Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calculating sample size factors and their effects
Uploaded by
Hazem El SayedOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calculating sample size factors and their effects
Uploaded by
Hazem El SayedCopyright:
Available Formats
1)
aeor
The lower the tolerable misstatement, the lar-
Tolerable misstatement Inverse ger the sample
Allowable risk of incorrect accep- Inverse The higher the allowable risk of incorrect ac-
Allowable Risk of Incorrect Acceptance
ceptance, the lower the expected reliability,
I
The allowable risk of incorrect acceptance can be calculated based on other factors
tance and the smaller the sample
1) Determine acceptable audit risk (AR)
Expected amount of 2)
misstatement Direct
Measure inherent risk (IR) The higher the expected amount of misstate-
3) Assess level of control risk (eR)
4) Use AR, IR, ment,acceptable
& eR to calculate the larger the sample
level of detection risk
(OR)
AR + (JR x eR)
Assessed level of control risk
= ORDirect The higher the assessed level of control risk,
the larger the sample
5) At various levels of OR, measure
Direct the allowable riskthe
The larger of population,
incorrect acceptance
the larger the sam-
Population size Allowable level of incorrect acceptance = AR + (IR
pie size x eR x OR)
Example
If AR = 5%, IR = 100%, & eR is assessed at 50%
OR = .05 + (1.00 x .50) = .10 or 10%
If OR is set at level
Allowable 30% of incorrect acceptance = .05 (1.00 x .50 x .30) = .333 or 33 1/3%
Focus on
Audit Sampling - Module 5 242
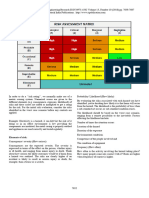
Calculating Sample Size
Various factors affgGt amplg sze
Relationship to
Ft sample size Effect
Focus on
Audit Sampling - Module 5 243
You might also like
- What Is Measurement RiskDocument4 pagesWhat Is Measurement RiskhoussNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument3 pagesDocxyvonneberdosNo ratings yet
- 1bootstrap Control Charts in Monitoring Value at Risk in InsuranceDocument11 pages1bootstrap Control Charts in Monitoring Value at Risk in InsuranceRadia AbbasNo ratings yet
- The Fraud Audit: Responding to the Risk of Fraud in Core Business SystemsFrom EverandThe Fraud Audit: Responding to the Risk of Fraud in Core Business SystemsNo ratings yet
- CONTROL RISKS WITH HIRARCDocument15 pagesCONTROL RISKS WITH HIRARCAwatifNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Determining The Extent of TestingDocument3 pagesChapter 11 - Determining The Extent of TestingJean GarciaNo ratings yet
- McaDocument9 pagesMcaamit singhNo ratings yet
- Important FormulasDocument1 pageImportant FormulasAli AadilNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment & Statistical Sampling in AuditDocument21 pagesRisk Assessment & Statistical Sampling in Auditaymen marzoukiNo ratings yet
- ЛЕК 3 РИЗИК_en-USDocument41 pagesЛЕК 3 РИЗИК_en-USsva1.1nbNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Risk Calculation in Cybersecurity: The Value of Quantifying RiskDocument6 pagesQuantitative Risk Calculation in Cybersecurity: The Value of Quantifying RiskJabar KholiqNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory 2nd Sem PrelimsDocument6 pagesAuditing Theory 2nd Sem PrelimsAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Us Faa RBSM AriaDocument7 pages1.2 Us Faa RBSM AriaAhmad Aiman Mohd NasirNo ratings yet
- Step 5 and 6Document6 pagesStep 5 and 6Diana Rose MitoNo ratings yet
- ISPE Indo Oct 2014 - Intro To QRM Oct - Linda AmbroseDocument46 pagesISPE Indo Oct 2014 - Intro To QRM Oct - Linda AmbrosePackaging Development BernofarmNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1B Risk Based AuditDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 1B Risk Based AuditLydelle Mae CabaltejaNo ratings yet
- AT - Chapter 9-Notes - Part 4Document2 pagesAT - Chapter 9-Notes - Part 4hoxhiiNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Techniques & FSA: "New Marine Fuels & Safety Risk"Document46 pagesRisk Management Techniques & FSA: "New Marine Fuels & Safety Risk"홍인기No ratings yet
- Attribute Sampling: Calculating Sample SizeDocument2 pagesAttribute Sampling: Calculating Sample SizeHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Compliance Report of Jajpur Oct 20 To Mar 21 1Document107 pagesCompliance Report of Jajpur Oct 20 To Mar 21 1WarrenNo ratings yet
- Auditing Notes - Chapter 5Document14 pagesAuditing Notes - Chapter 5Future CPA75% (4)
- Risk Management Approach OverviewDocument9 pagesRisk Management Approach OverviewsalmanNo ratings yet
- Risk Management ProcessDocument4 pagesRisk Management ProcessMelody M ChocolateNo ratings yet
- SCAP-Presentation at CsChE 2003Document51 pagesSCAP-Presentation at CsChE 2003api-3733731100% (1)
- Audit sampling (1983); Audit and accounting guide_Document4 pagesAudit sampling (1983); Audit and accounting guide_augustokita5No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment ProcedureDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment ProcedureDukhidilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 AnsDocument7 pagesChapter 11 AnsDave Manalo0% (1)
- Risk Assessment Worksheet BlankDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment Worksheet BlankisolongNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment and Materiality: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument38 pagesRisk Assessment and Materiality: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinZi VillarNo ratings yet
- AUDIT RISK (4)Document19 pagesAUDIT RISK (4)John diggleNo ratings yet
- 2.3.2.3 Hazard Assessment NotesDocument6 pages2.3.2.3 Hazard Assessment Noteskit_mak_5No ratings yet
- AUDIT II CH-1 eDocument92 pagesAUDIT II CH-1 eQabsoo FiniinsaaNo ratings yet
- CBOKDocument33 pagesCBOKvinodNo ratings yet
- Factors Influencing Compliance Test Sample SizeDocument11 pagesFactors Influencing Compliance Test Sample SizeJi YuNo ratings yet
- Risk Measurement: Frequency, Severity and ProbabilityDocument37 pagesRisk Measurement: Frequency, Severity and ProbabilityVirgilio Jay CervantesNo ratings yet
- AACONAPPS1 Reviews Audit Risk Model and Risk-Based ApproachDocument15 pagesAACONAPPS1 Reviews Audit Risk Model and Risk-Based ApproachClarisse Angela PostreNo ratings yet
- Risk Identification and MeasurementDocument14 pagesRisk Identification and Measurementyoshiharu.harano1726No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 To 29Document114 pagesChapter 11 To 29JadeNo ratings yet
- Predicting and assessing LHD machine breakdowns using FMEADocument8 pagesPredicting and assessing LHD machine breakdowns using FMEAjulio beniscelliNo ratings yet
- AT - Chapter 9-Notes - Part 3Document3 pagesAT - Chapter 9-Notes - Part 3hoxhiiNo ratings yet
- Ijaerv13n10 56-14Document1 pageIjaerv13n10 56-14nazasraf2012No ratings yet
- Biltrite Bicycles Inc. Equipment AuditDocument2 pagesBiltrite Bicycles Inc. Equipment Auditredearth2929No ratings yet
- Risk Analysis and Statistical Sampling in Audit - Methodology - Comptroller and Auditor General of IndiaDocument13 pagesRisk Analysis and Statistical Sampling in Audit - Methodology - Comptroller and Auditor General of IndiaIsmailNo ratings yet
- Audit Sample 2Document5 pagesAudit Sample 2Samantha IslamNo ratings yet
- Risk Based Inspection OverviewDocument51 pagesRisk Based Inspection Overviewmurali100% (1)
- Risk Assessment & Control Module 3Document38 pagesRisk Assessment & Control Module 3Marvin ReggieNo ratings yet
- LS 2.80B - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementDocument3 pagesLS 2.80B - PSA 315 - Identifying and Assessing The Risk of Material MissstatementSkye LeeNo ratings yet
- Semi Quantitative & Quantitative Risk AssessmentDocument83 pagesSemi Quantitative & Quantitative Risk Assessmentstefani laurenzaNo ratings yet
- Audit Risk Factors and ModelDocument10 pagesAudit Risk Factors and ModelpaponNo ratings yet
- AT 209 Handout Identifying and Assessing Risks of Material Misstatement (ROMM)Document7 pagesAT 209 Handout Identifying and Assessing Risks of Material Misstatement (ROMM)Jai BacalsoNo ratings yet
- CH - 1 - Materiality and Audit Risk (3 of 3)Document14 pagesCH - 1 - Materiality and Audit Risk (3 of 3)mamse08No ratings yet
- SamplingDocument16 pagesSamplingJamealla SabasNo ratings yet
- HIRADocument14 pagesHIRAGobindaSahu100% (2)
- Instructions For Using OHS Risk Assessment Template: Only Complete The Unshaded Cells All Others Are Locked 1. 2Document4 pagesInstructions For Using OHS Risk Assessment Template: Only Complete The Unshaded Cells All Others Are Locked 1. 2Abdelrahman N. AliNo ratings yet
- MATERIALITY AND RISK: KEY CONCEPTS FOR THE AUDITDocument48 pagesMATERIALITY AND RISK: KEY CONCEPTS FOR THE AUDITcarter PadNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AssesmentDocument189 pagesChemical Process Quantitative Risk Assesmentjfjd6889No ratings yet
- Risk Assessment TemplateDocument183 pagesRisk Assessment TemplateAkeem RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Contracts Module Multiple Choice AnswersDocument3 pagesContracts Module Multiple Choice AnswersHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Module 22 F Deral Sec Rities Cts and Antitrust La WDocument2 pagesModule 22 F Deral Sec Rities Cts and Antitrust La WHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Module 22 Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust Law: A. Securities Act ofDocument2 pagesModule 22 Federal Securities Acts and Antitrust Law: A. Securities Act ofHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Contracts Module SummaryDocument2 pagesContracts Module SummaryHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Module 22 Federal Securities CTS D Antitrust L: A AN AWDocument2 pagesModule 22 Federal Securities CTS D Antitrust L: A AN AWHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Professional Responsibilities and Accounting StandardsDocument2 pagesProfessional Responsibilities and Accounting StandardsHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Q: BANK-0001: AnswersDocument48 pagesQ: BANK-0001: AnswersHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Secured Transactions: MU IP E C Ce A Swe SDocument1 pageSecured Transactions: MU IP E C Ce A Swe SHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Scan 0006Document3 pagesScan 0006Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Form - 8582 PDFDocument3 pagesForm - 8582 PDFHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Module 21 Professional Responsibilities Multiple Choice AnswersDocument1 pageModule 21 Professional Responsibilities Multiple Choice AnswersHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Module 21 P Fessional Responsi I ES: RO B LitiDocument2 pagesModule 21 P Fessional Responsi I ES: RO B LitiHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Ac00unting 2Document45 pagesAc00unting 2Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Individ Income TaxDocument3 pagesIndivid Income TaxHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Form - 1040 - Schedule BDocument2 pagesForm - 1040 - Schedule BEl-Sayed FarhanNo ratings yet
- United States Estate (And Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax ReturnDocument31 pagesUnited States Estate (And Generation-Skipping Transfer) Tax ReturnHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Form - 1065 - Schedule - k1 PDFDocument2 pagesForm - 1065 - Schedule - k1 PDFHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Testing Application Control Activi Ies (Continued) : Auditing With Technology - Module 6Document1 pageTesting Application Control Activi Ies (Continued) : Auditing With Technology - Module 6Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Form 709 US Gift Tax ReturnDocument4 pagesForm 709 US Gift Tax ReturnHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Study Unit 20Document13 pagesStudy Unit 20Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- f1040 PDFDocument2 pagesf1040 PDFHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Infor - Mation Communication: Internal Control - Module 2Document1 pageInfor - Mation Communication: Internal Control - Module 2Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Net Income (Loss) Reconciliation For Corporations With Total Assets of $10 Million or MoreDocument3 pagesNet Income (Loss) Reconciliation For Corporations With Total Assets of $10 Million or MoreHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Subsequent Discovery of Facts: Evidence - Module 3Document1 pageSubsequent Discovery of Facts: Evidence - Module 3Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Assurance Provided Auditor: Responsibility To Detect Report Illegal Acts (Continued)Document1 pageAssurance Provided Auditor: Responsibility To Detect Report Illegal Acts (Continued)Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Responsibilities in An Infor - Mation Technology Environment: Audit Sampling - Module 5Document2 pagesResponsibilities in An Infor - Mation Technology Environment: Audit Sampling - Module 5Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Subsequent Events (Continued)Document1 pageSubsequent Events (Continued)Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Calculating sample size factors and their effectsDocument1 pageCalculating sample size factors and their effectsHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Audit Risk ComponentsDocument1 pageAudit Risk ComponentsHazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Working Papers (Continued) : Evidence - Module 3Document2 pagesWorking Papers (Continued) : Evidence - Module 3Hazem El SayedNo ratings yet
- Oaa Literature ReviewDocument29 pagesOaa Literature Reviewapi-290929891No ratings yet
- Master ThesisDocument91 pagesMaster ThesisDebabrat MishraNo ratings yet
- Risk and Return: Lessons From Market History: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinDocument24 pagesRisk and Return: Lessons From Market History: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwinfiza akhterNo ratings yet
- BS EN 62676 Standards For CCTV: Graded Requirements UnderDocument36 pagesBS EN 62676 Standards For CCTV: Graded Requirements UnderAzriNo ratings yet
- Brand Valuation Interbrand PDFDocument8 pagesBrand Valuation Interbrand PDFPazGonzaga100% (1)
- Release From Liability & Waiver of Claims KO Dance Co. (858) 228-6369Document1 pageRelease From Liability & Waiver of Claims KO Dance Co. (858) 228-6369api-147168701No ratings yet
- Infrastructure: Delhi-Mumbai Expressway To Spur NMPDocument5 pagesInfrastructure: Delhi-Mumbai Expressway To Spur NMPSuman DubeyNo ratings yet
- ELearning Manual Handling Tutorial V 9 - June 2015 - ACN Approved Feb 2016Document29 pagesELearning Manual Handling Tutorial V 9 - June 2015 - ACN Approved Feb 2016Ymon TuallaNo ratings yet
- Implementing Uganda's Rural Electrification ProjectDocument59 pagesImplementing Uganda's Rural Electrification ProjectRobert OtimNo ratings yet
- Hype Cycle For Life Insuranc2 2017 313260Document45 pagesHype Cycle For Life Insuranc2 2017 313260Dipak SahooNo ratings yet
- DOE - Vulnerability & Risk Assessment MethodologyDocument6 pagesDOE - Vulnerability & Risk Assessment Methodologyworld_ngineerNo ratings yet
- The National Academies PressDocument391 pagesThe National Academies PressDafny C. AroneNo ratings yet
- RA For Man Lift OperationDocument6 pagesRA For Man Lift Operationalla malikNo ratings yet
- ISO 14120 White Paper ProcterDocument10 pagesISO 14120 White Paper ProcterMarcoNo ratings yet
- Efsa Riscos em Carne de Aves 2012Document179 pagesEfsa Riscos em Carne de Aves 2012alberto.afonso3748No ratings yet
- UNIT 2:fundamentals of Business AnalyticsDocument30 pagesUNIT 2:fundamentals of Business AnalyticsJim AlabamaNo ratings yet
- Causes and Prevention of Injuries in Football (Soccer), Handball and Basketball at Adolescents Master - Thesis - Mladen - PranicDocument178 pagesCauses and Prevention of Injuries in Football (Soccer), Handball and Basketball at Adolescents Master - Thesis - Mladen - PranicMladen Pranić100% (1)
- PD Mhit Feb2024Document53 pagesPD Mhit Feb2024Aaron GumisNo ratings yet
- Environment Management NotesDocument12 pagesEnvironment Management NotesShreyansh JainNo ratings yet
- OS BBCW Level IDocument97 pagesOS BBCW Level IGudeta Jifara100% (7)
- NasaDocument2 pagesNasaThủy NguyênNo ratings yet
- Quality Center Certification Skill Test - Questions 1-390Document64 pagesQuality Center Certification Skill Test - Questions 1-390itsmeanup0% (1)
- CRR Deferred Tax Assets Risk Weight ReductionDocument2 pagesCRR Deferred Tax Assets Risk Weight ReductionCynical GuyNo ratings yet
- Trees Near BuildingsDocument13 pagesTrees Near BuildingsKemoHNo ratings yet
- RTCC-HS-FM-012 Waterproofing (Hotwork) (R.a.) Rev03Document15 pagesRTCC-HS-FM-012 Waterproofing (Hotwork) (R.a.) Rev03Hafiz M WaqasNo ratings yet
- Reinsurance Opinion Reinsurance Opinion: Actuarial FunctionDocument6 pagesReinsurance Opinion Reinsurance Opinion: Actuarial FunctionManuela ZahariaNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review Unit 1 Concept of DisasterDocument3 pagesPointers To Review Unit 1 Concept of DisasterRamona BaculinaoNo ratings yet
- NorthfieldDocument14 pagesNorthfieldKlaus Ørtoft MadsenNo ratings yet
- Greenonwall Business PlanDocument6 pagesGreenonwall Business PlanAmjad khanNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Simple STEAM: 50+ Science Technology Engineering Art and Math Activities for Ages 3 to 6From EverandSimple STEAM: 50+ Science Technology Engineering Art and Math Activities for Ages 3 to 6No ratings yet
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionFrom EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners: Simple Illustrated Guide to Discover with Practical Explanations the Paradoxes of the Life and Universe Reconsidering RealityRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- STEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8From EverandSTEM Labs for Physical Science, Grades 6 - 8Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- How to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasFrom EverandHow to Think Like a Lawyer--and Why: A Common-Sense Guide to Everyday DilemmasRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Nature Play Workshop for Families: A Guide to 40+ Outdoor Learning Experiences in All SeasonsFrom EverandNature Play Workshop for Families: A Guide to 40+ Outdoor Learning Experiences in All SeasonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Nature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningFrom EverandNature Preschools and Forest Kindergartens: The Handbook for Outdoor LearningRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenFrom EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenNo ratings yet
- The Big Book of Nature Activities: A Year-Round Guide to Outdoor LearningFrom EverandThe Big Book of Nature Activities: A Year-Round Guide to Outdoor LearningRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandThe Cell and Division Biology for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Cool Science Experiments for Kids | Science and Nature for KidsFrom EverandCool Science Experiments for Kids | Science and Nature for KidsNo ratings yet