Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Looping, Counting and Indexing Looping
Uploaded by
frank ansari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pagelooping concepts discussed.
Original Title
Web Security 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentlooping concepts discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageLooping, Counting and Indexing Looping
Uploaded by
frank ansarilooping concepts discussed.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
LOOPING, COUNTING AND INDEXING
LOOPING:
The programming technique used to instruct the microprocessor to repeat tasks is called
looping.
This task is accomplished by using jump instructions.
CLASSIFICATION OF LOOPS:
1.continuous loop
2.Unconditional loop
CONTINUOUS LOOP:
repeats a task continuously.
A continuous loop is set up by using the unconditional jump instruction
A program with a continuous loop does not stop repeating the tasks until the system is reset.
CONDITIONAL LOOP:
A conditional loop is set up by a conditional jump instructions.
These instructions check flags(Z,CY,P,S) and repeat the tasks if the conditions are satisfied.
These loops include counting and indexing.
CONDITIONAL LOOP AND COUNTER:
A counter is a typical application of the conditional loop.
A microprocessor needs a counter,flag to accomplish the looping task.
Counter is set up by loading an appropriate count in a register.
Counting is performed by either increment or decrement the counter.
Loop is set up by a conditional jump instruction.
End of counting is indicated by a flag.
CONDITIONAL LOOP,COUNTER AND INDEXING:
Another type of loop which includes counter and indexing .
INDEXING:
pointing of referencing objects with sequential numbers.
Data bytes are stored in memory locations and those data bytes are referred to by their
memory locations.
Example:
Steps to add ten bytes of data stored in memory locations starting ata given location and
display the sum.
The microprocessor needs
1. a counter to count 10 data bytes.
2. an index or a memory pointer to locate where data bytes are stored.
3. to transfer data from a memory location to the microprocessor(ALU)
4. to perform addition
5. registers for temporary storage of partial answers
6. a flag to indicate the completion of the stack
7. to store or output the result.
You might also like
- Looping CAMDocument3 pagesLooping CAMHarjot KaurNo ratings yet
- IT225: Computer Organizations: August 25, 2014 (Monday)Document12 pagesIT225: Computer Organizations: August 25, 2014 (Monday)skiloh1No ratings yet
- Lab 6Document13 pagesLab 6محمد حنظلہNo ratings yet
- The ProcessorDocument83 pagesThe Processortinni09112003No ratings yet
- CO Workbook - Updated - CounterDocument6 pagesCO Workbook - Updated - CounterDeepak KumbharNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving With Loop Logic StructureDocument8 pagesProblem Solving With Loop Logic StructureChengNo ratings yet
- Qamar, Bilal, FawazDocument9 pagesQamar, Bilal, FawazMUHAMMAD QAMAR CHAUDRYNo ratings yet
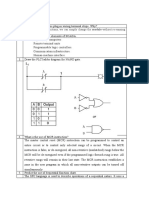
- Industrial Automation Using PLCs - System Design ProblemsDocument3 pagesIndustrial Automation Using PLCs - System Design ProblemsBonface MugwiraNo ratings yet
- Exp.4 PLC Timers and CountersDocument5 pagesExp.4 PLC Timers and CountersELaine Dichosa50% (4)
- Computer Science Department: Majlis Arts and Science College, PuramannurDocument20 pagesComputer Science Department: Majlis Arts and Science College, PuramannurJyothiNo ratings yet
- End Term Pratical: Diwesh Kumar Chaudhary REG No:12002572 Project TitleDocument7 pagesEnd Term Pratical: Diwesh Kumar Chaudhary REG No:12002572 Project TitleSagar singhNo ratings yet
- Ldcs MaterialDocument14 pagesLdcs MaterialMangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8Document33 pagesChapter 8Naho Senay IINo ratings yet
- Week 07Document14 pagesWeek 07lana_salahadinNo ratings yet
- Co Unit2 Part1Document11 pagesCo Unit2 Part1Manjushree N.SNo ratings yet
- 111.math InstructionsDocument65 pages111.math InstructionsDeborah MalanumNo ratings yet
- Bùi Văn Thi - 21522612 - LAB 2Document10 pagesBùi Văn Thi - 21522612 - LAB 221522612No ratings yet
- Important Questions For E8651Document2 pagesImportant Questions For E8651YotriNo ratings yet
- UNIT-3: MIPS InstructionsDocument15 pagesUNIT-3: MIPS InstructionsMukeshram.B AIDS20No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentUmar Sheikh PtiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Programming CountersDocument23 pagesChapter 6 - Programming CountersKhánh ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Microprogrammed ControlDocument27 pagesUnit 4 - Microprogrammed ControlPiyush KoiralaNo ratings yet
- Basic Processing Unit:: Fundamental ConceptsDocument35 pagesBasic Processing Unit:: Fundamental ConceptsJoseph JohnNo ratings yet
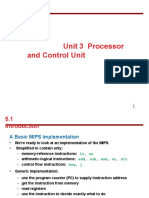
- Mips ImplementationDocument47 pagesMips ImplementationJEEVANANTHAM GNo ratings yet
- DLC LAB - 07 - Student - ManualDocument6 pagesDLC LAB - 07 - Student - Manualrk refatNo ratings yet
- DLC Lab - 07Document7 pagesDLC Lab - 07Didarul Alam AlifNo ratings yet
- Lab No.1 AV-312: Program CounterDocument6 pagesLab No.1 AV-312: Program CounterMUHAMMAD QAMAR CHAUDRYNo ratings yet
- Coeng3059:: Digital Logic DesignDocument72 pagesCoeng3059:: Digital Logic DesignALEMU DEMIRACHEWNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Control Unit: Micro OperationsDocument20 pagesChapter 5: Control Unit: Micro OperationsLui PascherNo ratings yet
- Ldcs Material 2Document14 pagesLdcs Material 2Mangaiyarkarasi VengatachalamNo ratings yet
- DEN5200 CONTROL SYSTEMS ANLAYSIS AND DESIGN ReportDocument15 pagesDEN5200 CONTROL SYSTEMS ANLAYSIS AND DESIGN Reportsilvia100% (1)
- Lectures Section 3 ModifiedDocument73 pagesLectures Section 3 ModifiedcoventryUkNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Karthik VyasNo ratings yet
- 04 Timer Counter DLLDocument37 pages04 Timer Counter DLLEldwinAdinataNo ratings yet
- CA Classes-66-70Document5 pagesCA Classes-66-70SrinivasaRaoNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument20 pagesContentsJagruti ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- PLC m3Document20 pagesPLC m3Goutham KNo ratings yet
- HDLDocument36 pagesHDLDeepanshu Midha5140No ratings yet
- Chap 3Document26 pagesChap 3Aaron Lewis DinkinNo ratings yet
- 5EC3-01: Computer Architecture: UNIT-3Document11 pages5EC3-01: Computer Architecture: UNIT-3Himanshi SainiNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 8 - PLC CountersDocument12 pagesLab Exercise 8 - PLC CountersMuhammad Saqlain AroonNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 The Control Unit: Structure NoDocument18 pagesUnit 4 The Control Unit: Structure NoanikhetNo ratings yet
- Activity No 4 - Controller OperationsDocument6 pagesActivity No 4 - Controller OperationsRonnel AgultoNo ratings yet
- Lab3 Rev eDocument13 pagesLab3 Rev eSaad Sulaiman KhanNo ratings yet
- EEE 303 Assignment - Group 03 SirajShovonPrantoDocument9 pagesEEE 303 Assignment - Group 03 SirajShovonPrantoMd Moinul Alom ShovonNo ratings yet
- Computer Instructions: Define Arithmetic and Logic Operations Such As Add, Subtract, Multiply, Shift, and ComplimentDocument10 pagesComputer Instructions: Define Arithmetic and Logic Operations Such As Add, Subtract, Multiply, Shift, and ComplimentGomathi SNo ratings yet
- RISC Instruction Set:: I) Data Manipulation InstructionsDocument8 pagesRISC Instruction Set:: I) Data Manipulation InstructionsSwarup BharNo ratings yet
- 11 12 Control UnitDocument10 pages11 12 Control UnitFuad YimerNo ratings yet
- Coa Viva QuestionsDocument15 pagesCoa Viva QuestionsSaif100% (1)
- Unit 2Document79 pagesUnit 2Sriram MurthyNo ratings yet
- Digital ApplicationsDocument14 pagesDigital Applications22e132No ratings yet
- A Level 9618 7Document4 pagesA Level 9618 7calvin esauNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 CoaDocument65 pagesUnit-3 CoatarunprovidesNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller - PDF 1411210674Document27 pagesMicrocontroller - PDF 1411210674Anney RevathiNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 16marksDocument12 pagesUnit 4 16markssramalingam288953No ratings yet
- Cap 301 RS1006B44Document9 pagesCap 301 RS1006B44ROhit NagPalNo ratings yet
- COA Unit 3Document28 pagesCOA Unit 3Shivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization and Architecture Cs2253: Part-ADocument21 pagesComputer Organization and Architecture Cs2253: Part-AjanukarthiNo ratings yet
- PUE COA Solution 2022-23Document30 pagesPUE COA Solution 2022-23Aviral TaraNo ratings yet
- 8085 and 8086 MicroprocessorDocument15 pages8085 and 8086 Microprocessorfrank ansariNo ratings yet
- Computer Application-BCA Fifth Sem (1) - 2 PDFDocument14 pagesComputer Application-BCA Fifth Sem (1) - 2 PDFfrank ansariNo ratings yet
- Android TutorialDocument836 pagesAndroid TutorialSheetaltwuNo ratings yet
- Instruction FormatDocument8 pagesInstruction Formatfrank ansariNo ratings yet
- Basics of E-Commerce:: - Electronic Commerce Draws On Technologies Such AsDocument39 pagesBasics of E-Commerce:: - Electronic Commerce Draws On Technologies Such Asfrank ansariNo ratings yet
- Computer Application-3-BCA-B PDFDocument1 pageComputer Application-3-BCA-B PDFfrank ansariNo ratings yet
- BootstrapDocument197 pagesBootstrappaulomdjNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Web Security ConsiderationsDocument3 pages8.1 Web Security Considerationsfrank ansariNo ratings yet
- Employee Management System ReportDocument205 pagesEmployee Management System Reportfrank ansariNo ratings yet
- Employee Management System: Project Report ONDocument79 pagesEmployee Management System: Project Report ONShefali RathiNo ratings yet