Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Functions of Nucleic Acids
General Functions of Nucleic Acids
Uploaded by
Ebram LouisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Functions of Nucleic Acids
General Functions of Nucleic Acids
Uploaded by
Ebram LouisCopyright:
Available Formats
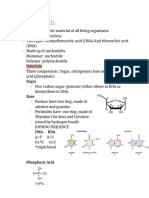
The main function of nucleic acids is to store and transmit genetic information and use
that information to direct the synthesis of new protein. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) is the
permanent storage place for genetic information in the nucleus of a cell. DNA controls the
synthesis of RNA (ribonucleic acid). RNA transmits genetic information from DNA to the
protein synthesizers in the cell. RNA is also responsible for directing the production of the
new protein by transmitting the genetic information to the protein building structures. The
nucleotide ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is closely related to DNA and RNA, is
the short-term energy storage for all life processes. The function of the sequence of
bases (adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine) in the backbone of DNA determine what
proteins are being synthesized and in what order (note that in RNA, thymine is replaced
by uracil). (Di Giuseppe , M.) The function of the double helix formation of DNA
molecules is to ensure that no disorders occur if genetic information is lost or damaged.
Examples of disorders related to damaged or lost genetic information are Down’s
Syndrome and Sickle Cell Anemia. (Kotz, J.)
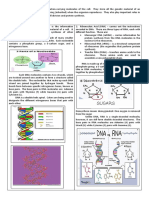
The following illustrates the chemical structure of the five types of nitrogenous bases
mentioned above:
(M.J. Farabee)
Important aspects of nucleic acid functions (summarized):
Functions of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid):
-DNA is a permanent storage place for genetic information.
-DNA controls the synthesis of RNA (ribonucleic acid).
-The sequence of nitrogenous bases in DNA determines the protein development in new
cells.
-The function of the double helix formation of DNA is to ensure that no disorders occur.
This is because the second identical strand of DNA that runs anti-parallel to the first is a
back up in case of lost or destroyed genetic information. Ex. Down’s Syndrome or Sickle
Cell Anemia.
Functions of RNA (ribonucleic acid):
-RNA is synthesized by DNA for the transportation of genetic information to the protein
building apparatus in the cell.
-RNA also directs the synthesis of new proteins using the genetic information it has
transported.
-mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) is used to transfer genetic information through
plasma membranes
Functions of Adenosine Phosphates:
-The nucleotide ATP (adenosine triphosphate) is the short-term energy storage for all
living organisms.
-cAMP (cyclic adenosine monophosphate) is a messenger in hormone regulation
-Nucleotide derivatives such as NAD + (nictinamide adenine dinucleotide) is used as a
coenzyme in photosynthesis.
You might also like
- Fats and Water Soluble VitaminsDocument31 pagesFats and Water Soluble VitaminshafizahhoshniNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument17 pagesAmino AcidsSiddharth Rohilla100% (2)
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- Study Dna DnaDocument45 pagesStudy Dna DnaKrystel BeltranNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFDocument55 pagesNucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis PDFAleine Leilanie Oro0% (1)
- The Importance of DNA and RNADocument13 pagesThe Importance of DNA and RNAJamieNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument50 pagesDNA StructureAngelo LucindoNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins & FatsDocument57 pagesBiological Molecules: Carbohydrates, Proteins & FatsSanthoshNo ratings yet
- Heredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA InformationDocument45 pagesHeredity - How A Protein Is Made Using DNA Informationkath chandriaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in Plants-NotesDocument6 pagesRespiration in Plants-NotesAnirudh KhannaNo ratings yet
- DR Linda Molecular BiosDocument73 pagesDR Linda Molecular BiosValency BathoNo ratings yet
- Nucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidDocument60 pagesNucleoprotein & Nucleic AcidWillar Deanson Navarro100% (1)
- Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument30 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular BiologyAlthea Mandal100% (1)
- Fat Soluble VitaminsDocument99 pagesFat Soluble VitaminsKamran ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument29 pagesStructure and Function of DNAMatthew Justin Villanueva GozoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LipidsDocument19 pagesChemistry of LipidsJohn Rick Orine100% (1)
- How Cells Work CompilationDocument18 pagesHow Cells Work CompilationJocelyn Diaz AbangNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidDocument88 pagesNucleic AcidJoyce Jimenez100% (1)
- Nucleic Acids: Biology Study GuideDocument2 pagesNucleic Acids: Biology Study GuideLaura MeowNo ratings yet
- Lesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2Document7 pagesLesson Discussion: Self-Learning Module (SLM) General Biology 2almafebe caselNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetDocument10 pagesLesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetEnriquez, Hannah Roniella R.No ratings yet
- DNA Into ChromosomesDocument10 pagesDNA Into Chromosomesu20036929No ratings yet
- The Role of RNA DNA and PROTEIN in The Transmission of TraitsDocument21 pagesThe Role of RNA DNA and PROTEIN in The Transmission of TraitsrebugiocosmeNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis 2023Document24 pagesProtein Synthesis 2023Arlene SantosNo ratings yet
- NucleotideDocument5 pagesNucleotideReign Aiken M. LaraNo ratings yet
- Types of Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTypes of Nucleic AcidsJomari Alipante100% (1)
- AsomaDocument45 pagesAsomaTetra HedronNo ratings yet
- Coursenotesdomain 4 InformationDocument29 pagesCoursenotesdomain 4 Informationapi-300668314No ratings yet
- The Role of Nucleic Acids in HeredityDocument4 pagesThe Role of Nucleic Acids in HeredityRaluca GladcencoNo ratings yet
- Proteins 123Document43 pagesProteins 123agnasvynlutaoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of DNADocument27 pagesStructure and Function of DNAHaniya RijaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of Dna and Rna: Jon Paul M. Reyes, RMT, MBA, MSMLS Program Chair College of Medical TechnologyDocument21 pagesStructure and Function of Dna and Rna: Jon Paul M. Reyes, RMT, MBA, MSMLS Program Chair College of Medical TechnologyRich Darlene Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAssignment No. 2Jane Valine BalinoNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesMolecular BiologyJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- Dogma GeneticDocument11 pagesDogma GeneticMarina Ivana MumpelNo ratings yet
- 471 - BCH 201-Lecture Note On WebDocument10 pages471 - BCH 201-Lecture Note On WebShaikh SalmanNo ratings yet
- UNIT5 Variation & Selection Chapters 16&17 NotesDocument30 pagesUNIT5 Variation & Selection Chapters 16&17 NotesMostafa A MansiNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiotechnology ReviewerPooten Helen LheaneNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid Functions and Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyDocument12 pagesNucleic Acid Functions and Central Dogma of Molecular BiologyJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document107 pagesLesson 3Christian CuevasNo ratings yet
- 2nd Bio AssgnmntDocument6 pages2nd Bio AssgnmntNitinmanubanshNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument5 pagesNucleic Acidsapi-308598460No ratings yet
- MBB425 Lecture 1 - COMPOSITION AND CHEMICAL STRUCTURE OF NUCLEIC ACIDS-Enoch 2019.09.03Document59 pagesMBB425 Lecture 1 - COMPOSITION AND CHEMICAL STRUCTURE OF NUCLEIC ACIDS-Enoch 2019.09.03EMMANUEL ABEL IMAHNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid STRUCTUREDocument5 pagesNucleic Acid STRUCTUREKalel SandovalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Genetics: BIO100 Sumaiya Afrin SohaDocument30 pagesIntroduction To Genetics: BIO100 Sumaiya Afrin SohaNafees Hasan Chowdhury100% (1)
- Bagong AlamatDocument11 pagesBagong Alamatmax delvalleNo ratings yet
- 2ndqbiotechweek5 7Document3 pages2ndqbiotechweek5 7Evefel Ruth Yparraguirre SanchezNo ratings yet
- Lect16 DnaDocument6 pagesLect16 DnaCrisJoy DiuyanNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids NotesDocument5 pagesNucleic Acids Notescherushii shiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Molecular GeneticsDocument53 pagesUnit 2. Molecular GeneticsRuben Ruiz MartinNo ratings yet
- Science Finals Reviewer: Nucleic Acid and Their Connection With Inheritance (E-Book Pages 261-262)Document5 pagesScience Finals Reviewer: Nucleic Acid and Their Connection With Inheritance (E-Book Pages 261-262)Mareck VerdanNo ratings yet
- Biol313 M5Document2 pagesBiol313 M5Fares SamirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. Nucleic Acid and Synthesis ProteinDocument32 pagesChapter 6. Nucleic Acid and Synthesis ProteinratuadhwaNo ratings yet
- Virology Assignment0Document11 pagesVirology Assignment0Affan sageNo ratings yet
- Genetics 1Document7 pagesGenetics 1Kaye CampbellNo ratings yet
- Genetics NotesDocument7 pagesGenetics NotesTiffany BheaNo ratings yet
- AFF1 - DNA-struktur Dan Fungsi-2009Document12 pagesAFF1 - DNA-struktur Dan Fungsi-2009Afiyan KristionoNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma: Dna ReplicationDocument18 pagesCentral Dogma: Dna ReplicationAkhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Structure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleDocument44 pagesStructure of DNA Science Presentation in Light Blue Green Lined StyleGxmini playsNo ratings yet
- THE Geneticists: Grade 11 St. John BoscoDocument24 pagesTHE Geneticists: Grade 11 St. John Boscojason balmasNo ratings yet
- Group 4 PresentationDocument14 pagesGroup 4 PresentationJanrei Devilla TeNo ratings yet
- D NA Vs RNA: A Comparison in Structure and FunctionDocument3 pagesD NA Vs RNA: A Comparison in Structure and FunctionHossam GamilNo ratings yet
- Bio ReviewerDocument5 pagesBio ReviewerFaye Lianne MaderoNo ratings yet
- Gene CloningDocument5 pagesGene CloningAriana LeeNo ratings yet
- DNA and Proteins Doodle Notes 2Document10 pagesDNA and Proteins Doodle Notes 2Leila BeyyoudhNo ratings yet
- Classroom Practice III: Bioenergetics Bioenergetics ExercisesDocument4 pagesClassroom Practice III: Bioenergetics Bioenergetics ExercisesValentina CretuNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation Glycolysis: 2 Phosphates Krebs/citric/TCA Cycle: 1 PhosphateDocument17 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation Glycolysis: 2 Phosphates Krebs/citric/TCA Cycle: 1 PhosphatereeNo ratings yet
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesDocument9 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2015 SeriesNerminNo ratings yet
- Technology and Innovation in Education (GROUP 12) : Topic: Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument19 pagesTechnology and Innovation in Education (GROUP 12) : Topic: Mechanism of Enzyme Actionfadzlin84No ratings yet
- ProlpDocument25 pagesProlpherryNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules ws2Document2 pagesMacromolecules ws2Lorraine Jumaquio RonquilloNo ratings yet
- Ds83-Replication Review Formative AssessmentDocument4 pagesDs83-Replication Review Formative Assessmentapi-110789702No ratings yet
- Test On Molecular Biology NEETDocument4 pagesTest On Molecular Biology NEETSadananda KumbhakarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 23 - EicosanoidsDocument22 pagesLecture 23 - Eicosanoidsapi-3703352100% (1)
- Test I. Puzzle Protein: Activity No. 4.1Document2 pagesTest I. Puzzle Protein: Activity No. 4.1Osas OsasNo ratings yet
- Classification of EnzymeDocument11 pagesClassification of Enzymeshamit big SAMNo ratings yet
- Full Download Biochemistry A Short Course 2nd Edition Tymoczko Test BankDocument6 pagesFull Download Biochemistry A Short Course 2nd Edition Tymoczko Test Bankgelnernita23741372100% (33)
- Mibeis45 GPT (Alt) - LQ 2017Document4 pagesMibeis45 GPT (Alt) - LQ 2017labo chetaibiNo ratings yet
- 4 End of Chapter QuestionsDocument2 pages4 End of Chapter QuestionsSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- 7 DNA DMG and RepairDocument9 pages7 DNA DMG and RepairSalaarNo ratings yet
- Julie Bui - Blood Typing LabDocument7 pagesJulie Bui - Blood Typing Labapi-522650514No ratings yet
- SKRIPSI PENGARUH BUBUK DAUN PEPAYA Caric PDFDocument77 pagesSKRIPSI PENGARUH BUBUK DAUN PEPAYA Caric PDFsalsaNo ratings yet
- Vitamin BasicsDocument102 pagesVitamin Basicslouise kartikaNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument2 pagesAmino AcidsMichelle FactoNo ratings yet
- Michaelis-Menten Type Kinetics: E S) ES) K K K E S) ES)Document2 pagesMichaelis-Menten Type Kinetics: E S) ES) K K K E S) ES)fintastellaNo ratings yet
- Ch18 - Amino Acid Oxidation Production of UreaDocument50 pagesCh18 - Amino Acid Oxidation Production of UreaSalma KhoirunnisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18: Anticancer Agents (Part B) : Patrick: An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 3eDocument65 pagesChapter 18: Anticancer Agents (Part B) : Patrick: An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 3eHussein Al-jmrawiNo ratings yet