Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sound Summary
Uploaded by
hweta173Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sound Summary
Uploaded by
hweta173Copyright:
Available Formats
Sound
Introduction:
The sensation felt by our years is called sound .Sound is a form of energy which makes us here
law of conservation of energy is also applicable to sound. Sound travels in the form of a wave.
Production/Propagation of Sound: Sound is produced when an object vibrates or is produced by
vibrating objects.
Characteristics of the medium required for the propagation of sound:
(i) Medium must be elastic so that the medium particles have the tendency to return back to their
original positions after the displacement.
(ii) Medium must have the inertia so that its particles have the capacity to store the energy.
The frictional resistance of the medium should be negligible to minimize the loss of energy in
propagation.
Medium:
The matter or substance through which sound is transmitted is called a medium. It can be solid,
liquid or gas. Air is the most common medium for sound propagation.
Wave: A wave is a disturbance that moves through a medium when the particles of the medium
set neighboring particles into motion. Sound is a mechanical, longitudinal wave.
Compression is the region of maximum density or pressured and rare faction is the region of
minimum density or pressure
There are 2 types of mechanical waves1) longitudinal eg Sound and 2) transverse eg waves on
the water surface,
Characteristics of a sound wave:
Frequency the number of complete waves produced in a second or the number of vibrations per
second is called frequency .The SI unit of frequency is Hertz holds s equal to 1 vibration per
second .The bigger unit of frequency is the kHz is equal to 1000Hz .
Time period :The time taken to complete one vibration is called the time period the SI unit of
time period is seconds time period is denoted by ‘t’ the frequency of a wave is the reciprocal of
1
the time period. v=
t
Amplitude :The maximum displacement of the particle of the medium from their original
undisturbed position is called amplitude of the wave .
Pitch: The pitch of a sound depends on the frequency of that sound .
Sound
Speed of sound:v=λ/t
Reflection of sound:Like light sound also bounces back when it falls on hard surface, it was
called reflection of sound. The laws of reflection of light are also obeyed in the reflection of
sound
Echo: Echo: In bigger monuments and in large empty halls you can hear reflections of your
sound after you speak something. This effect is known as echo. The sensation of sound persists
in our brain for 0.1 seconds, so to hear echo the time difference between original sound and
reflected sound should be more than that.
As you know speed of sound in air is = 344 m/s And 344 x 0.1 = 34.4 metre
So, the minimum distance required to hear an echo from a reflecting wall or surface should be
half of 34.4, means it should be 17.2 metres.
Reverberation: Repeated reflections of sound results in persistence of sound and is called
reverberation.Following instruments use this property of sound:Megaphones, Shehanais,
Trumpets, Stethoscope,Curved dome of concert halls
Range of Hearing in humans:
From 20 Hz to 20000 Hz, Sounds below 20 Hz are called infrasonic, Sounds above 20000 Hz are
Called ultrasonic
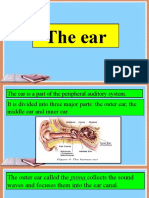
The ear is a sensitive organ of the human body. It
is mainly involved with detecting, transmitting and
transducing sound and maintaining a sense of Human Ear
balance is another important function of the human
ear. Human ear includes:
The outer ear or the visible part of the ear is
called the pinna.
Pinna collects sound from the surroundings.
Sound passes through a tube called an
auditory canal.
Eardrum (tympanic membrane) vibrates in
response to incident sound waves.
Vibrations are amplified and transmitted
further by three bones hammer, anvil and
stirrup in the middle ear to the inner ear.
In the inner ear, cochlea converts pressure
signals into electrical signals.
Electrical signals are transmitted by the
auditory nerve to the brain for
interpretation.
You might also like
- Class 9 Science Sound NCERT Notes PDFDocument8 pagesClass 9 Science Sound NCERT Notes PDFSulveNo ratings yet
- Sound Class 8Document5 pagesSound Class 8Sanjib MandalNo ratings yet
- Class 2 Spell BeeDocument48 pagesClass 2 Spell Beehweta173100% (5)
- English Arihant CBSE Class 10 Term 2 WWW - EXAMSAKHA.IN PDFDocument208 pagesEnglish Arihant CBSE Class 10 Term 2 WWW - EXAMSAKHA.IN PDFDevang Rane100% (5)
- SoundDocument28 pagesSoundKunal100% (1)
- List of Indian Standard Code For Civil and Structural Works PDFDocument148 pagesList of Indian Standard Code For Civil and Structural Works PDFKalipada Sen100% (1)
- Chemistry For Engineers REVIEWEEERDocument26 pagesChemistry For Engineers REVIEWEEERJames Philip Relleve100% (5)
- Sound PDFDocument23 pagesSound PDFOmer KaleemNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument7 pagesSoundTatenda ChirobeNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Question Bank Exam Guru LEARN VIBRANTDocument232 pagesClass 10 Social Science Term 2 Question Bank Exam Guru LEARN VIBRANThweta173100% (1)
- What is SoundDocument6 pagesWhat is SoundRavi Mehroliya100% (2)
- g9 Tle q3 Module 8 9 Week 5 6 Tech DraftDocument18 pagesg9 Tle q3 Module 8 9 Week 5 6 Tech Draftesller50% (2)
- GIS in Physical PlanningDocument7 pagesGIS in Physical PlanningGianni GorgoglioneNo ratings yet
- BNCA Architectural AcousticsDocument35 pagesBNCA Architectural AcousticsSakshi DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Science Class 9 Notes SoundDocument4 pagesScience Class 9 Notes SoundsonamalhotrakukNo ratings yet
- Sound Engineering FundamentalsDocument10 pagesSound Engineering FundamentalsRajnish AnandNo ratings yet
- Acoustics - Module 1Document40 pagesAcoustics - Module 1Ashna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Formation Damage and Horizontal WellsDocument14 pagesFormation Damage and Horizontal WellsAdhi100% (1)
- Sound Chapter of Class-9Document21 pagesSound Chapter of Class-9whitedevilm.k444No ratings yet
- SOUNDDocument4 pagesSOUNDHitesh kalraNo ratings yet
- 2312221519049139Document4 pages2312221519049139Shriya SNo ratings yet
- Propagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Document4 pagesPropagation-of-Sound-Waves 2Piyush RoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 SoundDocument10 pagesChapter 11 Soundkhushoodevi760No ratings yet
- Ch 12 Sound 1Document38 pagesCh 12 Sound 1amitvairagade32351No ratings yet
- Ound NotesDocument5 pagesOund Notesmokshithakapoor657No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 SOUND WAVESDocument10 pagesChapter 12 SOUND WAVESakash vermaNo ratings yet
- Sound Physics NotesDocument8 pagesSound Physics NotesWani Minham123No ratings yet
- SoundDocument5 pagesSoundAvinash MansukNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument2 pagesSoundthehonouredone1234No ratings yet
- The Physics of Sound, Music, and HearingDocument5 pagesThe Physics of Sound, Music, and HearingSun Hee ParkNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Sound WavesDocument44 pagesLesson 7 Sound WaveskhiananoribsNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch12 SoundDocument10 pages09 Science Notes Ch12 SoundHarshJangidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Physics Sound - HandwrittenDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Physics Sound - Handwrittenbr tiwariNo ratings yet
- Phạm Bùi Thảo Vy - HS186176Document5 pagesPhạm Bùi Thảo Vy - HS186176hung6d5No ratings yet
- Sound IXDocument35 pagesSound IXarpankrishna739No ratings yet
- Acoustic Sound and Human EarDocument26 pagesAcoustic Sound and Human EarEmmanuel EhuronNo ratings yet
- What is Sound? Understanding Sound Waves and Their PropertiesDocument6 pagesWhat is Sound? Understanding Sound Waves and Their PropertiesHina SharmaNo ratings yet
- Sound NotesDocument5 pagesSound NotesumaNo ratings yet
- AV Production Document on Sound Properties and ComponentsDocument38 pagesAV Production Document on Sound Properties and ComponentsFasihahIdrisNo ratings yet
- NCERT CBSE Notes for Class 9 Science physics Chapter 12 SOUNDDocument6 pagesNCERT CBSE Notes for Class 9 Science physics Chapter 12 SOUNDDark DevilNo ratings yet
- Class-9 ch-11 Sci NotesDocument15 pagesClass-9 ch-11 Sci NotesShifNo ratings yet
- RBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 10 Sound – RBSE GuideDocument3 pagesRBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 10 Sound – RBSE GuideAlpine AcademiaNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument4 pagesSoundmahammalik20142023No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Behaviour of Sound: Submitted by Chitra Rana 5 TH SemDocument18 pagesAssignment 1 Behaviour of Sound: Submitted by Chitra Rana 5 TH SemPrateekNo ratings yet
- Ear and Properties of SoundDocument15 pagesEar and Properties of SoundAnaliza ToledoNo ratings yet
- The Nature and Perception of SoundDocument21 pagesThe Nature and Perception of Soundsheila louiseNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Notes M1Document11 pagesAcoustics Notes M1ANNA PAULA R. DULAYNo ratings yet
- Sound Plays An Important Role in Our Daily LifeDocument5 pagesSound Plays An Important Role in Our Daily Lifevaishali14051980No ratings yet
- Acoustics 1 (Sound Theory)Document21 pagesAcoustics 1 (Sound Theory)bishal dasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SOUNDDocument18 pagesChapter 3 SOUNDGaliasis Akoualefo nkefackNo ratings yet
- 12. SoundDocument16 pages12. SoundRSNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Sound WaveDocument27 pagesLesson 4 - Sound WaveElijah AlcorezaNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Acoustic and Ultrasonic WavesDocument29 pagesUnit-4 Acoustic and Ultrasonic WavesSP.TrushadNo ratings yet
- Ch-13. SOUNDDocument6 pagesCh-13. SOUNDNiha KausarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound NotesDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 12 Sound Notessanthoshsabarish4No ratings yet
- SoundDocument5 pagesSoundOnlymexxNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Module FundamentalsDocument33 pagesAcoustics Module FundamentalsmariyaNo ratings yet
- 18 ARC 74 ACOUSTICSDocument25 pages18 ARC 74 ACOUSTICSsuryaa ksNo ratings yet
- Vũ Trư NG GiangDocument4 pagesVũ Trư NG Gianghung6d5No ratings yet
- Wave Motion: A Concise GuideDocument6 pagesWave Motion: A Concise GuideAKHILSTNo ratings yet
- Sound & AudioDocument37 pagesSound & Audioapi-27285803No ratings yet
- AR315 Topic2 ULOa ALOCELJA, L.Document5 pagesAR315 Topic2 ULOa ALOCELJA, L.Lourainnefaith aloceljaNo ratings yet
- Sound Formula SheetDocument3 pagesSound Formula SheetimkushofficialNo ratings yet
- 7 SoundDocument14 pages7 Soundvincesee85No ratings yet
- Sound Waves MYP4Document9 pagesSound Waves MYP4ehan.ilrnestersNo ratings yet
- Acoustic EnergyDocument3 pagesAcoustic EnergyHerjay Racho SulapasNo ratings yet
- Atomic Energy Central School-2, Mumbai PT-2 EXAMINATION 2021-22Document1 pageAtomic Energy Central School-2, Mumbai PT-2 EXAMINATION 2021-22hweta173No ratings yet
- Xth Class Science Exam Questions on Atoms, Electricity, ReproductionDocument2 pagesXth Class Science Exam Questions on Atoms, Electricity, Reproductionhweta173No ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper Class - X Session - 2021-22 Term 1 Subject-Mathematics (Standard) 041Document7 pagesSample Question Paper Class - X Session - 2021-22 Term 1 Subject-Mathematics (Standard) 041hweta173No ratings yet
- Class 10 SST, PT 2 (2022)Document4 pagesClass 10 SST, PT 2 (2022)hweta173No ratings yet
- Grade X English Term 2 Pre Board IDocument4 pagesGrade X English Term 2 Pre Board Ihweta173No ratings yet
- Class X-Science - PT3-February 2022Document3 pagesClass X-Science - PT3-February 2022hweta173No ratings yet
- Cbse Class 10 Introduction To Financial Markets Set 4 Compartment Annual Question Paper 2018 PDF Question Papers vqp2019.htmlDocument8 pagesCbse Class 10 Introduction To Financial Markets Set 4 Compartment Annual Question Paper 2018 PDF Question Papers vqp2019.htmlhweta173No ratings yet
- 19194class 10 PBDocument16 pages19194class 10 PBhweta173No ratings yet
- PW Handbook For Term 2 - Handbook - FinalDocument36 pagesPW Handbook For Term 2 - Handbook - FinalSomil GabaNo ratings yet
- 92 Introduction To Financial MarketsDocument7 pages92 Introduction To Financial Marketshweta173No ratings yet
- Introduction to Financial MarketsDocument8 pagesIntroduction to Financial Marketshweta173No ratings yet
- Your Child's Communication Skills CourseDocument7 pagesYour Child's Communication Skills Coursehweta173No ratings yet
- ..International School: Periodic Test - 2Document4 pages..International School: Periodic Test - 2hweta173No ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial MarketsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Financial Marketshweta173No ratings yet
- EVS PlantDocument2 pagesEVS Planthweta173No ratings yet
- ECAT STD 2 Sample Question PaperDocument7 pagesECAT STD 2 Sample Question PaperVinay Jindal0% (1)
- 815maths Sample PaperDocument7 pages815maths Sample Paperhweta173No ratings yet
- STD 2 SyllabusDocument6 pagesSTD 2 Syllabushweta173No ratings yet
- STD 2 SyllabusDocument1 pageSTD 2 Syllabushweta173No ratings yet
- STD 2 SyllabusDocument1 pageSTD 2 Syllabushweta173No ratings yet
- STD 2 Sample Question PaperDocument6 pagesSTD 2 Sample Question Paperhweta173100% (1)
- CBSE Class 10 MathsDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 10 MathsLokendra kumarNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - STD 2: Formal GrammarDocument1 pageSyllabus - STD 2: Formal Grammarhweta173No ratings yet
- STD 2 SyllabusDocument6 pagesSTD 2 Syllabushweta173No ratings yet
- Maths Class 10 Very Important QuestionsDocument12 pagesMaths Class 10 Very Important QuestionsmeowNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Qs Paper 2019 Set 3 PDFDocument11 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Qs Paper 2019 Set 3 PDFLokendra kumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Qs Paper 2019 Set 4Document11 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Qs Paper 2019 Set 4ᏗᎩᏬᏕᏂ ᎷᏋᏂᏒᏗNo ratings yet
- Ei Suender PLCopen V05 PicsDocument21 pagesEi Suender PLCopen V05 PicsLilamala LilavelikaNo ratings yet
- Reported To Another Basis ToleranceDocument15 pagesReported To Another Basis ToleranceYuliyanti YuliyantiNo ratings yet
- Mintzberg Strategic Thinking vs PlanningDocument2 pagesMintzberg Strategic Thinking vs PlanningRoshankumar BalasubramanianNo ratings yet
- MARE3Document42 pagesMARE3chuchu maneNo ratings yet
- Manyk Web Sharpening ActionDocument7 pagesManyk Web Sharpening ActionkbebakisNo ratings yet
- MulticollinearityDocument2 pagesMulticollinearityDipsubhra Chakraborty100% (1)
- Computer Literacy: Hardware & Software ClassificationDocument11 pagesComputer Literacy: Hardware & Software ClassificationAmadoUsla100% (1)
- Determination of Mechanical Properties For Cement-Treated Aggregate BaseDocument54 pagesDetermination of Mechanical Properties For Cement-Treated Aggregate BaseMarloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology: Joher B. Mendez, JR., R.N., M.DDocument65 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy and Physiology: Joher B. Mendez, JR., R.N., M.DJoherNo ratings yet
- Pci 22 PDFDocument322 pagesPci 22 PDFAnonymous pcNdMpNENo ratings yet
- EOWR CV-5X Combine 08may2008Document85 pagesEOWR CV-5X Combine 08may2008Them Bui XuanNo ratings yet
- Zonestar GuideDocument59 pagesZonestar GuidepepeNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Cashew Nut Shell Resin With Kenaf Natural Fiber Composite Treated and UntreatedDocument5 pagesAnalysis of Cashew Nut Shell Resin With Kenaf Natural Fiber Composite Treated and UntreatedEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Users Manual - EJX-A Series HART 5 - HART 7 Communication PDFDocument96 pagesUsers Manual - EJX-A Series HART 5 - HART 7 Communication PDFjashkishoreNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Modern ProcessorsDocument52 pagesUnit 1 Modern ProcessorsSudha PalaniNo ratings yet
- H5-311E Extracts Newsletter SMS MevacDocument36 pagesH5-311E Extracts Newsletter SMS MevacKetnipha SukwannawitNo ratings yet
- Kerosene Isosiv Process For Production of Normal Paraffins: Stephen W. SohnDocument6 pagesKerosene Isosiv Process For Production of Normal Paraffins: Stephen W. SohnAshraf SeragNo ratings yet
- The Cost of Uncertainty For Nitrogen Fertilizer Management: A Sensitivity AnalysisDocument8 pagesThe Cost of Uncertainty For Nitrogen Fertilizer Management: A Sensitivity AnalysisSha-ReeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationDocument19 pagesCambridge Secondary 1 Checkpoint: Cambridge Assessment International EducationArsen RahymbekovNo ratings yet
- 01 To UTBK Full Version (SAINTEK) - Bahasa InggrisDocument8 pages01 To UTBK Full Version (SAINTEK) - Bahasa Inggrissepia wulandariNo ratings yet
- Relational Database: Storing and Manipulating RecordsDocument34 pagesRelational Database: Storing and Manipulating RecordsaNo ratings yet
- Module-4: Numerical Differentiation and IntegrationDocument22 pagesModule-4: Numerical Differentiation and Integrationvenkat sathwik kethepalliNo ratings yet
- GR12 Business Finance Module 9-10Document7 pagesGR12 Business Finance Module 9-10Jean Diane JoveloNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Validation-Repassa PatrickDocument12 pagesCleaning Validation-Repassa PatrickIin Tirta SunartaNo ratings yet
- Heat Technology: Chapter 10 Section 4Document23 pagesHeat Technology: Chapter 10 Section 4thegedusNo ratings yet