Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chromosome Alignment. The Chromosomes Move
Chromosome Alignment. The Chromosomes Move
Uploaded by
Hamdan FatahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chromosome Alignment. The Chromosomes Move
Chromosome Alignment. The Chromosomes Move
Uploaded by
Hamdan FatahCopyright:
Available Formats
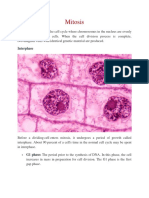
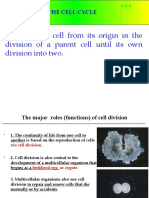
structures.
By G2
the centrioles have replicated to form daughter centrosomes.
(b) Prophase: centrosome migration. The centrosomes, each with a
daughter centriole, begin moving toward opposite poles of the cell.
The chromosomes begin to condense, appearing as long threads.
(c) Prometaphase: spindle formation. The nuclear envelope
fragments into small vesicles and spindle microtubules enter the
nuclear region. Chromosome condensation is completed; each
visible chromosome is composed of two chromatids held together
at their centromeres. Kinetochores at centromeres attach
chromosomes to spindle microtubules. (d) Metaphase:
chromosome alignment. The chromosomes move
toward the equator of the cell, where they become
aligned in the equatorial plane. (e) Anaphase:
chromosome separation. The two sister chromatids
separate into independent chromosomes. Each
chromosome, attached to a kinetochore microtubule,
moves toward one p
You might also like
- I. Binary FissionDocument4 pagesI. Binary FissionMarielle GeronimoNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument1 pageCell Divisionapi-237427942No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument7 pagesMitosisRishikesh BhintadeNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument32 pagesCell DivisionRhea GulayNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument1 pageCell CycleAndrey_gpNo ratings yet
- G2 of InterphaseDocument6 pagesG2 of Interphasekevin doeNo ratings yet
- Stages of Mitosis-E. SanaDocument2 pagesStages of Mitosis-E. SanaEvangelene Esquillo SanaNo ratings yet
- CN 6 BioDocument2 pagesCN 6 BioJanna PaduaNo ratings yet
- The Cell CycleDocument9 pagesThe Cell Cyclesalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- Unit 3 NotesDocument6 pagesUnit 3 NotesibtiNo ratings yet
- Interphase Prophase: ChromoDocument12 pagesInterphase Prophase: ChromoNkosi JupiterNo ratings yet
- Growth and Division of CellsDocument2 pagesGrowth and Division of CellsMargie OpayNo ratings yet
- Cycle CellDocument16 pagesCycle CellRohingya EnglishNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument6 pagesCell CycleRenzdy MejillaNo ratings yet
- SLK Sci8 Q4 W2Document18 pagesSLK Sci8 Q4 W2louisse veracesNo ratings yet
- CH 12 Online Study GuideDocument7 pagesCH 12 Online Study Guideюрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle: Mitosis & MeiosisDocument10 pagesCell Cycle: Mitosis & MeiosisdeepaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis and Sexual ReproductionDocument48 pagesMeiosis and Sexual Reproductionerdayu86100% (1)
- Lab Report BIoDocument3 pagesLab Report BIoAmy YayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 Part1Document62 pagesChapter8 Part1Glen MangaliNo ratings yet
- "Mitosis" (KEY) : Review Questions - Chapter 9Document7 pages"Mitosis" (KEY) : Review Questions - Chapter 9kylevNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument10 pagesMeiosisNoor Hafezah Mohd MokhtiarNo ratings yet
- Long QuizDocument4 pagesLong Quiz1 Estabillo, Roland Andrew T.No ratings yet
- 1.3 - Mitosis-1Document27 pages1.3 - Mitosis-1sophiewayman07No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument11 pagesCell DivisionDr Nicholas AdeNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument5 pagesMITOSISdeepaNo ratings yet
- Genetics: Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisDocument60 pagesGenetics: Cell Cycle Mitosis MeiosisPatches24 Patches24No ratings yet
- Complete Cell-Cycle. INTERPHASE (Purple) MITOTIC PHASE (Light-Red)Document5 pagesComplete Cell-Cycle. INTERPHASE (Purple) MITOTIC PHASE (Light-Red)Camille Ann Faigao FamisanNo ratings yet
- Mitosis 1Document27 pagesMitosis 1USAMA AHMEDNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleMoffat KaprezzoNo ratings yet
- Krause MitosisDocument7 pagesKrause Mitosisapi-280692584No ratings yet
- 1.2 Cell DivisionDocument92 pages1.2 Cell DivisionHarpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Mitosis, Meiosis I and IIDocument2 pagesMitosis, Meiosis I and IIYEO MING HUI MoeNo ratings yet
- Pembelahan Sel: Langsung Tidak Langsung Mitosis MeiosisDocument68 pagesPembelahan Sel: Langsung Tidak Langsung Mitosis MeiosisPutti AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Modeling The Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument4 pagesModeling The Cell Cycle and MitosisFroilan Mae Olado CahaponNo ratings yet
- The Life of A Cell From Its Origin in The Division of A Parent Cell Until Its Own Division Into TwoDocument27 pagesThe Life of A Cell From Its Origin in The Division of A Parent Cell Until Its Own Division Into TwoMENWER ALJOHANINo ratings yet
- Most Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GDocument8 pagesMost Neurons, Mature Muscle Cells and Brain Cells Are in GfredNo ratings yet
- Microsoft WordDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Wordaneyao9No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument28 pagesCell DivisionPalagiri MadhuNo ratings yet
- Nuclear DivisionDocument1 pageNuclear DivisionJing PanganNo ratings yet
- Meosis DescriptionDocument3 pagesMeosis DescriptionMarch Jillian Chloe Tan ViñarNo ratings yet
- Mito Group WorkDocument4 pagesMito Group WorkVikneswaran Gunahlan NeshNo ratings yet
- MODULE 3 - MitosisDocument3 pagesMODULE 3 - MitosisNicoleBenaguaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument80 pagesMitosis and MeiosisAmara TargaryenNo ratings yet
- Cell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisDocument27 pagesCell Division, Mitosis, Meiosis, AmitosisAngryBird_jinx100% (1)
- GenbioDocument3 pagesGenbioMhariane MabborangNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument35 pagesCell DivisionRosalina Bautista RamosNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis ExamDocument6 pagesMitosis and Meiosis ExamAishley BerdinNo ratings yet
- Mitosis MeiosisDocument19 pagesMitosis MeiosisNeo RilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9: The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction 9.1 The Cell CycleDocument4 pagesChapter 9: The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction 9.1 The Cell CycleJennifer Muñoz ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Biology Class 10 Icse Boards!Document10 pagesBiology Class 10 Icse Boards!nark.jf4No ratings yet
- Week 4 Genral Biology 1Document3 pagesWeek 4 Genral Biology 1Spade ObusaNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisKiMii EstebanNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle-TRFDocument8 pagesThe Cell Cycle-TRFmaniiiiiiiiNo ratings yet
- English BiologyDocument3 pagesEnglish Biologyhannabelewicz09No ratings yet
- Interphase: Cell Cycle Nucleus Daughter CellsDocument4 pagesInterphase: Cell Cycle Nucleus Daughter CellsKàtrįńá Jøÿ ÅgùśtïńNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and Cell DivisionanuminiatureNo ratings yet
- MITOSIS and MEIOSISDocument26 pagesMITOSIS and MEIOSISMuskan ShreeNo ratings yet
- Cell Division Mitosis 4 17 17 For Guided Notes PowerpointDocument20 pagesCell Division Mitosis 4 17 17 For Guided Notes Powerpointapi-262586446No ratings yet
- Transport Inhibitor NPADocument2 pagesTransport Inhibitor NPAHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- PISCESDocument27 pagesPISCESHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Root Gravitropism Occurs in Four PhasesDocument3 pagesRoot Gravitropism Occurs in Four PhasesHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- X 24Document3 pagesX 24Hamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Epinasty and Thermonasty Are Examples of NasticDocument2 pagesEpinasty and Thermonasty Are Examples of NasticHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Gravitropism Is Generally Absent in Plant Species ThatDocument3 pagesGravitropism Is Generally Absent in Plant Species ThatHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Equired For The Gravity Response of The Arabidopsis RootDocument2 pagesEquired For The Gravity Response of The Arabidopsis RootHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Avena Coleoptiles. First Positive, First Negative, and Second Positive Curvatures Are IndicatedDocument3 pagesAvena Coleoptiles. First Positive, First Negative, and Second Positive Curvatures Are IndicatedHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Phaseolus Vulgaris, Fully 30 Percent of The Osmotic Potential Change Can Be Accounted For by KDocument3 pagesPhaseolus Vulgaris, Fully 30 Percent of The Osmotic Potential Change Can Be Accounted For by KHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- IAA Is Also Synthesized From Indole or FromDocument4 pagesIAA Is Also Synthesized From Indole or FromHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid Red/Blue Light Photoreceptor Has Been Isolated From A FernDocument3 pagesA Hybrid Red/Blue Light Photoreceptor Has Been Isolated From A FernHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Ve in An Entirely Inorganic EnvironmentDocument4 pagesVe in An Entirely Inorganic EnvironmentHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Suberin. Suberin Acts As A Barrier To Water and Solute Movement. The EndodermisDocument2 pagesSuberin. Suberin Acts As A Barrier To Water and Solute Movement. The EndodermisHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 / Acclimation To Environmental Stress: Quencher of Energy. Support For The Molecular SwitchDocument4 pagesChapter 14 / Acclimation To Environmental Stress: Quencher of Energy. Support For The Molecular SwitchHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Array of Molecules With Auxin ActivityDocument3 pagesArray of Molecules With Auxin ActivityHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- E Power of Movement Is Not Normally Associated WithDocument2 pagesE Power of Movement Is Not Normally Associated WithHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Evious Chapters Have Focused On The UnderlyingDocument7 pagesEvious Chapters Have Focused On The UnderlyingHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Low Temperatures Induce Lipid Unsaturation and Cold Regulated Genes in Cold Tolerant PlantsDocument4 pagesLow Temperatures Induce Lipid Unsaturation and Cold Regulated Genes in Cold Tolerant PlantsHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- The Hormone Concept in Plants: Chapter 18 / Hormones I: AuxinsDocument4 pagesThe Hormone Concept in Plants: Chapter 18 / Hormones I: AuxinsHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- The Nitrogen Cycle: A Complex Pattern of ExchangeDocument4 pagesThe Nitrogen Cycle: A Complex Pattern of ExchangeHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 We Defined Stress As A Negative EffectDocument4 pagesChapter 13 We Defined Stress As A Negative EffectHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Cereale L. CV Musketeer) - Growth Irradiance Is inDocument5 pagesCereale L. CV Musketeer) - Growth Irradiance Is inHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Lants Are Chemical Machines and One Universal Characteristic of Chemical Machines Is Their Sensitivity ToDocument3 pagesLants Are Chemical Machines and One Universal Characteristic of Chemical Machines Is Their Sensitivity ToHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Acclimation To Drought Affects Shoot-Root Ratio and Leaf AreaDocument4 pagesAcclimation To Drought Affects Shoot-Root Ratio and Leaf AreaHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- The Power of Movement Is Not Normally Associated WithDocument2 pagesThe Power of Movement Is Not Normally Associated WithHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- The Discovery of Abscisic AcidDocument4 pagesThe Discovery of Abscisic AcidHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Kebutuhan Hara Bagi TumbuhanDocument2 pagesKebutuhan Hara Bagi TumbuhanHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- Platelet-Activating Factor Is Formed by Acetylation of 1-Alkyl-2-LysophosphatidylcholineDocument2 pagesPlatelet-Activating Factor Is Formed by Acetylation of 1-Alkyl-2-LysophosphatidylcholineHamdan FatahNo ratings yet
- FIGURE 21-10: Long-Chain Saturated Fatty Acids Are Synthesized From PalmitateDocument1 pageFIGURE 21-10: Long-Chain Saturated Fatty Acids Are Synthesized From PalmitateHamdan FatahNo ratings yet