Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concepts of Control Systems
Uploaded by
Ysabelle JimeneaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concepts of Control Systems
Uploaded by
Ysabelle JimeneaCopyright:
Available Formats
Concepts
1. For under this condition, the radian frequency is equal to the reciprocal of the
time constant. Underdamped
2. A measure of the oscillatory character of a second order system. ζ
3. The effect of this control is to anticipate the linear change in the error. Proportional-Derivative
4. For a quadratic lag, the phase angle approaches 180° asymptotically as ω increases
5. It is the change in any of the variable that may cause the controlled variable of the process to
change. Load
6. The ratio of the sizes of the successive peak. Decay Ratio
7. A condition in which the set point is being changed in accordance with the desired variation in the
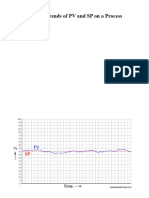
controlled variable.
8. The roots of the characteristic equation are positive and real, the system is Unstable
9. This represents the material equipment together with the physical and chemical operations that
occur. Chemical Process
10. Spot the odd one from the group. Ramp Function
11. The time needed for a particle of fluid to flow from the entrance of a pipe to the exit. τ
12. The error (expressed as a percentage of range of measured value) required to move the valve from
fully closed to fully open is called. Bandwidth/Proportional Band
13. It takes the output from the sensor and converts it to a signal that can be transmitted to the
controller. Transducer
14. If the roots are real, the response is Oscillatory
15. Mode of control which is a characteristic
16. The part of the deviation of the response which approaches zero as time approaches infinity.
17. The integral of the unit step function is also known as.
18. The Routh stability criteria can be applied to systems which contain a time delay. False
19. A proportional controller exhibits a large offset. This offset can be eliminated without altering the
proportionality constant Kc by Adding an integral control
20. The integral of a dirac function is a. Step Function
You might also like
- Control of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesFrom EverandControl of DC Motor Using Different Control StrategiesNo ratings yet
- Factorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodFrom EverandFactorization of Boundary Value Problems Using the Invariant Embedding MethodNo ratings yet
- Feedback Exam ReviewerDocument5 pagesFeedback Exam ReviewerShania LoveresNo ratings yet
- General EK (Control)Document22 pagesGeneral EK (Control)Maneesh100% (1)
- Toroy Experiment 5Document1 pageToroy Experiment 5anon ggNo ratings yet
- Automatic Controllers & Control ModesDocument74 pagesAutomatic Controllers & Control ModesVishal IyerNo ratings yet
- Water Tank System ResponseDocument23 pagesWater Tank System ResponseChristian Eduardo Fabian100% (1)
- Process Control Quiz AnswersDocument15 pagesProcess Control Quiz AnswersSatyamGuptaNo ratings yet
- First Principle Process RelationshipsDocument14 pagesFirst Principle Process RelationshipsSporkyNo ratings yet
- Ind Process ControlDocument12 pagesInd Process ControlMamnoon Akhter SyedNo ratings yet
- Things To Think About Ch.13 (Process Control A)Document21 pagesThings To Think About Ch.13 (Process Control A)Salsa NisaNo ratings yet
- NI Tutorial 3782 enDocument4 pagesNI Tutorial 3782 enpetergoodingNo ratings yet
- NI Tutorial 3782 enDocument4 pagesNI Tutorial 3782 enhiperboreoatlantecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document34 pagesChapter 4Sayed NagyNo ratings yet
- Ic1352 - Process Control-2 MarksDocument21 pagesIc1352 - Process Control-2 MarksKaushal Kishor100% (1)
- Experiment No.1: Now Manually Move The AVS-1 Bar To Control The Flow Through The Valve in To The ContainerDocument16 pagesExperiment No.1: Now Manually Move The AVS-1 Bar To Control The Flow Through The Valve in To The ContainerfahadfiazNo ratings yet
- Control System Viva QuestionDocument13 pagesControl System Viva QuestionMasudur RahmanNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument11 pagesExamplesdong_hkNo ratings yet
- Temperature Control Demonstration Unit: Experimental SetupDocument3 pagesTemperature Control Demonstration Unit: Experimental SetupHammad FazalNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems and Control Systems': An Open-Loop ControllerDocument5 pagesEmbedded Systems and Control Systems': An Open-Loop Controllermohed_kamalNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Control of Liquid Liquid ExtractorDocument8 pagesAdaptive Control of Liquid Liquid ExtractorSnehasish Barman RoyNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument75 pagesLab ManualaathiraNo ratings yet
- Control SystemDocument12 pagesControl SystemMedha ArunNo ratings yet
- AIS AnswersDocument37 pagesAIS AnswersSanatan DharmaNo ratings yet
- CS Lecture Notes Units 1 2 3Document88 pagesCS Lecture Notes Units 1 2 3sushinkNo ratings yet
- Conical Exp 8Document7 pagesConical Exp 8Mohd RehanNo ratings yet
- Unit No - II: Block Diagram RepresentationDocument56 pagesUnit No - II: Block Diagram RepresentationNamrta DeokateNo ratings yet
- PID Control Lab ReportDocument22 pagesPID Control Lab ReportErwin Setiawan0% (1)
- Instrumentation Engineering Questions & AnswersDocument10 pagesInstrumentation Engineering Questions & AnswerscontgautamNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Matrix Control - A Computer Control AlgorithmDocument7 pagesDynamic Matrix Control - A Computer Control Algorithmquinteroudina50% (2)
- Control Engineering: HapterDocument45 pagesControl Engineering: Hapterkyaw phone htetNo ratings yet
- Unit I NotesDocument43 pagesUnit I Notesaravinth69601No ratings yet
- Open Loop TestDocument5 pagesOpen Loop TestClarence Billy BijugNo ratings yet
- PID ControllersDocument58 pagesPID Controllerss12originalNo ratings yet
- Process Control Types PIDDocument4 pagesProcess Control Types PIDMad KhanNo ratings yet
- Group 6 report on automation controlDocument6 pagesGroup 6 report on automation controlCollim Hajime NivaledNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Mechatronics SystemsDocument48 pagesIntroduction to Mechatronics Systemsgiriaj kokareNo ratings yet
- Protect centrifugal compressor from surgeDocument5 pagesProtect centrifugal compressor from surges1308b100% (2)
- Process instrumentation and controlDocument23 pagesProcess instrumentation and controlLavanya ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Denavit Hartenberg MethodsDocument42 pagesDenavit Hartenberg MethodsShyamalNo ratings yet
- PID ControlDocument11 pagesPID Controlhd03No ratings yet
- PID controller basicsDocument21 pagesPID controller basicsSandesh Kumar B VNo ratings yet
- Frequency response analysis of closed-loop control performanceDocument1 pageFrequency response analysis of closed-loop control performanceEmEmTantengcoNo ratings yet
- Control: Rolta Academy:Engineering Design ServicesDocument41 pagesControl: Rolta Academy:Engineering Design ServicesRaj ChavanNo ratings yet
- Automation & Controls Processes ExplainedDocument17 pagesAutomation & Controls Processes ExplainedMalaka UdayangaNo ratings yet
- ConclusionDocument2 pagesConclusionMuhd AzimNo ratings yet
- Tuning A PID Controller: Guillermo J. CostaDocument6 pagesTuning A PID Controller: Guillermo J. CostaDeepak RainaNo ratings yet
- LabprocedurewriteupDocument3 pagesLabprocedurewriteupapi-355300487No ratings yet
- PID Theory ExplainedDocument9 pagesPID Theory ExplainedMansen NsubugaNo ratings yet
- Control DerivativoDocument27 pagesControl Derivativouriel cortesNo ratings yet
- Control Lab ReportDocument20 pagesControl Lab ReportRavi SainiNo ratings yet
- It Is The Automatic Control of An Output Variable by Sensing The Amplitude of The OutputDocument55 pagesIt Is The Automatic Control of An Output Variable by Sensing The Amplitude of The OutputSobhan Pattanaik100% (1)
- Designing PID AlgorithmDocument7 pagesDesigning PID AlgorithmVu Duc TruongNo ratings yet
- Control System PPKDocument8 pagesControl System PPKP Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Tut QuestionsDocument28 pagesTut QuestionsSbahleNo ratings yet
- Automatización 4ta Clase, Tipos de Opciones de ControlDocument6 pagesAutomatización 4ta Clase, Tipos de Opciones de Controlivandario17-1No ratings yet
- Assistant Professor Dr. Khalaf S Gaeid: Electrical Engineering Department/Tikrit UniversityDocument39 pagesAssistant Professor Dr. Khalaf S Gaeid: Electrical Engineering Department/Tikrit Universityaditee saxenaaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Control SystemsDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Control SystemsJenifer StalinNo ratings yet
- Exp - P9 - Pressure ControlDocument9 pagesExp - P9 - Pressure ControlPriyanshu LilhaNo ratings yet
- Electric Drives - Motor Controllers and Control SystemsDocument11 pagesElectric Drives - Motor Controllers and Control SystemsRam KumarNo ratings yet
- A - Has A Positve Effect A - Has A Slight, Positve Effect B - Has A Negatve Effect B - Has A Slight, Negatve Effect O - No Signifcant EffectDocument11 pagesA - Has A Positve Effect A - Has A Slight, Positve Effect B - Has A Negatve Effect B - Has A Slight, Negatve Effect O - No Signifcant EffectYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Proposed Wastewater Treatment Facility For Citric Acid ProductionDocument8 pagesProposed Wastewater Treatment Facility For Citric Acid ProductionYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Experimental Study On Use of Sugar Cane BagasseDocument12 pagesExperimental Study On Use of Sugar Cane BagasseYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- MRFDocument2 pagesMRFYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Solidwaste Notes 1Document60 pagesSolidwaste Notes 1Ysabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- MRFDocument2 pagesMRFYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering TabsDocument16 pagesChemical Engineering TabsMichael VxchoricNo ratings yet
- 8 Synthesis of AspirinDocument6 pages8 Synthesis of AspirinChelsea Reyna TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Strength SadiqDocument144 pagesStrength SadiqYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- (R) Philippines. Pilot Plant Production of Citric Acid. Activities at The Laboratories of Itdi, Bicutan, Metro Manila. Technical Report (17535.en)Document26 pages(R) Philippines. Pilot Plant Production of Citric Acid. Activities at The Laboratories of Itdi, Bicutan, Metro Manila. Technical Report (17535.en)Ysabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- The SQRT FunctionDocument3 pagesThe SQRT FunctionYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Material Balance: 1691.31 KG/HR Banana Powder 1691.31 KG/HRDocument7 pagesAppendix A Material Balance: 1691.31 KG/HR Banana Powder 1691.31 KG/HRMarielle Eden Ulanday TamboleroNo ratings yet
- 8 Synthesis of AspirinDocument1 page8 Synthesis of AspirinYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- 24 Aspirin NDocument5 pages24 Aspirin NDewi Anriani MunirNo ratings yet
- Summer WineDocument6 pagesSummer WineShaukat SaleemNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchangers: Principles and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesIon Exchangers: Principles and ApplicationsYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Control SystemsDocument1 pageConcepts of Control SystemsYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchangers: Principles and ApplicationsDocument5 pagesIon Exchangers: Principles and ApplicationsYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of Sulfuric Acid Using Contact Process: Prepared By: Moncatar, Merry Marielle MDocument5 pagesManufacture of Sulfuric Acid Using Contact Process: Prepared By: Moncatar, Merry Marielle MYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Test Chromium HexDocument8 pagesTest Chromium HexArturo PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Mercury RemovalDocument5 pagesIron Oxide Nanoparticles for Mercury RemovalYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Structure & Function of Macromolecules: Carbs, Lipids & PhospholipidsDocument34 pagesStructure & Function of Macromolecules: Carbs, Lipids & PhospholipidsYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Book 1 NNDocument3 pagesBook 1 NNYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- 4a Trig Word Problems - ANSWER KEY2Document4 pages4a Trig Word Problems - ANSWER KEY2Ysabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Word Problems.117200533nnnDocument16 pagesTrigonometry Word Problems.117200533nnnYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Energy Sources and UsesDocument4 pagesEnergy Sources and UsesYsabelle JimeneaNo ratings yet