Professional Documents
Culture Documents
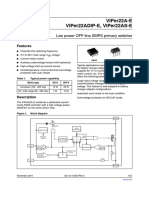
Viper22A-E Viper22Adip-E, Viper22As-E: Low Power Off-Line Smps Primary Switcher
Uploaded by
Marto DikromoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Viper22A-E Viper22Adip-E, Viper22As-E: Low Power Off-Line Smps Primary Switcher
Uploaded by
Marto DikromoCopyright:
Available Formats
VIPer22A-E
VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
Low power OFF-line SMPS primary switcher
Features
■ Fixed 60 kHz switching frequency
■ 9 V to 38 V wide range VDD voltage
■ Current mode control
SO-8 DIP-8
■ Auxiliary undervoltage lockout with hysteresis
■ High voltage start-up current source Typical applications cover off line power supplies
for battery charger adapters, standby power
■ Overtemperature, overcurrent and overvoltage supplies for TV or monitors, auxiliary supplies for
protection with auto-restart motor control, etc. The internal control circuit
offers the following benefits:
Table 1. Typical power capability
Large input voltage range on the VDD pin
Mains type SO-8 DIP-8 accommodates changes in auxiliary supply
European (195 - 265 Vac) 12 W 20 W voltage. This feature is well adapted to battery
charger adapter configurations.
US / wide range (85 - 265 Vac) 7W 12 W
Automatic burst mode in low load condition.
Description Overvoltage protection in HICCUP mode.
The VIPer22A-E combines a dedicated current
mode PWM controller with a high voltage power
MOSFET on the same silicon chip.
Figure 1. Block diagram
DRAIN
ON/OFF
60kHz
REGULATOR OSCILLATOR
INTERNAL PWM
S LATCH
SUPPLY OVERTEMP.
R1 FF
Q
DETECTOR
R2 R3 R4
VDD _ +
BLANKING
8/14.5V _ 0.23 V
+
OVERVOLTAGE
LATCH 230 Ω
R
+
S FF Q
42V _
1 kΩ
FB
SOURCE
November 2010 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 1/21
www.st.com 21
Contents VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
Contents
1 Electrical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.1 Maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2 Thermal data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
3 Pin connections and function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
4 Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4.1 Rectangular U-I output characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
4.2 Wide range of VDD voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4.3 Feedback pin principle of operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
4.4 Startup sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.5 Overvoltage threshold . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5 Operation pictures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
6 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
7 Order codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
8 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
2/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Electrical data
1 Electrical data
1.1 Maximum ratings
Stressing the device above the rating listed in the “absolute maximum ratings” table may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operating sections of
this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability.
Table 2. Absolute maximum rating
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
VDS(sw) Switching drain source voltage (TJ = 25 ... 125 °C) (1) -0.3 ... 730 V
(2)
VDS(st) Start-up drain source voltage (TJ = 25 ... 125 °C) -0.3 ... 400 V
ID Continuous drain current Internally limited A
VDD Supply voltage 0 ... 50 V
IFB Feedback current 3 mA
Electrostatic discharge:
VESD Machine model (R = 0 Ω; C = 200 pF) 200 V
Charged device model 1.5 kV
TJ Junction operating temperature Internally limited °C
TC Case operating temperature -40 to 150 °C
Tstg Storage temperature -55 to 150 °C
1. This parameter applies when the start-up current source is OFF. This is the case when the VDD voltage
has reached VDDon and remains above VDDoff.
2. This parameter applies when the start up current source is on. This is the case when the VDD voltage has
not yet reached VDDon or has fallen below VDDoff.
1.2 Thermal data
Table 3. Thermal data
Symbol Parameter SO-8 DIP-8 Unit
RthJC Thermal resistance junction - case Max 25 15 °C/W
RthJA Thermal resistance junction - ambient (1) Max 55 45 °C/W
1. When mounted on a standard single-sided FR4 board with 200 mm2 of Cu (at least 35 µm thick) connected
to all DRAIN pins.
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 3/21
Electrical characteristics VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
2 Electrical characteristics
TJ = 25 °C, VDD = 18 V, unless otherwise specified
Table 4. Power section
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min Typ Max Unit
BVDSS Drain-source voltage ID = 1 mA; VFB = 2 V 730 V
OFF state drain VDS = 500 V; VFB = 2 V;
IDSS 0.1 mA
current TJ = 125 °C
Static drain-source ID = 0.4 A 15 17
rDS(on) Ω
ON state resistance ID = 0.4 A; TJ = 100 °C 31
ID = 0.2 A; VIN = 300 V (1)
tf Fall time 100 ns
(See Figure 9 on page 13)
ID = 0.4 A; VIN = 300 V (1)
tr Rise time 50 ns
(See Figure 9 on page 13)
COSS Drain capacitance VDS = 25 V 40 pF
1. On clamped inductive load
Table 5. Supply section
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min Typ Max Unit
100 V ≤ VDS ≤ 400 V;
Start-up charging
IDDch VDD = 0 V ...VDDon -1 mA
current
(See Figure 10 on page 13)
Start-up charging
VDD = 5 V; VDS = 100 V
IDDoff current in thermal 0 mA
TJ > TSD - THYST
shutdown
Operating supply
IDD0 IFB = 2 mA 3 5 mA
current not switching
Operating supply
IDD1 IFB = 0.5 mA; ID = 50 mA (1) 4.5 mA
current switching
DRST Restart duty-cycle (See Figure 11 on page 13) 16 %
VDD undervoltage (See Figure 10,
VDDoff 7 8 9 V
shutdown threshold Figure 11 on page 13)
VDD start-up (See Figure 10,
VDDon 13 14.5 16 V
threshold Figure 11 on page 13))
VDD threshold
VDDhyst (See Figure 10 on page 13) 5.8 6.5 7.2 V
hysteresis
VDD overvoltage
VDDovp 38 42 46 V
threshold
1. These test conditions obtained with a resistive load are leading to the maximum conduction time of the
device.
4/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Electrical characteristics
Table 6. Oscillation section
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Oscillator frequency VDD = VDDoff ... 35 V;
FOSC 54 60 66 kHz
total variation TJ = 0 ... 100 °C
Table 7. PWM comparator section
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min Typ Max Unit
GID IFB to ID current gain (See Figure 12 on page 14) 560
Peak current VFB = 0 V
IDlim 0.56 0.7 0.84 A
limitation (See Figure 12 on page 14)
IFBsd IFB shutdown current (See Figure 12 on page 14) 0.9 mA
FB pin input ID = 0 mA
RFB 1.2 kΩ
impedance (See Figure 12 on page 14)
Current sense delay
td ID = 0.4 A 200 ns
to turn-OFF
tb Blanking time 500 ns
Minimum turn-ON
tONmin 700 ns
time
Table 8. Overtemperature section
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Thermal shutdown
TSD (See Figure 13 on page 14) 140 170 °C
temperature
Thermal shutdown
THYST (See Figure 13 on page 14) 40 °C
hysteresis
Table 9. Typical power capability (1)
Mains type SO-8 DIP-8
European (195 - 265 Vac) 12 W 20 W
US / Wide range (85 - 265 Vac) 7W 12 W
1. Above power capabilities are given under adequate thermal conditions
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 5/21
Pin connections and function VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
3 Pin connections and function
Figure 2. Pin connection
SOURCE 1 8 DRAIN SOURCE 1 8 DRAIN
SOURCE 2 7 DRAIN SOURCE 2 7 DRAIN
FB 3 6 DRAIN FB 3 6 DRAIN
VDD 4 5 DRAIN VDD 4 5 DRAIN
SO-8 DIP-8
Figure 3. Current and voltage conventions
I DD ID
VDD DRAIN
I FB
FB CONTROL
VDD VD
SOURCE
VFB
VIPer22A
Table 10. Pin function
Pin Name Pin function
Power supply of the control circuits. Also provides a charging current during start up
thanks to a high voltage current source connected to the drain. For this purpose, an
hysteresis comparator monitors the VDD voltage and provides two thresholds:
VDD - VDDon: Voltage value (typically 14.5 V) at which the device starts switching and turns
off the start up current source.
- VDDoff: Voltage value (typically 8 V) at which the device stops switching and turns on
the start up current source.
SOURCE Power MOSFET source and circuit ground reference.
Power MOSFET drain. Also used by the internal high voltage current source during
DRAIN
start up phase for charging the external VDD capacitor.
Feedback input. The useful voltage range extends from 0 V to 1 V, and defines the
FB peak drain MOSFET current. The current limitation, which corresponds to the
maximum drain current, is obtained for a FB pin shorted to the SOURCE pin.
6/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Operations
4 Operations
4.1 Rectangular U-I output characteristics
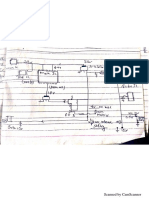
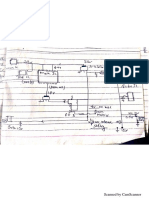
Figure 4. Rectangular U-I output characteristics for battery charger
DCOUT
R1 T1 C1
C2 D2
D1
D3
T2
F1
AC IN C3
D4 ISO1
+
U1
C4
VDD DRAIN
-
FB
C5 CONTROL
C6 SOURCE
VIPerX2A
C7
R2
D5
U2
R3 Vcc R4
Vref
R5 R6
C8 C9
- +
C10
+ -
GND
R7 R8 TSM101 R9
R10
GND
A complete regulation scheme can achieve combined and accurate output characteristics.
Figure 4. presents a secondary feedback through an optocoupler driven by a TSM101. This
device offers two operational amplifiers and a voltage reference, thus allowing the regulation
of both output voltage and current. An integrated OR function performs the combination of
the two resulting error signals, leading to a dual voltage and current limitation, known as a
rectangular output characteristic. This type of power supply is especially useful for battery
chargers where the output is mainly used in current mode, in order to deliver a defined
charging rate. The accurate voltage regulation is also convenient for Li-ion batteries which
require both modes of operation.
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 7/21
Operations VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
4.2 Wide range of VDD voltage
The VDD pin voltage range extends from 9 V to 38 V. This feature offers a great flexibility in
design to achieve various behaviors. In Figure 4 on page 7 a forward configuration has been
chosen to supply the device with two benefits:
● As soon as the device starts switching, it immediately receives some energy from the
auxiliary winding. C5 can be therefore reduced and a small ceramic chip (100 nF) is
sufficient to insure the filtering function. The total start up time from the switch on of
input voltage to output voltage presence is dramatically decreased.
● The output current characteristic can be maintained even with very low or zero output
voltage. Since the TSM101 is also supplied in forward mode, it keeps the current
regulation up whatever the output voltage is.The VDD pin voltage may vary as much as
the input voltage, that is to say with a ratio of about 4 for a wide range application.
4.3 Feedback pin principle of operation
A feedback pin controls the operation of the device. Unlike conventional PWM control
circuits which use a voltage input (the inverted input of an operational amplifier), the FB pin
is sensitive to current. Figure 5. presents the internal current mode structure.
Figure 5. Internal current control structure
8/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Operations
The Power MOSFET delivers a sense current Is which is proportional to the main current Id.
R2 receives this current and the current coming from the FB pin. The voltage across R2 is
then compared to a fixed reference voltage of about 0.23 V. The MOSFET is switched off
when the following equation is reached:
R 2 ⋅ ( I S + I FB ) = 0.23V
By extracting IS:
0.23V
I S = ---------------- – I FB
R2
Using the current sense ratio of the MOSFET GID:
I D = G ID ⋅ I S = G ID ⋅ ⎛ 0.23V
---------------- – I FB⎞
⎝ R ⎠
2
The current limitation is obtained with the FB pin shorted to ground (VFB = 0 V). This leads
to a negative current sourced by this pin, and expressed by:
I FB = – 0.23V
----------------
R1
By reporting this expression in the previous one, it is possible to obtain the drain current
limitation IDlim:
I Dlim = G ID ⋅ 0.23V ⋅ ⎛ ------
1 1-⎞
⎝ R - + ------ ⎠
2 R1
In a real application, the FB pin is driven with an optocoupler as shown on Figure 5. which
acts as a pull up. So, it is not possible to really short this pin to ground and the above drain
current value is not achievable. Nevertheless, the capacitor C is averaging the voltage on
the FB pin, and when the optocoupler is off (start up or short circuit), it can be assumed that
the corresponding voltage is very close to 0 V.
For low drain currents, the formula (1) is valid as long as IFB satisfies IFB < IFBsd, where
IFBsd is an internal threshold of the VIPer22A. If IFB exceeds this threshold the device will
stop switching. This is represented on Figure 12 on page 14, and IFBsd value is specified in the
PWM COMPARATOR SECTION. Actually, as soon as the drain current is about 12 % of
Idlim, that is to say 85 mA, the device will enter a burst mode operation by missing switching
cycles. This is especially important when the converter is lightly loaded.
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 9/21
Operations VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
Figure 6. IFB transfer function
IDpeak
IDlim
Part masked by the IFBsd
threshold
1
t ⋅V
ONmin IN
-----------------------------------------
L
85mA
t
ONmin
⋅V
2
IN
----------------------------------------
L
- IFB
0 IFBsd
It is then possible to build the total DC transfer function between ID and IFB as shown on
Figure 6 on page 10. This figure also takes into account the internal blanking time and its
associated minimum turn on time. This imposes a minimum drain current under which the
device is no more able to control it in a linear way. This drain current depends on the primary
inductance value of the transformer and the input voltage. Two cases may occur, depending
on the value of this current versus the fixed 85 mA value, as described above.
10/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Operations
4.4 Startup sequence
Figure 7. Startup sequence
This device includes a high voltage start up current source connected on the drain of the
device. As soon as a voltage is applied on the input of the converter, this start up current
source is activated as long as VDD is lower than VDDon. When reaching VDDon, the start up
current source is switched OFF and the device begins to operate by turning on and off its
main power MOSFET. As the FB pin does not receive any current from the optocoupler, the
device operates at full current capacity and the output voltage rises until reaching the
regulation point where the secondary loop begins to send a current in the optocoupler. At
this point, the converter enters a regulated operation where the FB pin receives the amount
of current needed to deliver the right power on secondary side.
This sequence is shown in Figure 7. Note that during the real starting phase tss, the device
consumes some energy from the VDD capacitor, waiting for the auxiliary winding to provide a
continuous supply. If the value of this capacitor is too low, the start up phase is terminated
before receiving any energy from the auxiliary winding and the converter never starts up.
This is illustrated also in the same figure in dashed lines.
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 11/21
Operations VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
4.5 Overvoltage threshold
An overvoltage detector on the VDD pin allows the VIPer22A to reset itself when VDD
exceeds VDDovp. This is illustrated in Figure 8. which shows the whole sequence of an
overvoltage event. Note that this event is only latched for the time needed by VDD to reach
VDDoff, and then the device resumes normal operation automatically.
Figure 8. Overvoltage sequence
VDD
VDDovp
VDDon
VDDoff
t
VDS
12/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Operation pictures
5 Operation pictures
Figure 9. Rise and fall time
ID
C L D
C << Coss
VDS
VDD DRAIN
FB 300V
90% CONTROL
SOURCE
tfv trv
VIPer22A
10% t
Figure 10. Start-up VDD current
IDD
IDD0
VDDhyst
VDD
VDDoff VDDon
IDDch
100 V≤ VDS ≤ 400 V
Fsw = 0 kHz
Figure 11. Restart duty-cycle
VDD
VDDon
VDD DRAIN
10 F FB
VDDoff CONTROL 100V
tCH tST 2V
SOURCE
t VIPer22A
t
ST -
DRST = --------------------------
t +t
ST CH
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 13/21
Operation pictures VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
Figure 12. Peak drain current vs feedback current
100V
ID 4mH
IDpeak
1/FOSC VDD DRAIN
t 18V FB CONTROL 100V
SOURCE
IFB 47nF VIPer22A
VFB
I ⋅R
FBsd FB
The drain current limitation is
obtained for VFB = 0 V, and a
negative current is drawn from
the FB pin. See the Application IFB
section for further details.
IDpeak
ΔI
IDlim Dpeak-
G = – -----------------------
ID ΔI FB
IFB
0 IFBsd
Figure 13. Thermal shutdown
14/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Operation pictures
Figure 14. Switching frequency vs temperature
Figure 15. Current limitation vs temperature
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 15/21
Package mechanical data VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
6 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK® packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
16/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Package mechanical data
Table 11. DIP-8 mechanical data
Databook (mm.)
Dim.
Min. Nom. Max.
A 5.33
A1 0.38
A2 2.92 3.30 4.95
b 0.36 0.46 0.56
b2 1.14 1.52 1.78
c 0.20 0.25 0.36
D 9.02 9.27 10.16
E 7.62 7.87 8.26
E1 6.10 6.35 7.11
e 2.54
eA 7.62
eB 10.92
L 2.92 3.30 3.81
Package Weight Gr. 470
Figure 16. Package dimensions
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 17/21
Package mechanical data VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
Table 12. SO-8 mechanical data
Databook (mm.
Dim.
Min. Nom. Max.
A 1.35 1.75
A1 0.10 0.25
A2 1.10 1.65
B 0.33 0.51
C 0.19 0.25
D 4.80 5.00
E 3.80 4.00
e 1.27
H 5.80 6.20
h 0.25 0.50
L 0.40 1.27
k 8° (max.)
ddd 0.1
Figure 17. Package dimensions
18/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E Order codes
7 Order codes
Table 13. Order codes
Order codes Package Packaging
VIPER22ASTR-E SO-8 Tape and reel
VIPer22AS-E SO-8 Tube
VIPer22ADIP-E DIP-8 Tube
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 19/21
Revision history VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
8 Revision history
Table 14. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
09-Feb-2006 1 Initial release.
25-Nov-2010 2 Updated Table 11.
20/21 Doc ID 12050 Rev 2
VIPer22A-E, VIPer22ADIP-E, VIPer22AS-E
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2010 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
Doc ID 12050 Rev 2 21/21
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Viper22A-E Viper22Adip-E, Viper22As-E: Low Power Off-Line Smps Primary SwitcherDocument21 pagesViper22A-E Viper22Adip-E, Viper22As-E: Low Power Off-Line Smps Primary Switcheraam hamzahNo ratings yet
- Viper22A-E Viper22Adip-E, Viper22As-E: Low Power Off-Line Smps Primary SwitcherDocument21 pagesViper22A-E Viper22Adip-E, Viper22As-E: Low Power Off-Line Smps Primary SwitcherAbd GhoniNo ratings yet
- Viper22A-E Viper22Adip-E, Viper22As-E: Low Power Off-Line Smps Primary SwitcherDocument21 pagesViper22A-E Viper22Adip-E, Viper22As-E: Low Power Off-Line Smps Primary SwitcherRaul Lopez ReinaNo ratings yet
- Viper 12ADocument21 pagesViper 12Aahmed hussainNo ratings yet
- Viper22a PDFDocument20 pagesViper22a PDFMosqueda Notarion Phil JamesNo ratings yet
- Viper12Adip Viper12As: Low Power Off Line Smps Primary SwitcherDocument15 pagesViper12Adip Viper12As: Low Power Off Line Smps Primary SwitcherMakhou SoyoNo ratings yet
- Viper12Adip Viper12As: Low Power Off Line Smps Primary SwitcherDocument16 pagesViper12Adip Viper12As: Low Power Off Line Smps Primary Switchermohammed el erianNo ratings yet
- Viper26: Fixed Frequency Viper Plus FamilyDocument25 pagesViper26: Fixed Frequency Viper Plus FamilyMaugrys CastilloNo ratings yet
- Viper17: Off-Line High Voltage ConvertersDocument31 pagesViper17: Off-Line High Voltage Convertersjuanchunga2952No ratings yet
- VIPER06Document28 pagesVIPER06MARIPANo ratings yet
- 3 A Low Drop Positive Voltage Regulator: Adjustable and FixedDocument27 pages3 A Low Drop Positive Voltage Regulator: Adjustable and FixedTT DVNo ratings yet
- High-Input Voltage, Adjustable, 3-Terminal, Linear RegulatorDocument19 pagesHigh-Input Voltage, Adjustable, 3-Terminal, Linear Regulatormarlon corpuzNo ratings yet
- PDF LR8 MicrochipDocument16 pagesPDF LR8 MicrochipElijah MathewNo ratings yet
- L7905CV Datasheet PDFDocument28 pagesL7905CV Datasheet PDFBehero MuNo ratings yet
- IPD60R360P7 InfineonDocument14 pagesIPD60R360P7 InfineonJimmy Varela TraderNo ratings yet
- Viper 22aDocument8 pagesViper 22aLuis Carlos Bonilla AldanaNo ratings yet
- datasheetDocument15 pagesdatasheetRenato Luiz TécnicoNo ratings yet
- f0855480 Automotive Multiple Supply For Engine ControlDocument30 pagesf0855480 Automotive Multiple Supply For Engine Controlalexander jose carrero lealNo ratings yet
- LTC4286Document43 pagesLTC4286Muhammad Qasim RaufNo ratings yet
- ACPL-C87AT/ACPL-C87BT: Data SheetDocument16 pagesACPL-C87AT/ACPL-C87BT: Data SheetMattias RahmNo ratings yet
- DSAEDA000142090Document19 pagesDSAEDA000142090dangthanhlinhNo ratings yet
- 1.5 A Very Low Drop Voltage Regulator IC: FeaturesDocument26 pages1.5 A Very Low Drop Voltage Regulator IC: Featuresleir2lNo ratings yet
- L5150GJDocument29 pagesL5150GJNoelNo ratings yet
- Transition-Mode PFC Controller: FeaturesDocument25 pagesTransition-Mode PFC Controller: FeaturesRodrigo BonfanteNo ratings yet
- Infineon IPZ60R125P6 DS v02 - 00 ENDocument15 pagesInfineon IPZ60R125P6 DS v02 - 00 ENJose Maria PerezNo ratings yet
- Multi-Phase DC/DC Controller For CPU Core Power Supply: General Description FeaturesDocument14 pagesMulti-Phase DC/DC Controller For CPU Core Power Supply: General Description FeaturesTeles SilvaNo ratings yet
- STPA003: 4 X 52 W Quad Bridge Power Amplifier With High Side Driver and Low Voltage OperationDocument25 pagesSTPA003: 4 X 52 W Quad Bridge Power Amplifier With High Side Driver and Low Voltage OperationBrian morenoNo ratings yet
- FAN7392 High-Current, High-And Low-Side, Gate-Drive IC: Features DescriptionDocument18 pagesFAN7392 High-Current, High-And Low-Side, Gate-Drive IC: Features DescriptionRaghu RamanNo ratings yet
- Automotive FET Driver For 3 Phase BLDC Motor: FeaturesDocument49 pagesAutomotive FET Driver For 3 Phase BLDC Motor: Featuresdhaniardian.2023No ratings yet
- Stcs2A: 2 A Max Constant Current LED DriverDocument18 pagesStcs2A: 2 A Max Constant Current LED DriverAndres Fernandez FernandezNo ratings yet
- Infineon-IPA60R360P7-DataSheet-v02_03-ENDocument14 pagesInfineon-IPA60R360P7-DataSheet-v02_03-ENcostelcnNo ratings yet
- VIPER22AS-E DatasheetDocument22 pagesVIPER22AS-E Datasheetnonyabizness2003No ratings yet
- Power Factor Corrector: 1 FeaturesDocument13 pagesPower Factor Corrector: 1 Featuresdeilyn rivasNo ratings yet
- Power Management Ics For Handheld Device: General Description FeaturesDocument33 pagesPower Management Ics For Handheld Device: General Description FeaturesHakim BenmajidNo ratings yet
- FAN73711 High-Current, High-Side Gate Drive IC: Features DescriptionDocument12 pagesFAN73711 High-Current, High-Side Gate Drive IC: Features DescriptionAndres AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Enersys SCR Charger ManualDocument95 pagesEnersys SCR Charger ManualMiguel Ayala67% (3)
- Datasheet 78m05 PDFDocument54 pagesDatasheet 78m05 PDFHưng HQNo ratings yet
- Fairchild - Semiconductor FAN73611MX DatasheetDocument14 pagesFairchild - Semiconductor FAN73611MX DatasheetDeddy WilopoNo ratings yet
- 2A Switch Step Down Switching Regulator: FeaturesDocument15 pages2A Switch Step Down Switching Regulator: FeaturesOrlando HernandezNo ratings yet
- Altair 05 TRDocument27 pagesAltair 05 TRGenivaldo CostaNo ratings yet
- Gate Driver L6385EDocument16 pagesGate Driver L6385EĆazim SinanagićNo ratings yet
- AD8212Document16 pagesAD8212Fernanda AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- L 5973 DDocument17 pagesL 5973 DahmedcoNo ratings yet
- VIPER22ADocument21 pagesVIPER22AanawintaNo ratings yet
- Description: Precision 500 Ma RegulatorsDocument47 pagesDescription: Precision 500 Ma RegulatorsVenancio GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Stcs1A: 1.5 A Max Constant Current LED DriverDocument19 pagesStcs1A: 1.5 A Max Constant Current LED DriverUdit AgrawalNo ratings yet
- TDA7851F: 4 X 48 W MOSFET Quad Bridge Power AmplifierDocument18 pagesTDA7851F: 4 X 48 W MOSFET Quad Bridge Power AmplifierChua BoonLianNo ratings yet
- TDA7851F: 4 X 48 W MOSFET Quad Bridge Power AmplifierDocument18 pagesTDA7851F: 4 X 48 W MOSFET Quad Bridge Power AmplifierMarcioNo ratings yet
- DM0265R ONSemiconductorDocument16 pagesDM0265R ONSemiconductorAdriano HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Mosfet de Potência 6R190E6 PDFDocument19 pagesMosfet de Potência 6R190E6 PDFÂngelo Márcio Ribeiro de BritoNo ratings yet
- High-Voltage Signal Conditioning For Low-Voltage Adcs: Application ReportDocument11 pagesHigh-Voltage Signal Conditioning For Low-Voltage Adcs: Application ReportOSCAR ANDRES BERMUDEZ HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- H-Bridge l9960tDocument95 pagesH-Bridge l9960tAdlan MessaoudNo ratings yet
- DatasheetDocument17 pagesDatasheetAlaa Ibrahem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Single Phase PWM Controller: FeatureDocument35 pagesSingle Phase PWM Controller: Featurebünyamin altunNo ratings yet
- SDC606 SDCDocument11 pagesSDC606 SDCGopalNo ratings yet
- SDC606 SDC PDFDocument11 pagesSDC606 SDC PDFGopalNo ratings yet
- KA1L0365R/KA1M0365R/KA1H0365R: Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)Document10 pagesKA1L0365R/KA1M0365R/KA1H0365R: Fairchild Power Switch (FPS)periNo ratings yet
- 5 6323113177441632437 PDFDocument32 pages5 6323113177441632437 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Reject List of Bihar Police ConstableDocument26 pagesReject List of Bihar Police ConstableAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Quanta - HK8 PVT MB 20130117 PDFDocument41 pagesQuanta - HK8 PVT MB 20130117 PDFalexjscNo ratings yet
- 5 6120694173394796658 PDFDocument27 pages5 6120694173394796658 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-12-09 10.32.13Document1 pageNew Doc 2019-12-09 10.32.13Akash KumarNo ratings yet
- Pest Management Services 001 PDFDocument1 pagePest Management Services 001 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- SM J100H Evapl 3 PDFDocument1 pageSM J100H Evapl 3 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Samsung Led TV d4000 d5000 Uexxd40xxnw Uexxd50xxnw TrainingDocument1 pageSamsung Led TV d4000 d5000 Uexxd40xxnw Uexxd50xxnw TrainingAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Pest Management Services 001 PDFDocument1 pagePest Management Services 001 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Usb4604 PDFDocument62 pagesUsb4604 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Reliance Jio December 2019 PlansDocument2 pagesReliance Jio December 2019 PlansSushubhNo ratings yet
- Reject List of Bihar Police ConstableDocument26 pagesReject List of Bihar Police ConstableAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- SM-J610F Common Tshoo 7 PDFDocument56 pagesSM-J610F Common Tshoo 7 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- DatseehtDocument1 pageDatseehtAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Ddr4 Sdram Rdimm: MTA9ASF51272PZ - 4GB FeaturesDocument24 pagesDdr4 Sdram Rdimm: MTA9ASF51272PZ - 4GB FeaturesSomendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Usb4604 PDFDocument62 pagesUsb4604 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- SM J100H Evapl 3 PDFDocument1 pageSM J100H Evapl 3 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- TP - vst59T.pb768 B16082 For LEDN32D61 Circuit DiagramDocument8 pagesTP - vst59T.pb768 B16082 For LEDN32D61 Circuit Diagramlalgalle43% (7)
- SM-J610F Common Tshoo 7 PDFDocument56 pagesSM-J610F Common Tshoo 7 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- LCD Modification 1Document159 pagesLCD Modification 1Jeank Rivadeneyra89% (19)
- Manual TesterBoardDocument4 pagesManual TesterBoardjagojago1100% (1)
- Laptop Trace PDFDocument4 pagesLaptop Trace PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- PC Laptop 101learn The Basics PDFDocument20 pagesPC Laptop 101learn The Basics PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- CamScanner Scans PDFs QuicklyDocument4 pagesCamScanner Scans PDFs QuicklyAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- 317495Document328 pages317495Lee OnNo ratings yet
- 317495Document328 pages317495Lee OnNo ratings yet
- TP - vst59T.pb768 B16082 For LEDN32D61 Circuit DiagramDocument8 pagesTP - vst59T.pb768 B16082 For LEDN32D61 Circuit Diagramlalgalle43% (7)
- PC Notebook Diagnostic Card: User's GuideDocument15 pagesPC Notebook Diagnostic Card: User's GuideAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- New Doc 2019-06-13 15.03.02 PDFDocument4 pagesNew Doc 2019-06-13 15.03.02 PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer - Hardware - Diagnosing & Fixing Motherboard FaultsDocument4 pagesComputer - Hardware - Diagnosing & Fixing Motherboard Faultsscribdraza786No ratings yet
- Thermistor Temperature Sensor Circuit AnalysisDocument7 pagesThermistor Temperature Sensor Circuit AnalysisKitty MinogueNo ratings yet
- Canon Ixus 265 HS ManualDocument163 pagesCanon Ixus 265 HS ManualMarcelo Peixoto Del PelosoNo ratings yet
- VC211LL TC V1 0 0109809Document20 pagesVC211LL TC V1 0 0109809Kerem OrNo ratings yet
- XP7202 Air Heli ManualDocument104 pagesXP7202 Air Heli ManualskigmataNo ratings yet
- Manitou Electric Aerial Work Platforms (EN)Document36 pagesManitou Electric Aerial Work Platforms (EN)Manitou100% (2)
- Linde EN Ds t25 t30 1153 en B 0620 WebDocument6 pagesLinde EN Ds t25 t30 1153 en B 0620 WebNadeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Masterguard SIII UPSDocument38 pagesMasterguard SIII UPSvayyikNo ratings yet
- SolarDocument150 pagesSolarArtefakt Novi SadNo ratings yet
- Catalogue For Btone ProductsDocument22 pagesCatalogue For Btone Productsstevex2No ratings yet
- UTP MKII Product Training SlidesDocument65 pagesUTP MKII Product Training Slidesberkahharian100% (1)
- DIY Automatic Alcohol Dispenser No Arduino NeededDocument16 pagesDIY Automatic Alcohol Dispenser No Arduino NeededAnkur RaiNo ratings yet
- Operators Manual 81 Xe ManitouDocument62 pagesOperators Manual 81 Xe ManitouГригорий Усачёв100% (1)
- BPAC SL User's Manual - V-2Document125 pagesBPAC SL User's Manual - V-2kumarbabuNo ratings yet
- Electric Bike Review 2 (Recovered)Document24 pagesElectric Bike Review 2 (Recovered)MarshalNo ratings yet
- Avionics-II B.tech (Mr. Rajendra) - 1Document134 pagesAvionics-II B.tech (Mr. Rajendra) - 1Niti LazNo ratings yet
- Parafusadeira 9078 Black & DeckerDocument4 pagesParafusadeira 9078 Black & DeckerFernandoNo ratings yet
- BT18 MANUAL Lights IonProRT 200RT FlareRT Web FinalDocument2 pagesBT18 MANUAL Lights IonProRT 200RT FlareRT Web FinalLuis Daniel Woiski GuilhermeNo ratings yet
- Packing Lists AbroadDocument9 pagesPacking Lists AbroadAdit PinheiroNo ratings yet
- SPECIFICATION SHEET - 3328 SpecialDocument2 pagesSPECIFICATION SHEET - 3328 SpecialElias ZabanehNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Charging Stations FactsheetDocument4 pagesLevel 3 Charging Stations FactsheetJorgeMelguizoNo ratings yet
- GMT Goldmaster E-Series enDocument30 pagesGMT Goldmaster E-Series enSalih Abdelrazig AbdelrhmanNo ratings yet
- Brochure DEYE Hybride SUN XKDocument6 pagesBrochure DEYE Hybride SUN XKSINES FranceNo ratings yet
- Sony fx200 Manual PDFDocument2 pagesSony fx200 Manual PDFChan TNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: S929 Helicopter (V757-V319-V398-V388-S977)Document7 pagesInstruction Manual: S929 Helicopter (V757-V319-V398-V388-S977)Mihai BordeianuNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 4347893Document40 pagesGrundfosliterature 4347893antonioNo ratings yet
- Fujikura 12s Manual PDFDocument83 pagesFujikura 12s Manual PDFAaron Garcia NaranjoNo ratings yet
- Essentials: Premium Quality. Extensive Range. We've Got It Covered!Document16 pagesEssentials: Premium Quality. Extensive Range. We've Got It Covered!Riverland Welding and Tool SuppliesNo ratings yet
- Samsung Galaxy S III Userguide PDFDocument183 pagesSamsung Galaxy S III Userguide PDFMonish KrishnaNo ratings yet
- PHOTOZUELA PicsDocument58 pagesPHOTOZUELA PicsChrisMartinNo ratings yet
- Prosim 4: Vital Signs SimulatorDocument32 pagesProsim 4: Vital Signs Simulatorroberto.aNo ratings yet