Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Flashcards Unit 7 Section 4 Measurement Geometry
Uploaded by
melissa0royalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flashcards Unit 7 Section 4 Measurement Geometry
Uploaded by
melissa0royalCopyright:
Available Formats
Revision Flashcards
Unit 7 Section 4 – Measurement geometry
Prisms Pyramids, cones and spheres
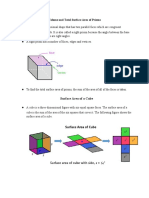
A prism is a solid shape with parallel sides A pyramid has four triangular sides and a
and a constant cross-section. Volume = area square base.
of cross-section × height. Volume = 1/3 × base area × vertical height.
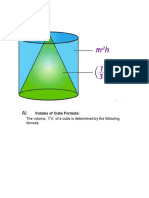
A cuboid is a prism with a rectangular cross- A cone is a pyramid with a circular base.
section. Volume = 1/3 πr2h.
Volume = width × depth × height. Surface area = 1/3 πrl, where l is the slant
Surface area = the sum of its six height.
rectangular faces. A sphere is a ball shape.
A cylinder is a prism with a circular cross- Volume = 4/3 πr3. Surface area = 4πr2.
section.
Volume = πr2h.
Surface area = 2πrh.
Areas of similar shapes Volumes of similar shapes
When a shape doubles in size, its area When a solid doubles in size, its volume
increases by a factor of four. The Length increases by a factor of eight. The Length Scale
Scale Factor is 2; the Area Scale Factor is Factor is 2; the Volume Scale Factor is 8.
4. If a solid increases by a Length Scale Factor of
If a shape trebles in size, its area increases k, the Volume Scale Factor increases by k3.
by a factor of nine. This applies even for irregular shapes, but they
If a shape increases by a Length Scale must be similar.
Factor of k, the Area Scale Factor increases
by k2.
This applies even for irregular shapes, but
they must be similar.
Similar shapes that are the same size are
congruent.
© Owned by or under licence to Pearson Education Limited 2010 1
You might also like
- 2 D 3 D Shapes WorkbookDocument26 pages2 D 3 D Shapes Workbooknia rahmayantiNo ratings yet
- Geometry EOC Review PacketDocument39 pagesGeometry EOC Review PacketVale MejiaNo ratings yet
- Geometry: B. Solid/Space Geometry 1. Position of Lines in SpaceDocument9 pagesGeometry: B. Solid/Space Geometry 1. Position of Lines in SpaceBagas FajriansyahNo ratings yet
- AREAcDocument20 pagesAREAcDexter AhamedNo ratings yet
- Individual Assignment English For Basics Mathematics Solid/ Space GeometryDocument7 pagesIndividual Assignment English For Basics Mathematics Solid/ Space GeometryNadya Zahwa LuthainNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Area and Volume Along The Concept of Integration With The Help of SlicingDocument9 pagesRelation Between Area and Volume Along The Concept of Integration With The Help of SlicingDuà Zàhrä RìzvîNo ratings yet
- Mensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleDocument5 pagesMensuration: Basic Concepts and Important Formulas Equilateral TriangleSrinu MaddikuntlaNo ratings yet
- Assignment CHP.12Document5 pagesAssignment CHP.12Noor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Volume FormulaDocument5 pagesVolume FormulachesteruytiepoNo ratings yet
- QuadrilateralsDocument3 pagesQuadrilateralsRed DeverraNo ratings yet
- Math 139-1 Lesson 6 and 7Document52 pagesMath 139-1 Lesson 6 and 7jenny teresa50% (2)
- Maths Portfolio: Rishit Joshi 10 Rangoli International SchoolDocument17 pagesMaths Portfolio: Rishit Joshi 10 Rangoli International SchoolRapidtg 1965No ratings yet
- Mathematics6 q4 Week1 v4Document9 pagesMathematics6 q4 Week1 v4Corazon Diong Sugabo-TaculodNo ratings yet
- Maths Volume and Area of Cone Presentation by Adeena Farooq (Class O1R)Document12 pagesMaths Volume and Area of Cone Presentation by Adeena Farooq (Class O1R)AdeenaNo ratings yet
- Geometry in SpaceDocument15 pagesGeometry in SpaceSislia UtinaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GeometryDocument14 pagesIntroduction To GeometryInga NaranbatNo ratings yet
- Mathe ReviwerDocument18 pagesMathe Reviwernelie tumpapNo ratings yet
- Area Wiki PDFDocument6 pagesArea Wiki PDFgooglepleckNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration REVIEWERDocument5 pagesSolid Mensuration REVIEWER21-07543No ratings yet
- Solid GeometryDocument9 pagesSolid Geometryfachira_humairaNo ratings yet
- A About Area and PerimeterDocument11 pagesA About Area and PerimeterAmiel ColanoNo ratings yet
- Let Review: MathematicsDocument102 pagesLet Review: MathematicsFghhNo ratings yet
- Rectangle MandouliDocument4 pagesRectangle Mandouliapi-3731257No ratings yet
- M4 Understanding Solid FiguresDocument35 pagesM4 Understanding Solid FiguresCrzl Jy BrcNo ratings yet
- TSA Andvolume of SolidsDocument14 pagesTSA Andvolume of SolidsJairNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface Area DalesandroDocument7 pagesVolume and Surface Area DalesandroAmalia AnNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface Area - Pyramids, Cones, and SphereDocument16 pagesVolume and Surface Area - Pyramids, Cones, and Sphereʀᴇᴀ ꜰᴏɴᴅNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Volume With Known Cross SectionsDocument14 pages7.2 Volume With Known Cross Sectionsi can eat a pack of chips without making a soundNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Volume With Known Cross SectionsDocument14 pages7.2 Volume With Known Cross SectionsMark JamesNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Volume With Known Cross SectionsDocument14 pages7.2 Volume With Known Cross SectionsMark JamesNo ratings yet
- 7.2 Volume With Known Cross SectionsDocument14 pages7.2 Volume With Known Cross Sectionsjerryck dulinNo ratings yet
- Ramon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra VenzueloDocument10 pagesRamon Teves Pastor Memorial - Dumaguete Science High School: Prepared By: Miss Kassandra Venzuelomarjun catanNo ratings yet
- Area and PerimeterDocument21 pagesArea and Perimetervgaurav3011100% (1)
- Solid Mensuration PDFDocument25 pagesSolid Mensuration PDFHEIDI ROSE MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Revcards Adam SSMDocument12 pagesRevcards Adam SSMHannah YeungNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument6 pagesFormula Sheetsangeethk1021No ratings yet
- Geometry Vocabulary and PostulatesDocument9 pagesGeometry Vocabulary and PostulatesWilson ZhangNo ratings yet
- Maths Holiday HomeworkDocument9 pagesMaths Holiday HomeworkTanishqNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 6 Mathematics Revision Notes Chapter - 5 Understanding Elementary ShapesDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 6 Mathematics Revision Notes Chapter - 5 Understanding Elementary ShapesVignesh SNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Note For Grade 10Document8 pagesMathematics Note For Grade 10darseziyad34No ratings yet
- of MensurationDocument18 pagesof MensurationSACHIN SHROTRI100% (1)
- Lesson 9: Three-Dimensional GeometryDocument12 pagesLesson 9: Three-Dimensional GeometryPatwari RajeshNo ratings yet
- What Is Perimeter - Definition & Formula - Video & Lesson Transcript PDFDocument13 pagesWhat Is Perimeter - Definition & Formula - Video & Lesson Transcript PDFjohn sinnyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Team 10 - Bip-2Document23 pagesGeometry Team 10 - Bip-2Rosiana RamadhaniNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Three-Dimensional Figures: ObjectivesDocument18 pages8.1 Three-Dimensional Figures: Objectiveszakaria shineeNo ratings yet
- Perimeter Formula of A SquareDocument6 pagesPerimeter Formula of A SquarereymaikovarquezNo ratings yet
- Space, Shape and Position: StudentDocument28 pagesSpace, Shape and Position: StudentKhaing PhyuNo ratings yet
- SimilarityDocument1 pageSimilarityoiu7hjjsNo ratings yet
- SAT Math - Plane and Solid GeometryDocument8 pagesSAT Math - Plane and Solid GeometryΜάριος Α. ΠαππάςNo ratings yet
- The Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaDocument12 pagesThe Volume,, of A Cube Is Determined by The Following FormulaMolla DerbewNo ratings yet
- M6u5 Parent LetterDocument2 pagesM6u5 Parent Letterapi-366304862No ratings yet
- Solid Geometry 1 PDFDocument24 pagesSolid Geometry 1 PDFBin-najir DilangalenNo ratings yet
- Geometry!!!Document19 pagesGeometry!!!Jane AnonasNo ratings yet
- Volume of Any Prism: V A × HeightDocument2 pagesVolume of Any Prism: V A × HeightCardo SihombingNo ratings yet
- Solids For Which Volume 1/3 BHDocument6 pagesSolids For Which Volume 1/3 BHJames Phillip CustodioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 1Document16 pagesChapter 3 Part 1KokieNo ratings yet
- ESHADocument5 pagesESHAHimanshu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Area Perimeter and Surface Area of ObjectsDocument9 pagesArea Perimeter and Surface Area of ObjectsElioz BatungwanayoNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Add Maths SBADocument40 pagesAdd Maths SBAmelissa0royalNo ratings yet
- Flashcards Unit 4 Section 5 Sets and StatisticsDocument1 pageFlashcards Unit 4 Section 5 Sets and Statisticsmelissa0royalNo ratings yet
- Cyberbullying in Schools - A Research Study On School Policies andDocument154 pagesCyberbullying in Schools - A Research Study On School Policies andmelissa0royalNo ratings yet
- 05 Sets Stats Vectors Matrices 001-007Document7 pages05 Sets Stats Vectors Matrices 001-007melissa0royalNo ratings yet
- Simplifying: X y 6x y B Ab B 4a B AbDocument5 pagesSimplifying: X y 6x y B Ab B 4a B Abmelissa0royalNo ratings yet
- 03 Relations Functions and Graphs 001-006 PDFDocument6 pages03 Relations Functions and Graphs 001-006 PDFmelissa0royalNo ratings yet
- 05 Sets Stats Vectors Matrices 001-007Document7 pages05 Sets Stats Vectors Matrices 001-007melissa0royalNo ratings yet
- Simplifying: X y 6x y B Ab B 4a B AbDocument5 pagesSimplifying: X y 6x y B Ab B 4a B Abmelissa0royalNo ratings yet
- Principles of Business CorrespondenceDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Business Correspondencemelissa0royalNo ratings yet
- Document 1Document1 pageDocument 1melissa0royalNo ratings yet