WheezingpediatricsshahinaNo ratings yet
- Beige and Brown Vintage Risograph Illustration Cutout Scrapbook Animated PresentationDocument38 pagesBeige and Brown Vintage Risograph Illustration Cutout Scrapbook Animated PresentationKyla Macauba VHNo ratings yet
- Pneumothorax-WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesPneumothorax-WPS Officelea jumawanNo ratings yet
- CP4. Respiratory SystemDocument28 pagesCP4. Respiratory Systemdafabc50No ratings yet
- PneumoniaDocument66 pagesPneumoniasamakayigrace808No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document54 pagesChapter 3Ayro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Respiratory: Welcome!Document119 pagesRespiratory: Welcome!Majo ParagasNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory SystemSonali PawarNo ratings yet
- Mtless 8 F 99 RespiratoryDocument28 pagesMtless 8 F 99 RespiratorytiejeitorresNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument24 pagesRespiratory SystemArjunNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The Respiratory SystemDocument58 pagesDisorders of The Respiratory SystemgogoNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology: Unit 13 Respiratory System and PulmonologyDocument43 pagesMedical Terminology: Unit 13 Respiratory System and PulmonologyShegzy Michael SolankeNo ratings yet
- Structurally, The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesStructurally, The Respiratory Systemyori rafiadliNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Pleural EffusionDocument4 pagesDefinition:: Pleural EffusionGetom NgukirNo ratings yet
- ImrozDocument57 pagesImrozSyed Imroz KhanNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument9 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesMukesh YadavNo ratings yet
- Dyspnea: Aris Nugroho S.Kep, NersDocument40 pagesDyspnea: Aris Nugroho S.Kep, NerscanNo ratings yet
- Jordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryDocument11 pagesJordan A. Mamalumpong Bsn-3 Clinical Instructor: Ma. Antonietta Edris Assignments For NCM 112 A. GlossaryJordan Abosama MamalumpongNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With Respiratory ProblemsDocument151 pagesNursing Management of Patient With Respiratory ProblemsAbirajan100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of COPD: Heart Failure Respiratory DisordersDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of COPD: Heart Failure Respiratory DisordersKath DeguzmanNo ratings yet
- Vishtasb DiagnosticDocument24 pagesVishtasb DiagnosticVishtasb KhaliliNo ratings yet
- resp د. وفاءDocument22 pagesresp د. وفاءProf. Wafaa Mohammed Al-AttarNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System-Review PathoDocument100 pagesRespiratory System-Review PathoSadiePartington-RiopelleNo ratings yet
- RESTRICTIVE LUNG DISEASES (Autosaved)Document40 pagesRESTRICTIVE LUNG DISEASES (Autosaved)Dr. Rabail MalikNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument101 pagesBasic Life SupportMasyfuk Zuhdi JamhurNo ratings yet
- Disorders of The PleuraDocument31 pagesDisorders of The PleuraKathleen Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- RESPIVIEWDocument4 pagesRESPIVIEWclarke skaikruNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesRespiratory Systemshubham royalNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesRespiratory Systemtheodore_estradaNo ratings yet
- Bronchitis: Matrix No: I674 Group: 29 (2 / 2005)Document150 pagesBronchitis: Matrix No: I674 Group: 29 (2 / 2005)nur syafiqah kamaruzamanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument85 pagesRespiratory SystemDr:-Ustaad Aakass Ahmed Junejo SahabNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Management of Common IllnessDocument27 pagesReviewer For Management of Common Illnessmarie vennis hamchawanNo ratings yet
- MedSurg Ch30-31Document8 pagesMedSurg Ch30-31Vanessa Da Cruz100% (1)
- Respiratory System OutlineDocument9 pagesRespiratory System OutlineAnonymous a8oxLgNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument40 pagesRespiratory SystemJezebel MolinoNo ratings yet
- W1. Pendekatan Sesak Pada AnakDocument32 pagesW1. Pendekatan Sesak Pada Anaksekrekomdik RSPDNo ratings yet
- Heart Sounds and MurmursDocument38 pagesHeart Sounds and MurmursLaura Moise100% (5)
- 0900 0920 Antiplatelet and Anticoaulation Therapy Aleti FINALDocument31 pages0900 0920 Antiplatelet and Anticoaulation Therapy Aleti FINALMarcelliaNo ratings yet
- Application of King's Theory of Goal Attainment in Miocard Infarct PatientDocument34 pagesApplication of King's Theory of Goal Attainment in Miocard Infarct PatientYulis HatiNo ratings yet
- Theileria Annulata Induced Brisket Oedema in A Bull and Its Successful TreatmentDocument4 pagesTheileria Annulata Induced Brisket Oedema in A Bull and Its Successful TreatmentshivarajuNo ratings yet
- (P) Ana - UermDocument19 pages(P) Ana - UermAj BrarNo ratings yet
- Atls & AclsDocument49 pagesAtls & AclsSanjay SathasevanNo ratings yet
- (Date) : Sir Marco Ryan BatacDocument8 pages(Date) : Sir Marco Ryan BatacNickaela CalalangNo ratings yet
- Physical Education UGC NET Examination Question Paper 2 2006 June PDFDocument24 pagesPhysical Education UGC NET Examination Question Paper 2 2006 June PDFsandwwpNo ratings yet
- EstateDocument38 pagesEstateMichael_Lee_RobertsNo ratings yet
- 3d Tissues From IPSCDocument10 pages3d Tissues From IPSCRamakanth SatthenapalliNo ratings yet
- British Biology Olympiad Part A QuestionsDocument22 pagesBritish Biology Olympiad Part A Questionsmartynapet25% (4)
- Cardiopulmonary CalculationDocument44 pagesCardiopulmonary CalculationziadNo ratings yet
- ( ( ( (The Luo Vessels) ) ) ) : Paula Chin's Class Notes Fall 2003Document66 pages( ( ( (The Luo Vessels) ) ) ) : Paula Chin's Class Notes Fall 2003DK100% (1)
- H.A Rle First Lecture B5Document8 pagesH.A Rle First Lecture B5MARIANNE JOY ELEAZARNo ratings yet
- Emergency Nursing Pediatric CourseDocument7 pagesEmergency Nursing Pediatric Coursefagawe7100% (1)
- PBL 2 - StrokeDocument14 pagesPBL 2 - StrokeKong Pei IngNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature:Aloe Vera Gel As An Anti Blood CoagulantDocument8 pagesReview of Related Literature:Aloe Vera Gel As An Anti Blood CoagulantDanica Bondoc50% (2)
- First Aid & CPR Manual: Brought To You byDocument51 pagesFirst Aid & CPR Manual: Brought To You byAbbas AidinNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument6 pagesCongestive Heart Failureseigelystic100% (1)
- Doctors NoteDocument3 pagesDoctors NotenanaikungaNo ratings yet
- ShockDocument72 pagesShockWOne Wann100% (1)
- Module 11Document7 pagesModule 11Jamille Nympha C. BalasiNo ratings yet
- Clinical Practice Guidelines - 2017 PDFDocument820 pagesClinical Practice Guidelines - 2017 PDFvijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Final TCS ModuleDocument24 pagesFinal TCS Modulemae cudalNo ratings yet
- Pericardial DiseseasDocument38 pagesPericardial Diseseasmameekasim75No ratings yet
- Atrial Septal DefectDocument38 pagesAtrial Septal DefectJelita SihombingNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument169 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsKRIZZAPEARL VER100% (1)
- Heart Failure CaseDocument2 pagesHeart Failure CasePaulo Arwin BaduriaNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography 1Document8 pagesAnnotated Bibliography 1api-432883682No ratings yet
- Updated - Prioritization of ProblemsDocument1 pageUpdated - Prioritization of ProblemsKaycelyn JimenezNo ratings yet