Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Contraception and Sterilization Final
Uploaded by
RasheedAladdinNGuiomala0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesThe document discusses various methods of contraception and sterilization. It describes permanent methods like bilateral tubal ligation and vasectomy. It also discusses temporary methods including hormonal options like oral contraceptive pills, patches, implants and injections. Barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms are also covered. The document provides information on the effectiveness, advantages, and disadvantages of different contraceptive methods to help individuals determine the best option. It also discusses contraindications and health effects of various methods.
Original Description:
Family planning contraceptive methods
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses various methods of contraception and sterilization. It describes permanent methods like bilateral tubal ligation and vasectomy. It also discusses temporary methods including hormonal options like oral contraceptive pills, patches, implants and injections. Barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms are also covered. The document provides information on the effectiveness, advantages, and disadvantages of different contraceptive methods to help individuals determine the best option. It also discusses contraindications and health effects of various methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views2 pagesContraception and Sterilization Final
Uploaded by
RasheedAladdinNGuiomalaThe document discusses various methods of contraception and sterilization. It describes permanent methods like bilateral tubal ligation and vasectomy. It also discusses temporary methods including hormonal options like oral contraceptive pills, patches, implants and injections. Barrier methods like condoms and diaphragms are also covered. The document provides information on the effectiveness, advantages, and disadvantages of different contraceptive methods to help individuals determine the best option. It also discusses contraindications and health effects of various methods.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
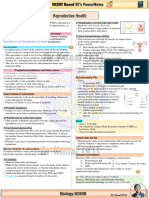
GYNE How does it work?
Contraception and Sterilization Hormonal contraceptives
Dr. Ababon Oral contraceptive pills
Contraceptive patches
Earth: A crowded place Injectables
Subdermal implants
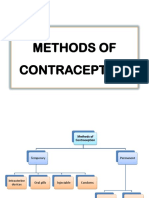
Family planning methods Spray-on contraceptives
Permanent methods Intrauterine devices
o There are two types of permanent methods or Nuva ring
sterilization, namely: Barrier methods
Bilateral tubal ligation Male condoms
Vasectomy Diaphragm
Classic
No scalpel vasectomy What method is best for me?
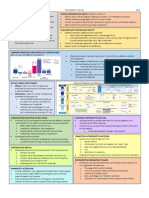
Temporary methods Indications
o The two main temporary methods of Adolescents
contraception are the following: o Low dose pills at least two years after puberty
Natural FP methods o Injectables (depo-MPA)
Fertility-based method o Local spermicides
Artificial FP methods Under 35 years old
Hormonal o All forms or methods may be used but depends
Barrier on different conditions
Over 35 years old
What do you think is happening in the reproductive tract of a o Sequential progestins to compensate for luteal
woman every cycle of her life? insufficiency
Pre-menopausal women
o Continuous progestins to treat luteal
insufficiency, mastopathies, and endometrial
hypertrophies
Post-partum women
o Minidose combined OCPs
o Injectables (depo-MPA)
o Local spermicides
o Lactational amenorrhea method (LAM) for 6
months only
Contraindications
Intrauterine device
o Are not recommended for adolescents
o Should not be used when the uterus is
retroverted
o Should be avoided in cases of local infections
o Should not be performed by non-experts
Standard days method How will it affect me?
Symptothermal method ORAL CONTRACEPTIVE PILLS
Basal body temperature Advantages:
Billings ovulation method Very efficient when used correctly
Does not interrupt sex
Why does continuous breastfeeding prevent pregnancy? Increased sexual enjoyment
Light, regular monthly periods
Reversible
Can be used by women at any age or parity
Non-contraceptive benefits, prevents:
o Endometrial cancer
o Ovarian cancer
o Pelvic inflammatory disease
o Benign breast disease
o Iron-deficiency anemia
o Dysmenorrhea
Disadvantages
Need to take the pill everyday
Not recommended for breastfeeding women (combined
Lactational amenorrhea method OCP)
Does not protect against STIs
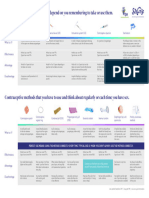
INJECTABLE CONTRACEPTIVES FERTILITY-BASED METHODS
Advantages Advantages
Private No physical side effects
Can be use by breastfeeding women Very little or no cost
No estrogen side effects Can be used by most couples
No daily pill-taking Effective if used correctly and consistently
Allows some flexibility in return visits (2 weeks early or 2 Immediately reversible
weeks late) Acceptable to some religious groups
Does not interrupt sex Involves men in family planning
Increased sexual enjoyment Disadvantages
Long-term pregnancy prevention but reversible Usually somewhat effective
Other health benefits, prevents Will not work without cooperation commitment of both
o Endometrial and ovarian cancer couples
o Uterine fibroids Requires daily recording and close attention to body
o Iron deficiency anemia changes
o Pelvic inflammatory disease May require long periods of abstinence
Disadvantage Does not protect against STIs
Delayed return of fertility of about 8-10 months after its
contraceptive effects Issues and choices
Requires regular injections every 3 months (DMPA) or 2
months (Noristerat) Quiz: essay
Does not protect against STIs including AIDS
--END--
CONDOMS
Advantages
Private
No daily pill-taking
Can be used whenever it is needed
Cheap and readily available everywhere
Non-contraceptive benefits, prevents
o STI effectively
o Conditions caused by STIs (PID, ectopic
pregnancy, infertility)
Disadvantages
Interferes with sex
Supply must be ready at all times
Possibility that the condom will slip off or break
Condom can weaken and tear if not stored properly
Man's cooperation is needed for the woman to protect
herself from pregnancy and disease
Embarrassing for some people to buy, ask partner to use,
take or throw away
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE
Advantages
Effective long-term prevention of pregnancy
Easy to use and does not interfere with sexual intercourse
Increased sexual enjoyment because no need to worry
about pregnancy
Has no systemic, hormonal side effects
Provides immediate return to fertility upon removal
Can be used during breastfeeding
No interactions with medications
Disadvantages
Client cannot start or discontinue IUD use on her own
May be expelled
Need to check the position of the IUD strings from time to
time
May increase the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Does not protect against STDs
You might also like
- Case Study 1Document9 pagesCase Study 1Mark SanchezNo ratings yet
- The Miracle Results of Fasting - Dave WilliamsDocument129 pagesThe Miracle Results of Fasting - Dave WilliamsGikonyo Stellar94% (17)
- Raja Maya Case StudyDocument3 pagesRaja Maya Case StudyKrishna100% (1)
- ATI Maternal Newborn Chapter 1-ContraceptionDocument23 pagesATI Maternal Newborn Chapter 1-ContraceptionVin Lorenzo Campbell100% (4)
- Solution Manual For Understanding Human Sexuality 14th Edition Janet Hydejohn DelamaterDocument37 pagesSolution Manual For Understanding Human Sexuality 14th Edition Janet Hydejohn DelamaterMarieHughesebgjp100% (81)
- Katie Humphrey-Freedom From PCOS-lulu - Com (2010)Document131 pagesKatie Humphrey-Freedom From PCOS-lulu - Com (2010)Patricia ReynosoNo ratings yet
- Christine Henseler (Auth.) - Spanish Fiction in The Digital Age - Generation X Remixed-Palgrave Macmillan US (2011)Document270 pagesChristine Henseler (Auth.) - Spanish Fiction in The Digital Age - Generation X Remixed-Palgrave Macmillan US (2011)VictoriaNo ratings yet
- CONTRACEPTION LectureDocument49 pagesCONTRACEPTION LectureAnton OcampoNo ratings yet
- Keluarga Berencana: Oleh. Dr. Lidia Hastuti, M.KesDocument67 pagesKeluarga Berencana: Oleh. Dr. Lidia Hastuti, M.Kestri wahyudiNo ratings yet
- Contraception: Nur Hafizah Ainaa Abu HassanDocument53 pagesContraception: Nur Hafizah Ainaa Abu Hassanshravani100% (1)
- Contraception Part 1Document50 pagesContraception Part 1Aman ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Coc 1Document17 pagesCoc 1Ahmed AnwarNo ratings yet
- ContraceptivesDocument7 pagesContraceptivesdhavalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Contraceptive Methods TableDocument3 pagesOverview of Contraceptive Methods Tablelarazahabi0% (1)
- Contraceptivemethods 150521003728 Lva1 App6892Document59 pagesContraceptivemethods 150521003728 Lva1 App6892Michael John Anicas LozanoNo ratings yet
- ContraceptiveDocument53 pagesContraceptiveAbas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Contraception CMEDocument57 pagesContraception CMEstephaniesoniamethewNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive Methods Infographic - New - by BRIAN JUDE LASAN (Infographic)Document2 pagesContraceptive Methods Infographic - New - by BRIAN JUDE LASAN (Infographic)BRIAN JUDE LASANNo ratings yet
- 4 Reproductive Health-NotesDocument3 pages4 Reproductive Health-NotesKamalNo ratings yet
- Family Planning: By: Khalid Jemal (MD, Assistant Prof. of Obstetrics & Gynecology)Document73 pagesFamily Planning: By: Khalid Jemal (MD, Assistant Prof. of Obstetrics & Gynecology)Degefaw BikoyNo ratings yet
- 4 Reproductive HealthDocument3 pages4 Reproductive Healthgauravkr.928373717No ratings yet
- Reproductive HealthDocument39 pagesReproductive Health179.AADHIRAI SEMMOZHI.BNo ratings yet
- Contraception and Women Health 2 1Document18 pagesContraception and Women Health 2 1nusaiba0313No ratings yet
- 2 3 Contraceptive Methods 1 Idris 2021 2Document77 pages2 3 Contraceptive Methods 1 Idris 2021 2Jihan RayNo ratings yet
- PGI MANIMTIM - OBGYN - Family PlanningDocument9 pagesPGI MANIMTIM - OBGYN - Family PlanningKim Adarem Joy ManimtimNo ratings yet
- Male and Female Contraception MethodsDocument5 pagesMale and Female Contraception MethodsJhaypeeh VerzoNo ratings yet
- Birth ControlDocument13 pagesBirth Controlapi-374195102No ratings yet
- t12 - Buku Aman & Sehat - KontrasepsiDocument67 pagest12 - Buku Aman & Sehat - KontrasepsiAyuNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health PowerNotes by KT SirDocument2 pagesReproductive Health PowerNotes by KT Sirjumihuss08No ratings yet
- 04 Reproductive HealthDocument3 pages04 Reproductive HealthashbaNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive Choices at A Glance Chart Sexwise FpaDocument1 pageContraceptive Choices at A Glance Chart Sexwise FpaMai SomaaNo ratings yet
- Your Contraceptive Choices ChartDocument1 pageYour Contraceptive Choices ChartM Cecilia DFNo ratings yet
- Contraception - #2Document4 pagesContraception - #2Eingel Mer EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- (GYNE) Menopause-Dr. Palaypayon (M. ALdana Med 2021)Document10 pages(GYNE) Menopause-Dr. Palaypayon (M. ALdana Med 2021)adrian kristopher dela cruzNo ratings yet
- Birth Control ProjectDocument16 pagesBirth Control ProjectTishana Thompson100% (1)
- Contraceptive Methods and Issues Around The MenopauseDocument18 pagesContraceptive Methods and Issues Around The MenopauseLakshmi DheviNo ratings yet
- Birth Control MethodsDocument51 pagesBirth Control MethodsLamis AlianNo ratings yet
- Sexual Self: Presented By: Group 1Document26 pagesSexual Self: Presented By: Group 1Vanessa Joyce Isleta100% (3)
- Contraceptive Choices FactsheetDocument2 pagesContraceptive Choices FactsheetCahyawati Arisusilo MarzuqiNo ratings yet
- Contraception: Sara Alhaddab Lama AlshwairikhDocument9 pagesContraception: Sara Alhaddab Lama AlshwairikhRyubusa HayabusaNo ratings yet
- Contraception: DR Husni SamarahDocument15 pagesContraception: DR Husni Samarahpal_pal_palNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Contraception Webinar KOGS 13.10Document44 pagesHormonal Contraception Webinar KOGS 13.10Alice KaariaNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive MethodDocument45 pagesContraceptive MethodSidra SoniaNo ratings yet
- The REPRODUCTION-PROCESSDocument30 pagesThe REPRODUCTION-PROCESSEJ GolimlimNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive Methods: A Review of Nonbarrier and Barrier ProductsDocument6 pagesContraceptive Methods: A Review of Nonbarrier and Barrier Productsعبد الله الخالدNo ratings yet
- Bc-Across-Gender-Spectrum 1Document4 pagesBc-Across-Gender-Spectrum 1api-646865632No ratings yet
- Contraception OBG PresentationDocument15 pagesContraception OBG Presentationfawkesrox03No ratings yet
- ContaceptionDocument66 pagesContaceptionSadaf AfzalNo ratings yet
- Contraception: Prevention of Pregnancy Birth ControlDocument8 pagesContraception: Prevention of Pregnancy Birth ControlMay KiNo ratings yet
- Chart For Contraception:: PreventsDocument1 pageChart For Contraception:: PreventsAngelica May ClaritoNo ratings yet
- MOA Advantages Disadvantages Efficacy AdminDocument4 pagesMOA Advantages Disadvantages Efficacy AdminmeilunlyNo ratings yet
- Intercourse and IslamDocument52 pagesIntercourse and IslamEngr. Khandaker Marsus75% (4)
- Correct Use of Misoprostol For Induction of Labour KLMNSDocument31 pagesCorrect Use of Misoprostol For Induction of Labour KLMNSsabellanabimanya9No ratings yet
- Types of Birth ControlDocument2 pagesTypes of Birth ControlMayara WalterNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Family PlanningDocument9 pages3.3 Family PlanningGayle Regine DaquialNo ratings yet
- Paper Anticonceptivos Ingles ExponerDocument18 pagesPaper Anticonceptivos Ingles ExponermariaNo ratings yet
- ContraceptionDocument12 pagesContraceptionkellyjackykjNo ratings yet
- Contraceptive Assignment AdihailuDocument46 pagesContraceptive Assignment AdihailuAbas AhmedNo ratings yet
- Hormonal Contraceptive MethodsDocument5 pagesHormonal Contraceptive MethodsBai Norhamah HassanNo ratings yet
- ContraceptionDocument79 pagesContraceptionMeekel SusikuNo ratings yet
- Contraception & HRTDocument14 pagesContraception & HRTWheezy BruhNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Health McqsDocument19 pagesReproductive Health McqsM.Tharun KumarNo ratings yet
- Family PlanningDocument4 pagesFamily PlanningJennica BubanNo ratings yet
- Birth Control: Mr. K. WaiteDocument18 pagesBirth Control: Mr. K. WaiteKUWAYNE WAITENo ratings yet
- Methods of ContraceptionDocument24 pagesMethods of ContraceptionAnonymous XLMsbQqNo ratings yet
- My Mifespristone and Misoprostol Story: How I used mifepristone and misoprostol for a successful medical abortion and all you must know about these abortion pillsFrom EverandMy Mifespristone and Misoprostol Story: How I used mifepristone and misoprostol for a successful medical abortion and all you must know about these abortion pillsNo ratings yet
- 3 RO102 CDE Road and Traffic Rules ExpresswayDocument7 pages3 RO102 CDE Road and Traffic Rules ExpresswayRasheedAladdinNGuiomalaNo ratings yet
- ECG - ACLS 2020 ModuleDocument68 pagesECG - ACLS 2020 ModuleRasheedAladdinNGuiomala100% (1)
- The Well-Spoken Thesaurus The Most Powerful Ways To Say Everyday Words and Phrases by Tom HeehlerDocument401 pagesThe Well-Spoken Thesaurus The Most Powerful Ways To Say Everyday Words and Phrases by Tom HeehlerRasheedAladdinNGuiomala100% (1)
- NMDs OrientationDocument31 pagesNMDs OrientationRasheedAladdinNGuiomalaNo ratings yet
- Schizophrenia 1Document4 pagesSchizophrenia 1RasheedAladdinNGuiomalaNo ratings yet
- CALIMOVEDocument46 pagesCALIMOVERasheedAladdinNGuiomala0% (1)
- What Aragorn Can Teach Us About Masculinity - by Edward Marotis - MediumDocument5 pagesWhat Aragorn Can Teach Us About Masculinity - by Edward Marotis - MediumRasheedAladdinNGuiomalaNo ratings yet
- !physical Examination NormalDocument3 pages!physical Examination NormalRasheedAladdinNGuiomalaNo ratings yet
- 7 Best Places To Meet Single Women (2023)Document9 pages7 Best Places To Meet Single Women (2023)RasheedAladdinNGuiomalaNo ratings yet
- IM Oct 19 2018Document5 pagesIM Oct 19 2018RasheedAladdinNGuiomalaNo ratings yet
- Your Complete Guide To Birth Control Methods in The PhilippinesDocument8 pagesYour Complete Guide To Birth Control Methods in The PhilippinesJobert John BatallonesNo ratings yet
- Medical Eligibility Criteria For Contraceptive UseDocument294 pagesMedical Eligibility Criteria For Contraceptive UseStefanos RaptisNo ratings yet
- The Philippine Family Planning ProgramDocument40 pagesThe Philippine Family Planning ProgramAlexandria P. OrcajadaNo ratings yet
- Gender and Society Module 2Document12 pagesGender and Society Module 2Mary Rose Distura OnceNo ratings yet
- RH BillDocument13 pagesRH BillDr. Liza ManaloNo ratings yet
- Lupin Project CompatibleDocument97 pagesLupin Project CompatibleNitish SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Study: ScenarioDocument5 pagesCase Study: ScenarioCheska PalomaNo ratings yet
- Position Paper-RH Bill-Dr ManaloDocument14 pagesPosition Paper-RH Bill-Dr ManaloCBCP for LifeNo ratings yet
- 4 MG Drospirenone Only Pill New Data and A Review of The Literature PDFDocument8 pages4 MG Drospirenone Only Pill New Data and A Review of The Literature PDFJuly López LeitonNo ratings yet
- Aub Updated-1 PDFDocument87 pagesAub Updated-1 PDFEvelyn Pamela Espinoza Morales100% (2)
- Utilization of Family Planning ProjectDocument49 pagesUtilization of Family Planning ProjectUsman Ahmad TijjaniNo ratings yet
- NEET Reproductive HealthDocument24 pagesNEET Reproductive HealthDip KcNo ratings yet
- Population Dynamics NewDocument169 pagesPopulation Dynamics Newhiral mistryNo ratings yet
- Chapter 42: Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology Garzon Maaks: Burns' Pediatric Primary Care, 7th EditionDocument3 pagesChapter 42: Pediatric and Adolescent Gynecology Garzon Maaks: Burns' Pediatric Primary Care, 7th EditionHelen UgochukwuNo ratings yet
- 3 Antifertility PDFDocument7 pages3 Antifertility PDFmakram_0451No ratings yet
- ECPs and IUD NotesDocument8 pagesECPs and IUD NotesYu, Denise Kyla BernadetteNo ratings yet
- Fibroids ADocument242 pagesFibroids Anautilus81100% (1)
- Ob-Gyn Review Part 3Document101 pagesOb-Gyn Review Part 3filchibuffNo ratings yet
- PLMNursing - StudyMaterial - Reproductive PlanningDocument11 pagesPLMNursing - StudyMaterial - Reproductive PlanningGwyneth ManioNo ratings yet
- Contraception MethodsDocument38 pagesContraception MethodsDaisy NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Comprehensive Examination of The Female CheckedDocument3 pagesGynecology - Comprehensive Examination of The Female CheckedMuhammad AdnanNo ratings yet
- Obg LMRP 2019Document34 pagesObg LMRP 2019skNo ratings yet
- Approaches To Limit Systemic Antibiotic Use in AcneDocument12 pagesApproaches To Limit Systemic Antibiotic Use in Acnecc_msNo ratings yet
- CerazetteDocument36 pagesCerazetteSuhazeli AbdullahNo ratings yet