Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sound
Uploaded by
Aafan ShahidCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sound
Uploaded by
Aafan ShahidCopyright:
Available Formats
8th Science
Sound
Sound: Sound is a mechanical wave which gives us the sense of hearing.
Sound is produced by a vibrating body. A vibrating object produces sound. When a bell is hit by a gong,
the bell starts to vibrate and produces sound.
Sound Needs a Medium for Propagation:
Sound needs a medium through which it can travel. Sound cannot travel through vacuum. Sound can travel
through solid, liquid. Propagation of sound happens in all directions in a medium.
Vibration: The to and fro or back and forth motion in an object is called vibration or oscillation.
Traditional musical instruments produce sound because of vibration in some of their parts.
Sound Produced by Humans:
Sound is produced by voice box or larynx; in human beings. The voice box or larynx is situated in the
upper part of wind pipe. There are two vocal cords stretched across the larynx in way that there is a small
gap between them. When air is forced through the gap, vocal cords begin to vibrate and sound is produced.
Muscles which are attached to the vocal cord enable us to make the vocal cords tight or loose as per need.
Sound quality varies according to tension or slack in the vocal cords.
The vocal cords in men are longer (about 20 mm), but they are shorter in women and children. Due to this,
voices of men, women and children are different from each other.
Characters of Vibrations:
Vibration is also called oscillatory motion or oscillation. It has certain unique characteristics which are as
follows:
Frequency: Number of oscillations in unit time is called frequency of oscillation. Frequency is
expressed as Hertz (Hz). When an object is vibrating 1 time in a second, its frequency is 1 Hz.
Amplitude: Maximum displacement of a wave on either side from mean position is called amplitude.
Thus, amplitude shows how far the vibrating object moves from the mean position.
Time period:
The time taken by the vibrating body for one complete vibration is known as the time period of vibration. It
is denoted by T.
T=1/f and f=1/T
Time period and frequency are reciprocals of each other.
Address: Sheikh-Ul-Aalam (Ra) Complex, Near Police Station, Chadoora, Budgam
8th Science
Sound
Characters of Vibrations:
Loudness of Sound: Loudness of sound depends on amplitude of vibration. Loudness of sound is
directly proportional to square of amplitude of vibration. Louder sound has higher amplitude, while quieter
sound has lower amplitude. Loudness is expressed in terms of decibel. Loudness of some common sounds
is in the following table.
Sound Loudness
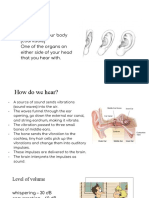
Normal breathing 10 dB
Soft whisper (at 5 m) 30 dB
Normal conversation 60 dB
Busy traffic 70 dB
Average factory 80 dB
Pitch of Sound: Pitch of sound depends on frequency of vibration. A high pitched sound has high
frequency, while a low pitched sound has low frequency. Children and women generally produce sound
with high pitch.
Quality (Timbre):
The quality of a sound is that property by virtue of which two sounds of the same pitch and loudness
produced by the two different musical instrument or people can be distinguished.
Audible and Inaudible Sounds:
Audible sounds are those that can be heard while inaudible sounds are those that cannot be heard.
Human beings can hear sounds between frequencies 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz. This range of frequencies is
called the hearing range for humans.
The sound with frequency below 20 Hz is called infrasound. On the other hand, the sound with
frequency above 20,000 Hz is called ultrasound.
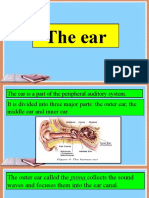
Human Ear
Human ear; which gives us the sense of hearing is a complex structure. It can be divided into three main
parts, viz. external ear, middle ear and internal ear.
Address: Sheikh-Ul-Aalam (Ra) Complex, Near Police Station, Chadoora, Budgam
8th Science
Sound
a. External Ear: The external ear or pinna appears like a funnel. Its function is to catch sound
waves and to direct them towards middle ear.
b. Middle Ear: The middle ear is composed of a stretched membrane and three small bones. The
stretched membrane is called the ear drum and small bones are called bony ossicles. These are
named sequentially from outside to inside as; malleus, incus, and stapes (hammer, anvil, and
stirrup). When sound wave comes to the middle ear, it sets vibrations in the ear drum. After that,
sound waves are transferred from ear drum transfers these vibrations to the three bones.
c. Internal Ear: The internal ear is composed of cochlea and semicircular canals. Cochlea appears
like a snail from outside. Vibrations from middle ear reach the cochlea. Signals from cochlea
reach the brain and we hear a sound. Semicircular canals have no role in sense of hearing, rather
they maintain the balance of the body.
Noise and Music: A sound which is pleasant to ears is called music. But any unpleasant sound is called
noise.
Noise Pollution: Presence of excess noise in environment is called noise pollution. Automobiles,
factories, loud music, construction works, firecrackers, stone quarry, etc. are sources of noise pollution.
The noise becomes physically painful above 80 dB.
Effects of Noise Pollution: Continuous exposure to noise pollution can result in lack of sleep (insomnia),
hypertension (high blood pressure), anxiety and many other disorders. Noise pollution can also lead to
partial loss of hearing; in some cases.
Measures to Limit Noise Pollution:
Aircraft engines and automobile engines should be fitted with silencing devices. The muffler (or
silencer) in a motorcycle is an example of such device.
Factories should be relocated far from residential areas. Many factories from Delhi had been shifted
to outskirts in the nineties.
Trees should be planted along the roads because trees absorb noise.
Sound barrier should be installed along flyovers.
Hearing Impairment: Loss of hearing is called hearing impairment. It can be total or partial, but total
hearing impairment is rare. Total hearing impairment is usually congenital, i.e. by birth. A person with
hearing impairment can learn sign language to communicate with others. Hearing aids can be used by
people who are suffering from partial hearing impairment.
QUESTIONS
Question 1: Sound can travel through
a. gases only
b. solids only
c. liquids only
d. solids, liquids and gases
Answer: (d) solids, liquids and gases
Question 2: Which of the following voices is likely to have minimum frequency?
a. Baby girl
b. Baby boy
3
Address: Sheikh-Ul-Aalam (Ra) Complex, Near Police Station, Chadoora, Budgam
8th Science
Sound
c. A man
d. A woman
Answer: (c) A man
Question 3: In the following statements, tick T against those which are true, and F against those which are
false:
a. Sound cannot travel in vacuum.
b. The number of oscillations per second of a vibrating object is called its time period.
c. If the amplitude of vibration is large, sound is feeble.
d. For human ears, the audible range is 20 Hz to 20,000 Hz.
e. The lower the frequency of vibration, the higher is the pitch.
f. Unwanted or unpleasant sound is termed as music.
g. Noise pollution may cause partial hearing impairment.
Answer: (a) T, (b) F, (c) F, (d) T, (e) F, (f) F, (g) T
Question 4: Fill in the blanks with suitable words.
a. Time taken by an object to complete one oscillation is called ....................
b. Loudness is determined by the .........................of vibration.
c. The unit of frequency is..........................
d. Unwanted sound is called ......................... .
e. Shrillness of a sound is determined by the ................. of vibration.
Answer: (a) time period, (b) amplitude, (c) hertz, (d) noise, (e) frequency and amplitude
Question 5: A pendulum oscillates 40 times in 4 seconds. Find its time period and frequency.
Answer: Given; number of oscillations = 40, time = 4 s
Time period can be calculated as follows:
Time taken for 40 oscillations = 4 second
Hence, time taken for 1 oscillation = 4 ÷ 40 = 0.1 second
Frequency can be calculated as follows:
Frequency = number of oscillations ÷ time
= 40 ÷ 4 = 10 Hz
Question 6: The sound from a mosquito is produced when it vibrates its wings at an average rate of 500
vibrations per second. What is the time period of the vibration?
Answer: Since time period is time taken to complete one oscillation,
Time taken for 500 oscillations = 1 s
Hence, time taken for 1 oscillation = 1 ÷ 500 = 0.002 s
Question 7: Identify the part which vibrates to produce sound in the following instruments:
a. Dholak
b. Sitar
c. Flute
Answer: (a) Stretched membrane, (b) String, (c) Air column
Question 8: What is the difference between noise and music? Can music become noise sometimes?
Answer: Unwanted sound that is unpleasant to ear is called noise. A pleasant sound is called music.
Music can become noise at many instances. When someone tries to enjoy very loud music, it can be noise
Address: Sheikh-Ul-Aalam (Ra) Complex, Near Police Station, Chadoora, Budgam
8th Science
Sound
for someone else. When loud music is played during religious celebrations or marriages, it can be
annoying for many people.
Question 9: List sources of noise pollution in your surroundings.
Answer: Running vehicles
Use of loudspeaker
Use of TV with high volume
Question 10: Explain in what way noise pollution is harmful to humans.
Answer: Noise pollution is harmful to humans in many ways. Constant exposure to noise pollution can
create many health related problems; like insomnia, hypertension and may even lead to loss of hearing.
Question 11: Your parents are going to buy a house. They have been offered one on the roadside and
another three lanes away from the roadside. Which house would you suggest your parents should buy?
Explain your answer.
Answer: I will suggest my parent to buy a house which is away from the roadside, because house at
roadside would be noisy because of running vehicles. On the other hand, the house which is three lanes
away from the roadside would be quieter.
Question 12: Sketch larynx and explain its function in your own words.
Answer: Larynx is composed of two stretched membranes; with some gap between them. When air
passes through the larynx, the membranes or vocal cords vibrate and produce sound. That is why larynx
is also known as sound box.
Question 13: Lightning and thunder take place in the sky at the same time and at the same distance from
us. Lightning is seen earlier and thunder is heard later. Can you explain?
Answer: We know that the speed of light much more than the speed of sound. Due to this, light reaches
to us faster than sound. Hence, during lightning we see the streak of light earlier than hearing the sound
of thunder.
Address: Sheikh-Ul-Aalam (Ra) Complex, Near Police Station, Chadoora, Budgam
You might also like
- Sound Class 8Document5 pagesSound Class 8Sanjib MandalNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About SoundDocument5 pagesEverything You Need to Know About SoundSyed MoinNo ratings yet
- Ear Foreign BodyDocument19 pagesEar Foreign BodyAristiyan LuthfiNo ratings yet
- 676 Hi-Fi Loudespeaker System PDFDocument2 pages676 Hi-Fi Loudespeaker System PDFSorin MaximNo ratings yet
- Sound - Class 8 - Notes - PANTOMATHDocument7 pagesSound - Class 8 - Notes - PANTOMATHsourav9823No ratings yet
- Sound: Sounds and VibrationsDocument7 pagesSound: Sounds and Vibrationschhabra navdeepNo ratings yet
- Equine Diagnostic Ultrasound PDFDocument556 pagesEquine Diagnostic Ultrasound PDFSara Perez PastranaNo ratings yet
- Inner EarDocument18 pagesInner EarSharmela BrijmohanNo ratings yet
- Adventures in Sound with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandAdventures in Sound with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- My Ears are Special : The Science of Sound - Physics Book for Children | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandMy Ears are Special : The Science of Sound - Physics Book for Children | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Irc SP.114.2018Document146 pagesIrc SP.114.2018Anonymous YHcvra8Xw6No ratings yet
- EDM Bass Sidechain Compression CheatsheetDocument6 pagesEDM Bass Sidechain Compression CheatsheetRui MigueisNo ratings yet
- Classical Orchestra, A-B StereoDocument5 pagesClassical Orchestra, A-B StereoZoran TevdovskiNo ratings yet
- BNCA Architectural AcousticsDocument35 pagesBNCA Architectural AcousticsSakshi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- ISO 140-4 Acoustics - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements (2484) PDFDocument30 pagesISO 140-4 Acoustics - Measurement of Sound Insulation in Buildings and of Building Elements (2484) PDFDenise PinheiroNo ratings yet
- Viii SoundDocument6 pagesViii Soundsmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Sound Plays An Important Role in Our Daily LifeDocument5 pagesSound Plays An Important Role in Our Daily Lifevaishali14051980No ratings yet
- Sound class8 living science key pointsDocument4 pagesSound class8 living science key pointsSarthak KarnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Sound WaveDocument27 pagesLesson 4 - Sound WaveElijah AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Ound NotesDocument5 pagesOund Notesmokshithakapoor657No ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 10 Sound – RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 10 Sound – RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes About SoundsDocument6 pagesLesson Notes About Soundsmark joseph cometaNo ratings yet
- Answers To Textbook QuestionsDocument4 pagesAnswers To Textbook QuestionsSiddharth SharmaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument3 pagesSoundPrathamesh . M LaddhadNo ratings yet
- 1693037026467Document8 pages1693037026467GunikaNo ratings yet
- Ch-13. SOUNDDocument6 pagesCh-13. SOUNDNiha KausarNo ratings yet
- 13 SoundDocument16 pages13 SoundBhaskar T IsacNo ratings yet
- VIII 13 SoundDocument16 pagesVIII 13 SoundBalaji ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- CH 13Document9 pagesCH 13Mayankkumar MistryNo ratings yet
- Uzl2EKtjJ5xJdcdX6p8JDocument5 pagesUzl2EKtjJ5xJdcdX6p8Jash839840No ratings yet
- Sound NotesDocument2 pagesSound NotesMouktthika SaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 16, SoundDocument29 pagesUnit 16, Soundaaronharper112No ratings yet
- SoundDocument5 pagesSoundOnlymexxNo ratings yet
- Noise pollution and its harmful effectsDocument7 pagesNoise pollution and its harmful effectsJayaprasanna VenkatesanNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument4 pagesSoundMala MathematicsNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Question Chapter 13 ExerciseDocument5 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Question Chapter 13 ExerciseloluNo ratings yet
- Revision Assignment SoundDocument17 pagesRevision Assignment Soundrajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - Chap 13 (Qns & Ans)Document6 pagesGrade 8 - Chap 13 (Qns & Ans)Sri DharshanNo ratings yet
- Sound EditedDocument27 pagesSound EditedChristopher Victor De LeonNo ratings yet
- Sound PPT-3Document23 pagesSound PPT-3prabhavkalsiNo ratings yet
- (462939) 1.2 BGE 1 - Sound Summary NotesDocument12 pages(462939) 1.2 BGE 1 - Sound Summary NotesVase VaseskiNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument7 pagesSoundGrace DesouzaNo ratings yet
- Sound Chapter ClassificationDocument2 pagesSound Chapter ClassificationMeenakshiNo ratings yet
- Ear and Properties of SoundDocument15 pagesEar and Properties of SoundAnaliza ToledoNo ratings yet
- Sound: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument5 pagesSound: Multiple Choice QuestionsAkash SahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Science of SoundDocument43 pagesChapter 1 - Science of SoundCristina LedfordNo ratings yet
- APznzaawQpvP1WSKnDfQxoPnLNvPPh8gzBo6etL9_hHTGmbq5XbhysZx9oDwWmi3PkEuHQ5vuHWeV5Z3VJiHx1EECKwUp8tmTbZ3SWD94pe5axP-cp4W_GEBfCyDPgw2lu0XYN6l4v7w-IpLTkeHiu1soptYcX-AGwX-L7WVUIYrqdorRsGMsn-ieMtXc-Ao5OepH-n1rzhhkPb7DWCNz2Document6 pagesAPznzaawQpvP1WSKnDfQxoPnLNvPPh8gzBo6etL9_hHTGmbq5XbhysZx9oDwWmi3PkEuHQ5vuHWeV5Z3VJiHx1EECKwUp8tmTbZ3SWD94pe5axP-cp4W_GEBfCyDPgw2lu0XYN6l4v7w-IpLTkeHiu1soptYcX-AGwX-L7WVUIYrqdorRsGMsn-ieMtXc-Ao5OepH-n1rzhhkPb7DWCNz2kalash iyerNo ratings yet
- Sound Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 13Document3 pagesSound Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 13zodika khiangteNo ratings yet
- Sound WavesDocument30 pagesSound WavesRidwan Pratama YudhaNo ratings yet
- Sound SummaryDocument2 pagesSound Summaryhweta173No ratings yet
- Theme 1 The Beautiful of Togetherness: Creative ThinkingDocument8 pagesTheme 1 The Beautiful of Togetherness: Creative ThinkingFitria Istikomah DewiNo ratings yet
- Sound Lesson 3Document27 pagesSound Lesson 3rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 13 - SoundDocument2 pagesRevision Notes Class - 8 Science Chapter 13 - SoundArpit Sharma100% (1)
- 1 - SoundDocument26 pages1 - SoundOSHIN BALASINGHNo ratings yet
- Noise Study ReportDocument4 pagesNoise Study ReportLiew Shu YanNo ratings yet
- 13. SOUND NOTEBOOK WORKDocument4 pages13. SOUND NOTEBOOK WORKlavanyadureja456No ratings yet
- Production of Sound and its PropertiesDocument2 pagesProduction of Sound and its PropertiesPianoPianistNo ratings yet
- Class-8 SoundDocument5 pagesClass-8 SoundMamta JoshiNo ratings yet
- How Sound is Produced and PropagatedDocument5 pagesHow Sound is Produced and PropagatedNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Acoustic Sound and Human EarDocument26 pagesAcoustic Sound and Human EarEmmanuel EhuronNo ratings yet
- 2016 SoundDocument69 pages2016 Soundryancasal959No ratings yet
- DOC 1702557535516 (2)Document4 pagesDOC 1702557535516 (2)goodshifa1No ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 13 SoundDocument5 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 13 Soundmuneebshabir23No ratings yet
- Introduction To Recording & Sound Reinforcement - Part 1 & 2Document14 pagesIntroduction To Recording & Sound Reinforcement - Part 1 & 2Alexander KohNo ratings yet
- Audio Production 1Document7 pagesAudio Production 1Sarah MbeweNo ratings yet
- Aurar 501 Architectural Acoustics Unit 1Document53 pagesAurar 501 Architectural Acoustics Unit 1Santhu DasariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Sound NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 10 Sound NotesAzaanNo ratings yet
- Chapter43 PDFDocument20 pagesChapter43 PDFyhproNo ratings yet
- Complex Modulus of ElasticityDocument14 pagesComplex Modulus of ElasticityYOGESH CHANDRANo ratings yet
- Ph.D. Course Comprehensive Viva and Research Proposal ReportDocument1 pagePh.D. Course Comprehensive Viva and Research Proposal ReportAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Reinforced HSC Beams Strengthened With CFRP Plates Under BendingDocument33 pagesReinforced HSC Beams Strengthened With CFRP Plates Under BendingAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- C78 PDFDocument4 pagesC78 PDFgrats_singcoNo ratings yet
- Compressive Behaviour of Concrete at High Strain RatesDocument26 pagesCompressive Behaviour of Concrete at High Strain RatesMohamed YasserNo ratings yet
- 17 RFP Vol III Feasibility Report Part III PDFDocument97 pages17 RFP Vol III Feasibility Report Part III PDFSrinivas PNo ratings yet
- Sunitha - FRCDocument1 pageSunitha - FRCAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Cupola Furnace and Blast Furnace Slags With Respect To Possibilities of Their UtilizationDocument10 pagesComparison of Cupola Furnace and Blast Furnace Slags With Respect To Possibilities of Their UtilizationAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- COSTWATHORADocument3 pagesCOSTWATHORAAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Optimal Design of Through-Truss Steel Bridges: C. Maraveas, A. Papagiannakis, K. Miamis & K. TasiouliDocument12 pagesOptimal Design of Through-Truss Steel Bridges: C. Maraveas, A. Papagiannakis, K. Miamis & K. TasiouliAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Are Accidental-Eccentricity Load Cases Not Required When Using Semi-Rigid Diaphragms?Document1 pageAre Accidental-Eccentricity Load Cases Not Required When Using Semi-Rigid Diaphragms?Aafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- 2.structural Drawing Deki LaneDocument65 pages2.structural Drawing Deki LanePacha Khan KhogyaniNo ratings yet
- 138 ExperimentalDocument10 pages138 ExperimentalAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- ChatLog Short Course On MIDAS Civil Engineering Solutions 2020-10-28 16 - 25Document1 pageChatLog Short Course On MIDAS Civil Engineering Solutions 2020-10-28 16 - 25Aafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Force Between Two Parallel Current Carrying ConductorDocument12 pagesForce Between Two Parallel Current Carrying ConductorAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Know Your Speaker Day 4Document1 pageKnow Your Speaker Day 4Aafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Processing Nested Complex Sequence Pattern Queries Over Event StreamsDocument34 pagesProcessing Nested Complex Sequence Pattern Queries Over Event StreamsAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Research ProposalDocument34 pagesResearch Proposalbinaljoshi1_13633864No ratings yet
- ETABS v9 Translator: Skip To End of Metadata Go To Start of Metadata Windows 8.1 Desktop App Certification ProgramDocument1 pageETABS v9 Translator: Skip To End of Metadata Go To Start of Metadata Windows 8.1 Desktop App Certification ProgramAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Concrete AggregatesDocument6 pagesConcrete AggregatesAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Aee Ee PDFDocument148 pagesAee Ee PDFSri RamNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete StructDocument29 pagesCorrosion Monitoring of Reinforced Concrete StructAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Cement CompositionDocument8 pagesCement CompositionAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12Document11 pagesChemistry 12Aafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- AI Seminar: Our Web Page Is At: WWW - Cs.nmsu - Edu/ Gradrep Under "Events" in Left FrameDocument44 pagesAI Seminar: Our Web Page Is At: WWW - Cs.nmsu - Edu/ Gradrep Under "Events" in Left FrameAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Properties of Concrete AggregatesDocument4 pagesProperties of Concrete AggregatesAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Technical Paper-Cement ChemistryDocument14 pagesTechnical Paper-Cement ChemistryhaibhNo ratings yet
- Concrete Fundamentals: Stages in Cement DevelopmentDocument9 pagesConcrete Fundamentals: Stages in Cement DevelopmentAafan ShahidNo ratings yet
- Health Science - Healthy EarsDocument11 pagesHealth Science - Healthy Earsapi-583392653No ratings yet
- MANUAL MESA SAMSON TXM1620 - OM - 5L - v3 PDFDocument132 pagesMANUAL MESA SAMSON TXM1620 - OM - 5L - v3 PDFJorgeSalasFernandezNo ratings yet
- Eatures: DSP 154H 15W Outdoor Waterproof Horn SpeakerDocument2 pagesEatures: DSP 154H 15W Outdoor Waterproof Horn SpeakerNatrajanNo ratings yet
- Hearing Impairment Lecture Notes 2016Document31 pagesHearing Impairment Lecture Notes 2016api-3138806570% (1)
- Brain Implants: Presented by Neseka.S 19BMR048Document17 pagesBrain Implants: Presented by Neseka.S 19BMR04819BMR048 Neseka SNo ratings yet
- Honor in Perseverance Excerpted From The Sermons by Shaykh Zulfiqar Ahmad (DB)Document9 pagesHonor in Perseverance Excerpted From The Sermons by Shaykh Zulfiqar Ahmad (DB)takwaniaNo ratings yet
- Reverb PDFDocument2 pagesReverb PDFbojanNo ratings yet
- Rizal Family Tree and Jose Rizal's SiblingsDocument7 pagesRizal Family Tree and Jose Rizal's SiblingsBadeth BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Tinnitus Handicap Inventory (THI)Document4 pagesTinnitus Handicap Inventory (THI)Dian SetyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 017Document11 pagesChapter 017api-281340024No ratings yet
- Auditorium Design Project ReportDocument13 pagesAuditorium Design Project ReportFirst name Last nameNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test in Science and Health IIIDocument4 pages1st Periodic Test in Science and Health IIIJenepher Ilagan IlaganNo ratings yet
- Audio Spotlighting - ECE Seminar TopicsDocument3 pagesAudio Spotlighting - ECE Seminar Topicsuday kumarNo ratings yet
- Sudden DeafnessDocument4 pagesSudden DeafnessferaNo ratings yet
- Biology New IADocument3 pagesBiology New IAyokuso100% (2)
- Imaging of Temporal Bone: I. Pyykkö J. Zou R. Gürkov S. Naganawa T. NakashimaDocument20 pagesImaging of Temporal Bone: I. Pyykkö J. Zou R. Gürkov S. Naganawa T. NakashimaVania Okta ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- 02 Flight Line SafetyDocument15 pages02 Flight Line SafetyNino AngobNo ratings yet
- Learner's Material: ScienceDocument14 pagesLearner's Material: ScienceElma MayNo ratings yet
- Moore, D (2018) Ear & Hearing Editorial - Auditory Processing DisorderDocument4 pagesMoore, D (2018) Ear & Hearing Editorial - Auditory Processing DisorderAnthonyNo ratings yet
- EarDocument84 pagesEarMahmoud Ashraf AttiyaNo ratings yet
- Audio Frequency Induction Loop System - OdtDocument19 pagesAudio Frequency Induction Loop System - OdtsnemalecNo ratings yet
- Sound Physics NotesDocument8 pagesSound Physics NotesWani Minham123No ratings yet
- Noise Dosimeter Lab8 HumanDocument5 pagesNoise Dosimeter Lab8 HumanAsif NawazNo ratings yet