0% found this document useful (0 votes)
78 views52 pagesSingle-Phase Controlled Rectifiers Guide
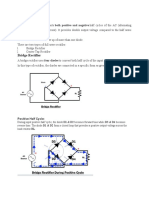
This document discusses single-phase controlled rectifiers. It introduces that controlled rectifiers use thyristors instead of diodes in rectifier circuits to allow control of the output voltage. The DC output is controlled through phase control by varying the timing of the gate signal applied to the thyristor. There are two types of controlled rectifiers: fully controlled rectifiers which can produce bidirectional DC voltage and half controlled rectifiers where diodes replace half the thyristors, producing unidirectional DC output. The document goes on to describe various half-wave and full-wave controlled rectifier circuit configurations with resistive and inductive loads.
Uploaded by
tsegayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
78 views52 pagesSingle-Phase Controlled Rectifiers Guide
This document discusses single-phase controlled rectifiers. It introduces that controlled rectifiers use thyristors instead of diodes in rectifier circuits to allow control of the output voltage. The DC output is controlled through phase control by varying the timing of the gate signal applied to the thyristor. There are two types of controlled rectifiers: fully controlled rectifiers which can produce bidirectional DC voltage and half controlled rectifiers where diodes replace half the thyristors, producing unidirectional DC output. The document goes on to describe various half-wave and full-wave controlled rectifier circuit configurations with resistive and inductive loads.
Uploaded by
tsegayCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd