0% found this document useful (0 votes)
271 views9 pagesUnderstand of The Topic: 1. Sales Quota and Its Importance 2. Case Study-NPL: Annual Planning
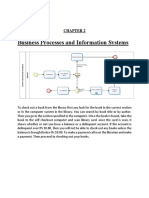
The document discusses sales quotas and provides a case study of National Pharmaceuticals Ltd.'s annual marketing planning process. It explains that sales quotas set goals for sales units like regions, branches, salespeople. Quotas can be based on sales volumes, expenses, profits, or activities. National Pharmaceuticals holds conferences to develop preliminary marketing plans, set targets for products to actively promote, and determine call norms and sales targets for salespeople and branches. The planning process involves contributions from various marketing departments.
Uploaded by
Shruti Suman MiddhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
271 views9 pagesUnderstand of The Topic: 1. Sales Quota and Its Importance 2. Case Study-NPL: Annual Planning
The document discusses sales quotas and provides a case study of National Pharmaceuticals Ltd.'s annual marketing planning process. It explains that sales quotas set goals for sales units like regions, branches, salespeople. Quotas can be based on sales volumes, expenses, profits, or activities. National Pharmaceuticals holds conferences to develop preliminary marketing plans, set targets for products to actively promote, and determine call norms and sales targets for salespeople and branches. The planning process involves contributions from various marketing departments.
Uploaded by
Shruti Suman MiddhaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd