Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ersid Ridge Resorp PDF
Ersid Ridge Resorp PDF
Uploaded by
drmezzo68Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ersid Ridge Resorp PDF
Ersid Ridge Resorp PDF
Uploaded by
drmezzo68Copyright:
Available Formats
Vol .
2, Issue 2 March 2010
RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION : A REVIEW
Dr. AJAY GUPTA MDS, Professor & Head Department of Prosthodontics (D. J. College of Dental Sciences &
Research, Modinagar - 201204 UP, India), Dr. BHAWANA TIWARI, Professor Department of Prosthodontics (D.
J. Collge of Dental Sciences & Rresearch, Modinagar - 201204 U.P. India), Dr. HEMANT GOEL MDS, Reader
Department of Prosthodontics, (D. J. Collge of Dental Sciences & Rresearch, Modinagar - 201204 U.P. India),
Dr HIMANSHU SHEKHAWAT, Department of Prosthodontics ((D. J. Collge of Dental Sciences & Rresearch,
Modinagar - 201204 U.P. India)
Introduction of the residual ridge.Due to loss of VDO lower face
Residual ridge is a term used to describe the shape of height is reduced and mandible is rotated anteriorly.
the clinical alveolar ridge after healing of bone and soft Patient may develop habitual prognathic
tissues following tooth extraction. Post tooth appearance.Inter-alveolar ridge relationship is altered.
extraction, a cascade of inflammatory reactions is Morphological changes in residual ridge may appear
immediately activated, and the extraction socket is such as sharp, spiny, uneven residual ridges.
temporarily sealed by blood clotting. Epithelial tissues Resorption of the mandibular canal wall and exposure
begin its proliferation and migration within the first of the mandibular nerve.Location of the mental
week and the disrupted tissue integrity is quickly foramina close to the top of the mandibular residual
restored. Histologic evidence of active bone formation ridge.This provides serious problems to the clinician
in the bottom of the socket is seen as early as 2 weeks on how to provide adequate support, stability and
after the extraction and the socket is progressively retention of the denture.1
filled with newly formed bone in about 6 months. The
most striking feature of the extraction wound healing is Pathology of RRR
that even after the healing of wounds, the residual ridge Gross Pathology:A frequent lay expression for RRR is
alveolar bone undergoes a lifelong catabolic “My gums have shrunk”. Actually the basic change in
remodeling. The size of the residual ridge is reduced RRR is a reduction in the size of the bony ridge under
most rapidly in the first six months, but the bone the mucoperiosteum. It is primarily a localized of bone
resorption activity of the residual ridge continues structure. Sometimes it may leave the overlying
throughout life at a slower rate, resulting in removal of mucoperiosteum excessive and redundant.There
a large amount of jaw structure. This unique exists a wide variety of shapes and sizes of residual
phenomenon has been described as residual ridge ridges. They are categorized into common residual
reduction. The rate of RRR is different among persons ridge configuration in a system of six orders given by
and even at different times and sites in the same Atwood.2
person. Residual ridge remodeling affects the function
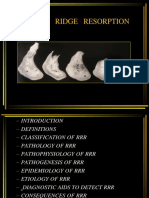
of removable prostheses, which rely greatly on the Order I - Pre-extraction.
quantity and the architecture of jaw bones. Hence Order II- Post-extraction.
treatment of edentulous patients requires a Order III- High, well rounded.
maintenance phase that must be carried out Order IV- Knife-edge.
throughout the life of a patient. Cost in economic and Order V- low, well-rounded.
human term makes RRR a major oral disease.1 Order VI- depressed.
Consequences of RRR RRR does not stop with residual ridge, but may go well
There is apparent loss of sulcus width and depth. below where apices of teeth were, sometimes leaving
Muscle attachments are displaced closer to the crest only a thin cortical plate on the inferior border of the
07 © Indian Journal of Dental Sciences. All rights are reserved
Vol .2, Issue 2 March 2010
mandible or virtually no maxillary alveolar process of effect, leaving less and less residual ridge.3 Tallgren4
the upper jaw. has presented an interesting graph of mean rates of
In clinical examination usually one can visually judge RRR of patients who were studied at various post-
the residual ridge form. However, sometimes a knife- extraction time periods over a 25 year period.In
edge ridge may be masked by redundant or inflamed separate studies in different parts of the world,
soft tissues. Tallgren, Atwood and Coy found that the mean ratio of
anterior maxillary RRR to anterior mandibular RRR
Microscopic Pathology: Microscopic studies have was 1:4.Therefore, it is true that, on the average, RRR
revealed osteoclastic activity on the external surface of is greater is greater in the mandible than in the maxilla,
the crest of residual ridges. The scalloped margins of the reverse may be true in any given patient who
Howship's lacunae sometimes contain visible comes for treatment. One must treat the particular
osteoclasts which cause bone resorption. There exists patient, not the “average” patient.
a wide variation in the configuration, density and
porosity of the residual ridges, sometimes even with Etiology of RRR:
evidence of osteoporosis. Studies have shown the RRR is a multi-factorial, biomechanical disease that
presence of new bone and reversal lines inside the results from a combination of anatomic, metabolic and
residual ridge and minute areas of bony repair on the mechanical determinants. Since all of these factors
periosteal side in some specimens.The vary from one patient to the next, these different co-
mucoperiosteum shows varying degrees of factors may combine in infinite variety of ways, thus
keratinization, acanthosis, edema and architectural explaining the variations in RRR between patients.1
pattern of mucosal epithelium in the same mouth and
between subjects.Similarly, varying degrees of Anatomic Factors:
inflammatory cells are found in areas that appear from
clinically normal to frankly inflamed in edentulous RRRAnatomic factors
patients or who were denture or non-denture wearers. i.e. amount of bone and quality of bone.
Inflammatory cells include lymphocytes and plasma
cells. There exists proximity of small blood vessels to Amount of bone: It is not a good prognostic factor for
area of bone resorption.2 the rate of RRR, because it has been seen that some
large ridges resorb rapidly and some knife edge ridges
Pathogenesis of RRR may remain with little changes for long periods of time.
Immediately following the extraction (order II), any Although the broad ridge may have a greater potential
sharp edges remaining are rounded off by external for bone loss, the rate of vertical bone loss may
osteoclastic resorption, leaving a high well rounded actually be slower than that of a small ridge because
residual ridge (order III). As resorption continues from there is more bone to be resorbed per unit of time and
the labial and lingual aspects, the crest of the ridge because the rate of resorption also depends on the
becomes increasingly narrow ultimately becoming density of bone.
knife-edged (order IV). As the process continues, the
knife-edge becomes shorter and even eventually Quality of bone: On theoretic grounds, the denser the
disappears, leaving a low well rounded or flat ridge bone, the slower the rate of resorption because there is
(order V). Eventually, this too resorbs, leaving a more bone to be resorbed per unit of time.5
depressed ridge (order VI). Metabolic factors:
RRR is chronic, progressive, irreversible and
cumulative. Usually, RRR proceeds slowly over a long RRRBone resorption factors
period of time, flowing from one stage imperceptibly to Bone formation factors
the next. Autonomous regrowth has not been reported.
Annual increments of bone loss have a cumulative General body metabolism is the net sum of all the
08 © Indian Journal of Dental Sciences. All rights are reserved
Vol .2, Issue 2 March 2010
building up (anabolism) and the tearing down of Type I and II osteoporosis.
(catabolism) going on in the body. In equilibrium the Type I osteoporosis is defined as the specific
two antagonistic actions (of osteoblasts and consequence of menopausal estrogen deprivation,
osteoclasts) are in balance. In growth, although and characteristically presents the bone mass loss,
resorption is constantly taking place in the remodeling notably in the trabecular bone.
of bones as they grow, increased osteoblastic activity Type II osteoporosis reflects a composite of age
more than makes up for the bone destruction. Whereas related changed in intestinal, renal and hormonal
in osteoporosis, osteoblasts are hypoactive, and, in function. Both cortical and trabecular bone are
the resorption related to hyperparathyroidism, affected in Type II osteoporosis.
increased osteoblastic activity is unable to keep up
with the increased osteoclastic activity. The normal Functional Factors:
equilibrium may be upset and pathologic bone loss Functional factors include the frequency, intensity,
may occur if either bone resorption is increased or duration and direction of forces applied to bone which
bone formation is decreased, or if both occur. Since are translated into cellular activity, resulting in either
bone metabolism is dependent on cell metabolism, bone formation or bone resorption, depending upon on
anything that influences cell metabolism of the patient's individual resistance to these forces.
osteoblasts and osteoclasts is important. When force within certain physiologic limits is applied
to living bone ,that force, whether compressive, tensile
• The thyroid hormone affects the rate of metabolism of shearing, brings about by some unknown
of cells in general and hence the activity of both, the mechanism the remodeling of bone through a
osteoblasts and osteoclasts. combination of bone resorption and bone formation.
• Parathyroid hormone influences the excretion of Masticatory and non-matiscatory force is ordinarily
phosphorous in the kidney and also directly influences transmitted to the dento-alveolar bone through the
osteoclasts. periodontal ligament. Once the teeth are removed, the
• The degree of absorption of Ca, P and proteins residual ridge is subjected to entirely different types of
determines the amount of building blocks available for forces. Some postulate that RRR is an inevitable
the growth and maintenance of bone. “disuse atrophy”. Others postulate that RRR is an
• Vit C aids in bone matrix formation. “abuse” bone resorption due to excessive forces
• Vit D acts through its influence on the rate of transmitted through dentures. Perhaps there is truth in
absorption of calcium in the intestines and on the citric both the hypotheses.1
acid content of bone.
• Various members of Vit B complex are necessary Prosthetic Factors:
for bone cell metabolism.6 Ridge resorption may or may not occur in patients for
whom dentures are not made. If resorption does occur,
In general terms, anabolism exceeds catabolism it is attributed either to disuse atrophy or as Lammie
during growth and convalescence, levels off during suggests, to an atrophying mucosa seeking a reduced
most of adult life and is exceeded by catabolism during area, thereby causing pressure resorption of the ridge.
disease and old age. Bone has its own specific If resorption does not occur, this is attributed either to
metabolism and undergoes equivalent changes. At no function by a patient who is able to “gum” food
time during life is bone static, but rather it is constantly because of a small inter-ridge space or unknown
rebuilding, resorbing and remodeling subject to factors. The prosthetic factors are extremely difficult to
functional and metabolic stresses. evaluate because of tremendous number of variables,
including anatomic, metabolic and functional factors.
Osteoporosis and residual ridge modeling The traditional design of dentures
The clinical and pathophysicologic views of includes many features whose goal is to reduce the
osteoporosis has been refined recently to the concept amount of force to the ridge and to thereby reduce
09 © Indian Journal of Dental Sciences. All rights are reserved
Vol .2, Issue 2 March 2010
RRR.7 These prosthetic factors include broad-area to manage RRR.It makes it possible to confine the
coverage (to reduce the force per unit area); decreased forces acting on the denture to the stress bearing areas
number of dental units, decreased buccolingual width This helps in better withstanding the mechanical
of teeth, and improved tooth form (to decrease the forces induced by denture wearing.
amount of force required to penetrate a bolus of food); • Winkler describes a technique which uses tissue
avoidance of inclined planes (to minimize conditioners. An over extended primary impression of
dislodgement of dentures and shear forces); alginate is made. Occlusal wax rims are constructed
centralization of occlusal contacts (to increase and the borders are adjusted so that the lingual flange
stability of dentures and to maximize compressive and sublingual crescent area are in harmony with the
forces); provision of adequate tongue room (to resting and acting phases of the floor of the mouth by
increase stability of denture in speech and an open and closed – mouth technique. 3 applications
mastication); adequate interocclusal distance during of conditioning material are used – each application
rest jaw relation (to decrease the frequency and approximately 3-10 minutes.9 The third and final
duration of tooth contacts) etc.Various clinical studies wash is made with a light bodied material. This
have attempted to correlate one or more of these technique results in the impression that has tissue
factors with the rate of RRR.8 Without exception, all of placing effect with relatively thick, buccal, lingual and
these studies have shown the same results, in regard sublingual crescent area borders. Miller used mouth-
to anyone factor, in a series of patients, some patients temperature waxes instead of tissue conditioners .
have RRR while others do not. Each group shows a Correcting the occlusal vertical dimension:
wide range of RRR and an overlap with other groups. Clinical studies have shown increased(excessive)
TREATMENT AND PREVENTION OF RRR OVD to be a common fault in many
dentures.Guidelines suggest 2-5 mm of freeway
The best way to manage the problem of residual ridge space, but this may need to be increased in order
reorption is by using every means to prevent it. patients or for those patients with atrophic mucosa
Clinicians must try to retain residual roots whenever verlying the residual ridges.
feasible.Overdentures help minimize ridge resorption
and contribute to enhanced retention stability ,support Reducing the forces required to drive the denture teeth
of prosthesis along with preser vation of through the bolus of food:
proprrioception. This may be achieved by either increasing the denture
The introduction of dental implants has revoluitionized bearing area or reducing the size and altering the
clinical practice.Use of implants for providing implant morphology of the occlusal table.
supported or implant assisted prosthesis also helps
avert continuing residual ridge resorption.1 1) Increasing the denture bearing area:
Impression technique Although prosthodontic norms recommend full use of
In patients with severely resorbed ridges, lack of ideal the functional denture bearing area, this is rarely
amount of supporting structures decreases support achieved. A consequence of this is that the smaller the
and the encroachment of the surrounding mobile size of the fitting surface of the denture, the greater are
tissues onto the denture border reduces both stability the loads applied to the underlying mucosa. In such
and retention.2 Thus the main aim of the impression cases, the denture bearing area may be increased
procedure is to gain maximum area of coverage. For using green stick impression compound before
e.g., in mandibular ridge, obtaining a fairly long relining or by using a chairsid relining material prior to
retromylohyoid flange helps to achieve a better border the denture being relined conventionally.1,2
seal and retention.
• Selection of proper trays and the correct impression 2) Reducing the size and altering the morphology of the
procedure is very essential for an accurate impression. occlusal table:
Selective pressure technique is most widely advocated Clinical experience indicates that many complete
10 © Indian Journal of Dental Sciences. All rights are reserved
Vol .2, Issue 2 March 2010
lower dentures have posterior teeth set without 1972; 27: 120-132.
consideration of possible support problems. In 5) Winkler: Essentials of complete denture
general, occlusal tables tend to be too large. This leads prosthodontics IInd edition.
to problems of support and stability which singly and 6) Wyatt C.C.L. Effects of prosthodontic treatment on
in combination, put too much pressure on the atrophic alveolar bone loss: A review of literature. J. Prosthet
mucosa during function. The combination of reduced Dent. 1998; 80: 362-366.
occlusal table and if necessary, increased denture 7) Atwood DA,Coy WA.Clinial ,cephalometric and
bearing area can greatly reduce the load per unit area densometric study of reduction of residual ridges .J
on the underlying mucosa and improve denture Prosthet Dent 1971;26:280-95
comfort, always assuming that the OVD is not 8) Enlow DH.The remodeling of the edentulous
excessive.10,1,2 mandible.J Prosthet Dent 1976;36:685-939)Mc Cord
JF,Tysown KW.A conservative prosthodontic option for
- Eliminating disruptive occlusal contacts which lead the treatment of edentulous patients with atrophic
to denture in stability: (flat)mandibular ridges.Brit Dent J 1997
Disruptive occlusal contacts may present in any ;186(12):469-72
border position and in 'normal' function as well as
parafunction. Their detection and elimination must be 10) Mc Cord JF,Tyson KW.Chairside Options for the
carried out where changes in OVD and elimination of treatment of complete denture problems associated
such disruptive forces are indicated, occlusal pivots with the atrophic mandibular ridge. Brit Dent J
can be of great benefit. 2000;188(1):10-14
Summary and Conclusion
RRR is a multi-factorial, biomechanical disease that
results from a combination of anatomic, metabolic and
mechanical determinants. Since all of these factors
vary from one patient to the next, these different co-
factors may combine in infinite variety of ways, thus
explaining the variations in RRR between patients.
RRR is chronic, progressive, irreversible and
cumulative.
It is important to incorporate measures so as to
minimize resorption of residual ridges in our treatment
plan.
References:
1) Atwood D.A. Reduction of residual ridges: A major
oral disease entity. J Prosthet Dent 1971; 26: 266-279.
2) Atwood D.A. Some clinical factors related to
resorption of residual ridge. J Prosthet Dent 1962; 12:
441-450.
3) Jahangiri L. Current prospective in residual ridge
remodelling and its clinical implications: A review. J
Prosthet Dent 1998; 80: 224-237.
4) Tallgren A. A continuing reduction of the residual
alveolar ridges in complete denture wearer: A mixed-
longitudinal study covering 25 years. J Prosthet Dent
11 © Indian Journal of Dental Sciences. All rights are reserved
You might also like
- Family Guide To Homeopathy PDFDocument216 pagesFamily Guide To Homeopathy PDFDebojyoti Roy100% (10)
- Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation of Deficient Maxilla and Mandible For Implant Placement. Amanda AndreDocument21 pagesVertical and Horizontal Augmentation of Deficient Maxilla and Mandible For Implant Placement. Amanda AndreAmani Fezai100% (1)
- Biology of Tooth MovementDocument5 pagesBiology of Tooth MovementPatterson Macharia100% (1)
- Mariyam Zehra PG 1St Year Department of OrthodonticsDocument101 pagesMariyam Zehra PG 1St Year Department of OrthodonticsMariyam67% (3)
- Residual Ridge ResorptionDocument57 pagesResidual Ridge ResorptionPhoebe DavidNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation QuizDocument3 pagesOxygenation QuizPOTENCIANA MAROMANo ratings yet
- Osseteointegration of Dental ImplantDocument24 pagesOsseteointegration of Dental ImplantFajar Kusuma Dwi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Management of Highly Resorbed Mandibular RidgeDocument11 pagesManagement of Highly Resorbed Mandibular RidgeAamir BugtiNo ratings yet
- Surgical Instruments Names and Uses PDF DownloadDocument4 pagesSurgical Instruments Names and Uses PDF DownloadAmmar KadariNo ratings yet
- Management of Residual Ridge Reduction (RRR)Document23 pagesManagement of Residual Ridge Reduction (RRR)drmohitmalviyaNo ratings yet
- Occlusion and Periodontal HealthDocument8 pagesOcclusion and Periodontal Healthemchen11No ratings yet
- Biological Considerations Related To OsseointegrationDocument7 pagesBiological Considerations Related To OsseointegrationIOSRjournalNo ratings yet
- Residual Ridge ResorptionDocument91 pagesResidual Ridge ResorptionAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKA100% (2)
- Arch Width and Form - A ReviewDocument9 pagesArch Width and Form - A ReviewMafe SalazarNo ratings yet
- Orthodontics and Bioesthetics: A Perfect SymbiosisDocument22 pagesOrthodontics and Bioesthetics: A Perfect Symbiosishot_teeth100% (1)
- Biology of Tooth MovementDocument22 pagesBiology of Tooth MovementsakshiNo ratings yet
- Residual Ridge Resorpion With ManagementDocument47 pagesResidual Ridge Resorpion With ManagementAbhishek Gupta0% (1)
- Book Tissue EnggDocument1,016 pagesBook Tissue EnggRajib Barua100% (3)
- Biological Mechanism in The Thoot MovementDocument18 pagesBiological Mechanism in The Thoot MovementMargarita Lopez MartinezNo ratings yet
- Emsculpt Apresentação Do ProdutoDocument53 pagesEmsculpt Apresentação Do ProdutoCarlos Eduardo MirandaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan MSC Nursing 1st Year PDFDocument19 pagesUnit Plan MSC Nursing 1st Year PDFDivya Thomas50% (4)
- Residual Ridge ResorptionDocument113 pagesResidual Ridge ResorptionMayank Aggarwal33% (3)
- WD 4-Travel Health 2go HermanmayfieldDocument4 pagesWD 4-Travel Health 2go HermanmayfieldDrake Miller78% (9)
- Residual Ridge ResorptionDocument78 pagesResidual Ridge ResorptionsaksheeNo ratings yet
- Pros Lec 1Document15 pagesPros Lec 1ريام الموسويNo ratings yet
- Done By: Dr. Farah RagheedDocument34 pagesDone By: Dr. Farah Ragheedايه حسن عبد الرحمنNo ratings yet
- 5 Exclusive Techniques - RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION - ExtoothDocument18 pages5 Exclusive Techniques - RESIDUAL RIDGE RESORPTION - ExtoothHugo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Presented By: Dr. Swarnali Biswas, PG 1 Year Department of Prosthodontics Chandra Dental College and HospitalDocument52 pagesPresented By: Dr. Swarnali Biswas, PG 1 Year Department of Prosthodontics Chandra Dental College and HospitalankitaNo ratings yet
- Residual Ridge ResorptionDocument13 pagesResidual Ridge ResorptionsankarNo ratings yet
- Residual Ridge ResorptionDocument38 pagesResidual Ridge Resorptionwaf51No ratings yet
- 2366-Article Text-6003-1-10-20190926Document8 pages2366-Article Text-6003-1-10-20190926Hugo MoralesNo ratings yet
- Rrrresidual Ridge ResorbtionDocument54 pagesRrrresidual Ridge Resorbtionsrinivaskalluri100% (1)
- Residual Ridge Resorption in Complete Denture WearersDocument5 pagesResidual Ridge Resorption in Complete Denture WearersFiru LgsNo ratings yet
- Changes in The Form and Structure of Residual Ridges: An OverviewDocument13 pagesChanges in The Form and Structure of Residual Ridges: An OverviewHeng SiekhongNo ratings yet
- Week 12 Article 1 BrickleyDocument16 pagesWeek 12 Article 1 BrickleyJean-Claude TissierNo ratings yet
- Internal and External Changes in The Edentulous MandibleDocument7 pagesInternal and External Changes in The Edentulous MandibleEm EryNo ratings yet
- Residual Ridge Resorption - RevisitedDocument5 pagesResidual Ridge Resorption - RevisitedHeng SiekhongNo ratings yet
- Understanding OsteoporosisDocument6 pagesUnderstanding OsteoporosisPriyank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Florid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia A ContraindicatioDocument9 pagesFlorid Cemento-Osseous Dysplasia A ContraindicatioHien TruongNo ratings yet
- Periodontal SurgeriesDocument46 pagesPeriodontal SurgeriesnutacosmynNo ratings yet
- Complete Dentures: Bone Resorption and ProsthodonticsDocument7 pagesComplete Dentures: Bone Resorption and ProsthodonticsPriyanka GandhiNo ratings yet
- A Review of Residual Ridge Resorption and Bone DensityDocument3 pagesA Review of Residual Ridge Resorption and Bone DensityrekabiNo ratings yet
- Westjmed00101 0065Document15 pagesWestjmed00101 0065zarrougonesNo ratings yet
- Alveolar Process: Wandee Apinhasmit DDS, PHDDocument35 pagesAlveolar Process: Wandee Apinhasmit DDS, PHDVeerawit LukkanasomboonNo ratings yet
- Residual Ridge Resorption Seminar PART 2Document144 pagesResidual Ridge Resorption Seminar PART 2ksowmyasreeNo ratings yet
- Intern Journal Reading-Paget's Disease-Root Resorption-Oral Surg-2008Document4 pagesIntern Journal Reading-Paget's Disease-Root Resorption-Oral Surg-2008Nurani AtikasariNo ratings yet
- In English On GoingDocument4 pagesIn English On GoingAdimas Yuniar WNo ratings yet
- Factors of Bone Resorption of The Residual Ridge Ortman1962Document12 pagesFactors of Bone Resorption of The Residual Ridge Ortman1962AbdelKhalek BouararaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis 2: Cli Ord J. RosenDocument13 pagesPathogenesis of Osteoporosis 2: Cli Ord J. RosenRonald TejoprayitnoNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Bone Density Resorption Remodelling of Residual Ridge - FinalDocument14 pagesFactors Affecting The Bone Density Resorption Remodelling of Residual Ridge - FinalradhikamiNo ratings yet
- Maxilary Sinus Graft ArunDocument181 pagesMaxilary Sinus Graft ArunJose Fernando Fragozo MendozaNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of OrthodonticDocument43 pagesBasic Principles of Orthodonticbob0% (1)
- 3.the Remodeling of The Edentulous MandibleDocument9 pages3.the Remodeling of The Edentulous MandibleNathawat PleumsamranNo ratings yet
- Ijpi 2 (4) 136-140Document5 pagesIjpi 2 (4) 136-140salman khawarNo ratings yet
- Bone Loss AND Patterns of Bone LossDocument24 pagesBone Loss AND Patterns of Bone LossPrathik RaiNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Relapse Versus Natural DevelopmentDocument2 pagesOrthodontic Relapse Versus Natural DevelopmentCatherine NocuaNo ratings yet
- Corticotomy Assisted Orthodontic TreatmentDocument6 pagesCorticotomy Assisted Orthodontic TreatmentAniket PotnisNo ratings yet
- Atwood 1971 JPD Reduction of Residual Ridges A Major Oral Disease EntityDocument19 pagesAtwood 1971 JPD Reduction of Residual Ridges A Major Oral Disease EntitySolano Barboza Carlos GaelNo ratings yet
- Effects of Ageing On Edentulous Mouth: BoneDocument6 pagesEffects of Ageing On Edentulous Mouth: BoneShahrukh ali khanNo ratings yet
- Reference and Techniques Used in Alveolar Bone ClassificationDocument5 pagesReference and Techniques Used in Alveolar Bone ClassificationAna Carolina LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Biology of Tooth MovementDocument120 pagesBiology of Tooth Movementheena malikNo ratings yet
- Resorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture WearersDocument5 pagesResorptive Changes of Maxillary and Mandibular Bone Structures in Removable Denture WearersAhmed SamirNo ratings yet
- Histologic Comparison of Biologic Width Around Teeth Versus Implants: The Effect On Bone PreservationDocument5 pagesHistologic Comparison of Biologic Width Around Teeth Versus Implants: The Effect On Bone PreservationPaul CerdaNo ratings yet
- Alveolar BoneDocument18 pagesAlveolar BoneGabriela ChapaNo ratings yet
- Alveolar BoneDocument26 pagesAlveolar Bonelokesh_045No ratings yet
- Orthodontically Driven Corticotomy: Tissue Engineering to Enhance Orthodontic and Multidisciplinary TreatmentFrom EverandOrthodontically Driven Corticotomy: Tissue Engineering to Enhance Orthodontic and Multidisciplinary TreatmentFederico BrugnamiNo ratings yet
- Hypersensitivity To Temporary Soft Denture LinersDocument3 pagesHypersensitivity To Temporary Soft Denture LinersManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Ijms 23 01049Document14 pagesIjms 23 01049Manjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Reliability, Validity, and Utility of Various Occlusal Measurement Methods and TechniquesDocument7 pagesReliability, Validity, and Utility of Various Occlusal Measurement Methods and TechniquesManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Titanium Framework Removable Partial Denture Used ForDocument4 pagesTitanium Framework Removable Partial Denture Used ForManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Sdarticle PDFDocument9 pagesSdarticle PDFManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Sdarticle PDFDocument2 pagesSdarticle PDFManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Luzerne Jordan, Washington, D. CDocument2 pagesLuzerne Jordan, Washington, D. CManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- President'S Address: Detroit, MichDocument2 pagesPresident'S Address: Detroit, MichManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Luzerne Jordan, Washington, D. CDocument2 pagesLuzerne Jordan, Washington, D. CManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Joel Friedman, Brooklyn, N. Y.: Received 82Document5 pagesJoel Friedman, Brooklyn, N. Y.: Received 82Manjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Abraham E-I. Lazarus,: New York, N. IDocument5 pagesAbraham E-I. Lazarus,: New York, N. IManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Wilfrid Hall Terrell, Calif.: ExaminationDocument25 pagesWilfrid Hall Terrell, Calif.: ExaminationManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Arthur Roberts, U.D.S. Aurora. IllDocument16 pagesArthur Roberts, U.D.S. Aurora. IllManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0022391302002998 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S0022391302002998 MainManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Dcpavtmelzt of Prosthetics, Ivrrrthsarstcrn Unioersity Dental School, Chicago, 111Document3 pagesDcpavtmelzt of Prosthetics, Ivrrrthsarstcrn Unioersity Dental School, Chicago, 111Manjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- 2 The ValueDocument8 pages2 The ValueManjeev GuragainNo ratings yet
- Dr. Vinod CVDocument2 pagesDr. Vinod CVVinodNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0378517322004793 MainDocument16 pages1 s2.0 S0378517322004793 MainAnand SolomonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Genito UrinaryDocument26 pagesLesson Plan Genito UrinaryEllen AngelNo ratings yet
- Surgically-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion For Management of Transverse Maxillary DeficiencyDocument3 pagesSurgically-Assisted Rapid Palatal Expansion For Management of Transverse Maxillary DeficiencyDaniela CastilloNo ratings yet
- Legal Medicine Project-FinalDocument24 pagesLegal Medicine Project-FinalAnonymous VtsflLix1No ratings yet
- Psych ReportDocument80 pagesPsych ReportPaul Carlo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Kel 5 Roleplay Past TenseDocument5 pagesKel 5 Roleplay Past TenseDesma LindaNo ratings yet
- Brochure BupaDocument9 pagesBrochure BupaprinceNo ratings yet
- Course: Physioteraphy - Mentor: Dijana Njerš - Class: English II - Student: Ella DaradkehDocument9 pagesCourse: Physioteraphy - Mentor: Dijana Njerš - Class: English II - Student: Ella DaradkehEllaNo ratings yet
- Promkes Naidoo (Indonesia)Document496 pagesPromkes Naidoo (Indonesia)plinzzyNo ratings yet
- REVISEDDocument13 pagesREVISEDCaryl Anne Dumdum CagaraNo ratings yet
- IAM Powerfully Responsive: Equipment Delivred WithDocument8 pagesIAM Powerfully Responsive: Equipment Delivred WithilietisbitulNo ratings yet
- Catalogo IFOBDocument8 pagesCatalogo IFOBKaarem LasmarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 MAA PresentationDocument21 pagesChapter 5 MAA PresentationAaron WallaceNo ratings yet
- Administration of Drugs in Experimental AnimalsDocument3 pagesAdministration of Drugs in Experimental AnimalsswetaNo ratings yet
- Cancer Program Standards 2012Document140 pagesCancer Program Standards 2012woihon0% (1)
- 2023 CalPERS Plan RatesDocument2 pages2023 CalPERS Plan RatesJose GonzalezNo ratings yet
- George Papanicolaou (1883-1962) Discoverer of THDocument1 pageGeorge Papanicolaou (1883-1962) Discoverer of THhellenkayleNo ratings yet
- Anesthesia: Ucsd Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Policy Manual POLICY 34.06Document10 pagesAnesthesia: Ucsd Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee Policy Manual POLICY 34.06Ahmad HendawiNo ratings yet
- CPLD Final ProgramDocument3 pagesCPLD Final ProgramsriNo ratings yet
- Austin Journal of Nuclear Medicine and RadiotherapyDocument5 pagesAustin Journal of Nuclear Medicine and RadiotherapyAustin Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- PHS2010 March13.CompressedDocument231 pagesPHS2010 March13.CompressedK EV INNo ratings yet
- Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of 53 Cases of Feline Lymphoplasmacytic Enteritis and Low-Grade Alimentary LymphomaDocument12 pagesHistopathological and Immunohistochemical Evaluation of 53 Cases of Feline Lymphoplasmacytic Enteritis and Low-Grade Alimentary LymphomaEunice RamosNo ratings yet