Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Bitumen Penetration Test
Uploaded by
HOSEOK therealhorseCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bitumen Penetration Test
Uploaded by
HOSEOK therealhorseCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 10 Standard Test Procedures
Tests For Bitumen & Bituminous Materials
CHAPTER 10
TESTS FOR BITUMEN & BITUMINOUS MATERIALS
10.1 Bitumen Penetration Test
10.1.1 General requirements
10.1.1.1 Scope. This is a basic test for determining the grades of bitumen. In effect, the test is
an indirect determination of high temperature viscosity and low temperature stiffness.
The scope of this is to provide a method for determining the consistency of semi-solid
and solid bituminous materials in which the sole or major constituent is either bitumen
or tar pitch.
10.1.1.2 Definition. The penetration of bituminous material is its consistency expressed as
the distance in tenths of a millimeter that a standard needle penetrates vertically into
a specimen of the material under specified conditions of temperature, load and
duration of loading.
Grades of straight-run bitumen are designated by two penetration values, for
example, 40/50, 60/80, 80/100 etc.; the penetration of an actual sample of the
bitumen in any grade should fall between the lower and upper value given.
10.1.1.3 Apparatus
a) The test apparatus consists of a right frame which holds the needle spindle in a
vertical position and allows it to slide freely without friction. A dial gauge
calibrated in millimeters measures the penetration. The total weight of the needle
and spindle must be 50 ± 0.05 grams and facilities for adding additional weights
of 50 ± 0.05 grams and 100 ± 0.05 grams must be provided. The surface on
which the sample container rests must be flat and at right angles to the needle.
b) A penetration needle made of fully hardened and tempered stainless steel of
1.00mm in diameter and 50mm in length, with one end ground to a truncated
cone as shown in Figure 10.1.1. The needle is held by brass or stainless steel
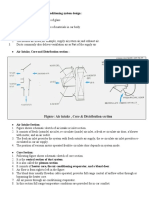
ferrule. The test is shown diagrammatically in Figure 10.1.1.
c) The sample is placed in a metal or glass flat bottom container of the following
dimensions:-
For penetrations below 200 mm:
Diameter 55 mm
Internal depth 35 mm
For penetrations between 200 and 350 mm
Diameter 70 mm
Internal depth 45 mm
The sample and dish are brought to the required temperature in a water bath
which is maintained at a temperature within ±0.1/oC of the test temperature. The
sample container must be placed on a perforated shelf which is between 50 and
100 mm below the surface of the water.
MAY 2001 Page 10.1
Chapter 10 Standard Test Procedures
Tests For Bitumen & Bituminous Materials
DIAL GAUGE READS
PENETRATION (in mm)
100 gms.
100 gms.
START AFTER 5 SECS
Penetration Test
0 0
840’ to 940’ 0.14 to 0.16 mm
1.00 to 1.02 mm
Approx.
Approximately 6.35 mm
50.8 mm (2’)
Penetration Needle
Figure 10.1.1 Penetration needle
MAY 2001 Page 10.2
Chapter 10 Standard Test Procedures
Tests For Bitumen & Bituminous Materials
d) To maintain the sample at the correct temperature during the test, a glass
transfer dish is used. This dish of at least 350 ml capacity is fitted with a suitable
support to hold the sample container firm and level during testing.
e) A stopwatch is required to measure the time of penetration.
10.1.2 Sample preparation
a) A sample of bitumen is first heated carefully in an oven or on a hotplate until it
has become sufficiently fluid to pour. When using a hotplate, the bitumen should
be stirred as soon as possible to prevent local overheating. In no case should the
temperature be raised more than 900C above the softening point, and samples
must not be heated for more then 30 minutes.
b) When sufficiently fluid a portion of the sample is poured into the sample container
to a depth of at least 10mm greater than the depth to which the needle is
expected to penetrate.
c) The sample is then covered loosely to protect against dust, and allowed to cool in
the atmosphere between 15 and 300C for 1 to 1½ hours for the small container
and 1½ to 2 hours for the large container.
d) After cooling in air, the sample containers together with the transfer dishes
should be placed in the water bath at the required temperature, for a period of 1
to 1½ hours for the small container and 1½ to 2 hours for the large container.
10.1.3 Conditions of test
The test is normally carried out at a temperature of 250C with the total weight of the
needle, spindle and added weights being 100 grams, the needle is released for a
period of 5 seconds. If it is not possible to obtain these conditions or if there are
special circumstances, one of the following alternative conditions may be used:-
Temperature, Total sliding Time,
0
C (0F) weights, grams seconds
0 (32) 200 60
4 (39.2) 200 60
46.1 (115) 50 5
It will be noted that, to obtain the standard temperature of 250C in Bangladesh,
cooling of the water bath is normally required, it may, therefore, be more convenient
in many cases to use a temperature of 46.10C.
10.1.4 Test procedure
a) The needle should be examined for damage or surface roughness; it should be
dry and clean. To ensure the needle is perfectly cleaned, it should be wiped with
a cloth soaked in toluene or another suitable bitumen solvent and then dried with
a clean cloth.
b) The clean needle should be inserted into the penetrometer apparatus and the
total sliding weight made up to the required value, if necessary by adding
additional weights. For example, if 100 grams is required, and the needle and
spindle weigh 50 grams, an additional weight of 50 grams must be added.
c) The sample container is then placed in the transfer dish complete with water at
the required temperature from the constant temperature bath, the sample being
completely covered with water at all times. The transfer dish is then placed on the
stand of the apparatus.
MAY 2001 Page 10.3
Chapter 10 Standard Test Procedures
Tests For Bitumen & Bituminous Materials
d) The penetrometer needle is then slowly lowered until it just touches the surface of
the sample. This point is best judged by using a strong source of light and
determining the point where the tip of the needle just meets its image reflected by
the surface of the sample. The initial dial gauge reading is taken.
e) The needle is then released for the specified time and re-locked immediately at
the end of the period. Care should be taken not to disturb or jolt the apparatus
when releasing the needle, if this occurs or the sample moves, the test must be
repeated. The final dial gauge reading is taken.
f) The transfer dish should then be returned to the water bath and a clean needle
fitted to the machine. The test is then repeated on the same sample. This
procedure is repeated so that at least 3 determinations are made on each
sample, taking care that each point is at least 10mm from the side of the sample
container and at least 10mm from the other determinations. If the penetration
exceeds 200mm, the needles should be left in the sample until all three
determinations have been completed.
10.1.5 Calculation
The penetration is given by:
Penetration = (Initial dial gauge reading (mm) - Final dial gauge reading (mm)) x 10
A typical worksheet is shown as Form 10.1.1.
The three penetration values obtained on the sample must agree to within the
following limits:-
Penetration 0 to 49 50 to 149 150 to 249 250
Maximum difference between highest
and lowest determination 2 4 6 8
If the differences exceed the above values, the results are ignored and the test must
be repeated on the second sample. If the differences are again exceeded by the
second sample, the results must be ignored and the test completely repeated.
If the determinations are within the above tolerances, the penetration is quoted as
the average of the individual results.
10.1.6 Test report
The report shall contain at least the following information:
a) Identification of the material tested
b) A reference to the test method used.
c) A statement of any deviation from the method stated for 25C/100g/5 seconds.
d) The test result
e) Date of test.
MAY 2001 Page 10.4
Chapter 10 Standard Test Procedures
Tests For Bitumen & Bituminous Materials
MAY 2001 Page 10.5
You might also like
- Softening N Penetration Test (Bitumen)Document11 pagesSoftening N Penetration Test (Bitumen)Thamilaarasan SonOf Nathan29% (7)
- T2Document6 pagesT2Anzai HikariNo ratings yet
- (COMPLETE) Ring Ball and Penetration Test PDFDocument10 pages(COMPLETE) Ring Ball and Penetration Test PDFAthirah DinataNo ratings yet
- Standard Penetration Test For BitumenDocument6 pagesStandard Penetration Test For BitumenHans IzairiNo ratings yet
- S406 Specifications For The Supply of Stone PDFDocument6 pagesS406 Specifications For The Supply of Stone PDFMfanelo MbanjwaNo ratings yet
- Bulk Density and Voids TestDocument4 pagesBulk Density and Voids TestAyo Osho100% (1)
- Fault Codes: Brake (DSC/DXC (Dynamic Stability Control) - Bosch 8.0 - Tyre Pressure Monitoring)Document5 pagesFault Codes: Brake (DSC/DXC (Dynamic Stability Control) - Bosch 8.0 - Tyre Pressure Monitoring)zacarias NiquiceNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual of Transportation EngineeringDocument67 pagesLab Manual of Transportation EngineeringRafiqulIslamNo ratings yet
- Penetration Test On BituminousDocument3 pagesPenetration Test On BituminousM Zeeshan Haider100% (2)
- Penetration Test of Bitumen: (AASHTO T-49, ASTM D-5)Document5 pagesPenetration Test of Bitumen: (AASHTO T-49, ASTM D-5)Yasir Dharejo100% (1)
- Test 12Document15 pagesTest 12Amit KumarNo ratings yet
- Penetration Mon Group6Document5 pagesPenetration Mon Group6Rana Abdelbaset BostanjiNo ratings yet
- معامل طرقDocument2 pagesمعامل طرقalshutuNo ratings yet
- Nadeem Penetration Test On Bituminous MateriaDocument8 pagesNadeem Penetration Test On Bituminous MateriaM Zeeshan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Determination of Bitumen PenetrationDocument4 pagesDetermination of Bitumen PenetrationAshishJamadarNo ratings yet
- Determination of Penetration Value of Bitumen: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesDetermination of Penetration Value of Bitumen: ObjectiveSudip Shrestha100% (1)
- Bitumen Test ManualDocument15 pagesBitumen Test Manualanon_274484994100% (1)
- Bitumen Penetration ReportDocument10 pagesBitumen Penetration Reportmuhd qayyumNo ratings yet
- Highway Paving Materials Laboratory Manual: Prepared By: Yazid Al-MomaniDocument28 pagesHighway Paving Materials Laboratory Manual: Prepared By: Yazid Al-MomaniMohammad AlmafrajiNo ratings yet
- Quality of Bituminous MaterialsDocument6 pagesQuality of Bituminous MaterialsNorhazerahYussopNo ratings yet
- جميع اختبارات الاسفلتDocument41 pagesجميع اختبارات الاسفلتحسين الشهريNo ratings yet
- Penetration TestDocument7 pagesPenetration TestCiera Rameli75% (4)
- Softening N Penetration Test BitumenDocument11 pagesSoftening N Penetration Test BitumenEdwin LeonNo ratings yet
- PENETRATION TEST OF BITUMENDocument6 pagesPENETRATION TEST OF BITUMENmwaqas250No ratings yet
- Asphalt Tests ExplainedDocument10 pagesAsphalt Tests ExplainedscwanhkerNo ratings yet
- Highway Lab. CE-444L: Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument7 pagesHighway Lab. CE-444L: Jordan University of Science and Technology Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentAzeezan AlessaNo ratings yet
- University of Dar Es Salaam: Coordinator: Mr. Bisachi Lecturer: Dr. BujuluDocument7 pagesUniversity of Dar Es Salaam: Coordinator: Mr. Bisachi Lecturer: Dr. BujuluBernard KitosiNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 20 Penetration of Bituminous Materials: Referenced Standard: ASTM D 5-86 AASHTO T 49-93Document6 pagesExperiment No. 20 Penetration of Bituminous Materials: Referenced Standard: ASTM D 5-86 AASHTO T 49-93Meriann May Sacayan DivinagraciaNo ratings yet
- Penetration Test On Bituminous Materials.Document6 pagesPenetration Test On Bituminous Materials.Shaheer AhmadNo ratings yet
- Penetration PDFDocument4 pagesPenetration PDFAli Muhsen MzoreNo ratings yet
- Highway Practical NdiiDocument18 pagesHighway Practical NdiiMuniru QudusNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 05 Ductility of Bituminous MaterialDocument2 pagesExperiment No: 05 Ductility of Bituminous MaterialZakirul Aslam ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Rapid Chloride Penetration Test ProcedureDocument3 pagesRapid Chloride Penetration Test ProcedureShyamNo ratings yet
- Procedure For Rapid Chloride Penetration Test: 1.1 Personnel, Material, and Equipment RequirementsDocument3 pagesProcedure For Rapid Chloride Penetration Test: 1.1 Personnel, Material, and Equipment RequirementsShyamNo ratings yet
- Astm D 5 PenetrationDocument2 pagesAstm D 5 Penetrationibad ullahNo ratings yet
- Penetration Test Lab ReportDocument7 pagesPenetration Test Lab ReportAmirul Faris100% (1)
- Standard Bitumen Penetration TestDocument3 pagesStandard Bitumen Penetration TestMohammad IhsanNo ratings yet
- Penetration of Bituminous Materials: Standard Test Method ForDocument4 pagesPenetration of Bituminous Materials: Standard Test Method ForNeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Penetration of Bituminous Materials: Standard Test Method ForDocument4 pagesPenetration of Bituminous Materials: Standard Test Method ForNeeraj KumarNo ratings yet
- D 139 - 95 R01 - RdezoqDocument3 pagesD 139 - 95 R01 - RdezoqHans AbantoNo ratings yet
- Method of Testing Determination of Resistance To FragmentationDocument3 pagesMethod of Testing Determination of Resistance To Fragmentationshahrilzainul77No ratings yet
- Astmd5 2006Document4 pagesAstmd5 2006Rabbani RxgNo ratings yet
- Procedure of Penetration Test On BitumenDocument3 pagesProcedure of Penetration Test On BitumenDhanyaUnniNo ratings yet
- Asphalt Laboratory ManualDocument26 pagesAsphalt Laboratory ManualSanthaKumar Muthu ThankaveluNo ratings yet
- Experiment NoDocument2 pagesExperiment Nomaged1998No ratings yet
- Penetration of Bituminous Materials: Standard Test Method ForDocument4 pagesPenetration of Bituminous Materials: Standard Test Method ForBlack GokuNo ratings yet
- Penetration Is Defined As The Consistency of A Bituminous Material Expressed As The DistanceDocument7 pagesPenetration Is Defined As The Consistency of A Bituminous Material Expressed As The DistanceJohn MarkNo ratings yet
- Penetration BitumenDocument7 pagesPenetration BitumennabihahNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Testing of Bituminous Material For Road WorksDocument74 pagesLaboratory Testing of Bituminous Material For Road WorksSourav MohantyNo ratings yet
- BitumenDocument2 pagesBitumenNFZBHSNo ratings yet
- Saso 87Document8 pagesSaso 87Ayman EwaisNo ratings yet
- D1665-98 (2014) Standard Test Method For Engler Specific Viscosity of Tar ProductsDocument4 pagesD1665-98 (2014) Standard Test Method For Engler Specific Viscosity of Tar ProductsRonnyNo ratings yet
- Tests On Asphalts RevDocument16 pagesTests On Asphalts RevkbgainsanNo ratings yet
- FilterationDocument22 pagesFilterationMohit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 01-01 DOCU-Asphalt ManualDocument160 pages01-01 DOCU-Asphalt ManualJeronimo FatimaNo ratings yet
- Testing of Concrete Joint SealerDocument23 pagesTesting of Concrete Joint SealerEvaresto Cole MalonesNo ratings yet
- Transportation LabDocument32 pagesTransportation LabBiplob GhoshNo ratings yet
- Ductilty of Bituminous Material (AASHTO T-51, ASTM D-113) Object: To Determine The Ductilty Value of The Given Bitumen Sample. DuctilityDocument4 pagesDuctilty of Bituminous Material (AASHTO T-51, ASTM D-113) Object: To Determine The Ductilty Value of The Given Bitumen Sample. DuctilityYasir DharejoNo ratings yet
- G E C V: Overnment Ngineering Ollege AlsadDocument50 pagesG E C V: Overnment Ngineering Ollege AlsadAditya PatelNo ratings yet
- Suvarnaprashan Sanskar EnglishDocument4 pagesSuvarnaprashan Sanskar EnglishLifecare Ayurveda Drnikul PatelNo ratings yet
- EA PSC Substation Earthing Course Leaflet PSC006CL MAR15Document2 pagesEA PSC Substation Earthing Course Leaflet PSC006CL MAR15David RothwellNo ratings yet
- Joe Rozencwajg InterviewDocument17 pagesJoe Rozencwajg InterviewGold SunriseNo ratings yet
- Polish Words Minimum To Learn DictionaryDocument69 pagesPolish Words Minimum To Learn DictionaryAndras KondratNo ratings yet
- Metacut 350: Operating and Instructions ManualDocument20 pagesMetacut 350: Operating and Instructions ManualRohman AzizNo ratings yet
- Storm Water Drainage GuidelinesDocument16 pagesStorm Water Drainage GuidelinesSeeni GovindNo ratings yet
- Chords ListDocument5 pagesChords ListakshayNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Representation in Psychology: January 1995Document11 pagesThe Concept of Representation in Psychology: January 1995laith AtekNo ratings yet
- Official All Things Turmeric PPT GuidebookDocument14 pagesOfficial All Things Turmeric PPT Guidebookapi-507527047No ratings yet
- Just-in-Time and Lean Production Systems: Professor AhmadiDocument29 pagesJust-in-Time and Lean Production Systems: Professor AhmadiawaisjinnahNo ratings yet
- Despiece Motor Mono PDFDocument55 pagesDespiece Motor Mono PDFGabriel OyagaNo ratings yet
- Bangla FoodsDocument6 pagesBangla FoodsSubadrika DarmadewiNo ratings yet
- CV Electrical Engineer 2.7 Yrs ExpDocument4 pagesCV Electrical Engineer 2.7 Yrs ExpShams Tabrez0% (1)
- Internal II BEEE QPDocument1 pageInternal II BEEE QPsivaNo ratings yet
- MandrakeDocument6 pagesMandrakeEmry Kamahi Tahatai KereruNo ratings yet
- KFS Ut U3Document5 pagesKFS Ut U3Ana DuarteNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training IntroductionDocument1 pageIndustrial Training Introductionsgurjar07No ratings yet
- Joycie 4-7Document2 pagesJoycie 4-7Jay VillasotoNo ratings yet
- ISO Standards in ProcessDocument20 pagesISO Standards in ProcessYeni OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Sample Final OutputDocument3 pagesSample Final OutputRey Dominique VillarNo ratings yet
- Datasheet GenDocument2 pagesDatasheet GenEdgar Bonilla MuñozNo ratings yet
- Philosophy, Logic, & Rhetoric SyllabusDocument3 pagesPhilosophy, Logic, & Rhetoric SyllabusBrynja KnappNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Case and Duct SystemDocument11 pagesCh.2 Case and Duct Systemcpt.ghostNo ratings yet
- Curriculum MapDocument3 pagesCurriculum MapSem PerezNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Safety Issues in ICTDocument15 pagesGroup 3 Safety Issues in ICTRoseAnnNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic System and Basic Valve UsedDocument401 pagesPneumatic System and Basic Valve Usedtarang srivasNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Plant Extracts Against Two Spotted Spider MiteDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Plant Extracts Against Two Spotted Spider MiteAnkaranaRenvaNo ratings yet
- IC TDA-11115, TDA-11145 Service Manual enDocument24 pagesIC TDA-11115, TDA-11145 Service Manual enJeank Rivadeneyra50% (2)
- Remote Controlled Home Appliances Project ReportDocument5 pagesRemote Controlled Home Appliances Project ReportASHU KNo ratings yet