Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cilia and Flagella Structures
Uploaded by
Thiody Hope MongasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cilia and Flagella Structures
Uploaded by
Thiody Hope MongasCopyright:
Available Formats
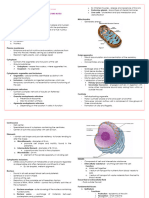
CELL SURFACE MODIFICATIONS Structure of cilia:
Cilia: Axoneme:
• A cilium (plural cilia) is an organelle found in • Inner core of cilia consists of a cytoskeleton
eukaryotic cells. called axoneme
• Cilia are slender protuberances that project • The axoneme of primary cilia typically has a
from the much larger cell body. ring of nine outer microtubule doublets
(called a 9+0 axoneme),
Types of cilia:
• The axoneme of a motile cilium has two
1. Motile cilia central microtubule doublets in addition to
• Motile cilia are usually present on a cell's the nine outer doublets (called a 9+2
surface in large numbers and beat in axoneme).
coordinated waves.
• For example, motile cilia are found in the
lining of the trachea (windpipe), where they
sweep mucus and dirt out of the lungs.
Function of motile cilia
• Motile cilia for the transport of fluids (e.g.
transport of mucus by stationary ciliated cells
in the trachea). However, cilia are also used
for locomotion (through liquids) in organisms
such as Paramecium .
• In female mammals, the beating of cilia in the
Fallopian tubes moves the ovum from the
ovary to the uterus
Functions of primary cilia:
• Mechanoreceptors
• A primary cilium extends from the
apical surface of the epithelial cells
lining the kidney tubules and
monitors the flow of fluid through the
tubules.
• Chemoreceptors
• Detect odors by receptors on the
primary cilium of olfactory neurons.
• Photoreceptors
2. Non-motile. (Primary cilia): • The outer segment of the rods in the
vertebrate retina is also derived from
• Usually occur one per cell; all mammalian
a primary cilium.
cells have a single non-motile primary cilium.
• For example, sensory organs like eye and
nose
Flagella:
• It is a tail-like projection that protrudes from
the cell body of certain prokaryotic and
eukaryotic cells, and functions in locomotion.
Function of flagella:
• Flagella serve for the propulsion of single
cells (e.g. swimming of protozoa and
spermatozoa), and motile cilia for the
transport of fluids (e.g. transport of mucus by
Structure of flagellum: stationary ciliated cells in the trachea).
• A eukaryotic flagellum is a bundle of nine However, cilia are also used for locomotion
fused pairs of microtubule doublets (through liquids) in organisms such as
surrounding two central single microtubules. Paramecium .
• The so-called "9+2" structure is characteristic Microvilli:
of the core of the eukaryotic flagellum called • Microvilli (singular: microvillus) are
an axoneme. At the base of a eukaryotic microscopic cellular membrane protrusions
flagellum is a basal body. that increase the surface area of cells
• Basal bodies are structurally identical to
centrioles. The flagellum is encased within
the cell's plasma membrane, so that the
interior of the flagellum is accessible to the
cell's cytoplasm.
Location of microvilli:
• Thousands of microvilli form a structure
called the brush border that is found on the
apical surface of some epithelial cells,
Flagella v/s cilia: • Example
• • Small intestinal enterocyte
• Though eukaryotic flagella and motile cilia • Kidney proximal tubule.
are ultrastructurally identical, the beating
pattern of the two organelles can be different. • In sensory cells of the inner ear (as
stereocilia),
• In the case of flagella (e.g. the tail of a sperm)
the motion is propeller-like. • In the cells of taste buds.
• Beating of motile cilia consists of coordinated • In olfactory receptor cells.
back-and-forth cycling of many cilia on the
cell surface.
Structure of microvilli
• Microvilli are covered in plasma membrane,
which encloses cytoplasm and
microfilaments.
• These are cellular extensions; there are little
or no cellular organelles present in the
microvilli.
• Each microvillus has a dense bundle of cross-
linked actin filaments, which serves as its
structural core. 20 to 30 tightly bundled actin
filaments are cross-linked by bundling
proteins fimbrin and villin to form the core of
the microvilli.
Functions of microvilli:
• Absorption in intestine
• Secretion
• Cellular adhesion
• Mechanotransduction in kidney proximal
tubules.
You might also like
- Chapter - 3 Cell: The Cell History Structure of Cell Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesChapter - 3 Cell: The Cell History Structure of Cell Cell OrganellesShubham ShawNo ratings yet
- CellDocument27 pagesCellTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Section - A: Model Paper - 1 Diploma in Medical Lab Technician Second Year Paper - IDocument19 pagesSection - A: Model Paper - 1 Diploma in Medical Lab Technician Second Year Paper - IMohammed MjdNo ratings yet
- The CellDocument25 pagesThe CellmaryshealshealNo ratings yet
- Apical Modification Group 1 GaiaDocument30 pagesApical Modification Group 1 GaiaPatrick Rómulo CabilingNo ratings yet
- Cells: The basic units of lifeDocument7 pagesCells: The basic units of lifeliverlyn babes BacunawaNo ratings yet
- Biology 100 Discoveries in Biology: Lecture: 03 CellsDocument20 pagesBiology 100 Discoveries in Biology: Lecture: 03 CellsMD Arshadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: A Guide to the OrganellesDocument11 pagesCell Structure: A Guide to the OrganellesAli MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Histo 2 PDFDocument13 pagesHisto 2 PDFabdulrazaqNo ratings yet
- Se Mi N Nhóm 1Document87 pagesSe Mi N Nhóm 1Trịnh Bảo MinhNo ratings yet
- Cell Modification Lecture ReviewerDocument2 pagesCell Modification Lecture ReviewerIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.No ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument35 pagesBioenergeticsJaine LuzNo ratings yet
- 01-The CellDocument25 pages01-The Cellfordgt989No ratings yet
- Prokariotik Dan Eukariotik 2Document22 pagesProkariotik Dan Eukariotik 2hanumNo ratings yet
- More Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesDocument7 pagesMore Cells. The Cell Theory Can Be Summarized As:: Biology 12 - Cell Structure & Function: Chapter NotesJaveed KassamNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Biology Notes by Jake NunerDocument44 pagesPreliminary Biology Notes by Jake Nunerpinidi kasturiNo ratings yet
- Cell - The Unit of Life - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pagesCell - The Unit of Life - Mind Maps - Arjuna NEET 2024Wind Follower MusicNo ratings yet
- Structure of Cilia and Flagella: - by Neha LoharDocument18 pagesStructure of Cilia and Flagella: - by Neha Loharjoy parimalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structure and Function 2016Document11 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structure and Function 2016GunnNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure: Structural Functional Unit: UnitDocument13 pagesCell Structure: Structural Functional Unit: UnitHaya Attieh100% (1)
- The CellDocument15 pagesThe CellSoft BoiNo ratings yet
- Oral Histology First Grading NotesDocument24 pagesOral Histology First Grading NotesAli,morwan HydarNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure ASDocument40 pagesCell Structure ASYasmine HadiastrianiNo ratings yet
- Key Notes: Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument2 pagesKey Notes: Chapter - 8 Cell - Structure and FunctionsAnjali KumariNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & OrganizationDocument34 pagesCell Structure & OrganizationMoza AlaliliNo ratings yet
- Cell-The Fundamental Unit of Life. NotesDocument15 pagesCell-The Fundamental Unit of Life. Notesparth jainNo ratings yet
- General Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellDocument18 pagesGeneral Medical Biology: Lecture 2: The World of CellRasan QadrNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Document7 pagesCell Organelles & Their Functions 1112Amrul Zlalu AdaNo ratings yet
- Cell Modification, Cell Cycle, MitosisDocument9 pagesCell Modification, Cell Cycle, MitosisIgnacio, Moira Jomille K.No ratings yet
- Cell Biology: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument76 pagesCell Biology: The Building Blocks of LifeDave Arthur Robledo100% (11)
- Lesso N1:: Components of CellDocument48 pagesLesso N1:: Components of CellKristine MoresNo ratings yet
- CellDocument4 pagesCellAlexa MacailoNo ratings yet
- Chapter_-_5_The_Fundamental_Unit_of_LifeDocument16 pagesChapter_-_5_The_Fundamental_Unit_of_Lifekarunadawar.11No ratings yet
- 2nd Q CEellDocument30 pages2nd Q CEellDeserie ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Histology: First Semester A.Y. 2021 - 2022Document22 pagesHistology: First Semester A.Y. 2021 - 2022Fea Kristine PacquiaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell Division: Learning Outcomes Laboratory SuppliesDocument6 pagesCell Structure and Cell Division: Learning Outcomes Laboratory SuppliespedroNo ratings yet
- Cell PhysiologyDocument31 pagesCell PhysiologyJulie Calo PugiesNo ratings yet
- EukaryoticDocument19 pagesEukaryoticwongyikyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter at A Glance: Study Key PointsDocument14 pagesChapter at A Glance: Study Key PointssatishNo ratings yet
- Membrane Bound Organelles and Non Membrane Bound OrganellesDocument25 pagesMembrane Bound Organelles and Non Membrane Bound OrganellesAshlee Venice CebuNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsDocument27 pagesLESSON 3 Parts of The Cell and Their FunctionsSophia CamachoNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio - First GradingDocument5 pagesGen Bio - First GradingCasey PedrayaNo ratings yet
- CellDocument34 pagesCellSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1: CELL - : How Were Cells Discovered?Document5 pagesCHAPTER 1: CELL - : How Were Cells Discovered?Joy Mazo FaderagaoNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure & Function 02 - Theory Notes - PDF Only - NSEJS 2023Document38 pagesCell - Structure & Function 02 - Theory Notes - PDF Only - NSEJS 2023wigiye6232No ratings yet
- The Structure and Functions of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsDocument25 pagesThe Structure and Functions of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic CellsdeweweweweweNo ratings yet
- Cells2008 2009Document43 pagesCells2008 2009jroharaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document44 pagesChapter 3Altaf Hussain KhanNo ratings yet
- 1Q Gen Bio ReviewerDocument8 pages1Q Gen Bio ReviewerNonoy VictimNo ratings yet
- Cell - Structure and FunctionsDocument63 pagesCell - Structure and FunctionsAdvayNo ratings yet
- Lecture #3: Theme: Epithelial TissuesDocument45 pagesLecture #3: Theme: Epithelial TissuesKhurshidbuyamayumNo ratings yet
- Ila College of Health Kuje: Cell PhysiologyDocument28 pagesIla College of Health Kuje: Cell PhysiologyDaniel DendaNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles PDFDocument23 pagesCell Organelles PDFEj AgsaldaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document39 pagesLecture 1Mohammed SindiNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Function MeetingDocument51 pagesCell Structure and Function MeetingenccaNo ratings yet
- Bio Cell Structure and Function Chart and Review PDFDocument27 pagesBio Cell Structure and Function Chart and Review PDFMuddihil MadzlanNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument22 pagesCell StructureAbdullah KhalidNo ratings yet
- PLANT CELL: Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesPLANT CELL: Parts and FunctionsnniChaNo ratings yet
- Biology Quick Notes by Disha PublicationDocument27 pagesBiology Quick Notes by Disha PublicationMunish Mechie100% (1)
- Life of Jose RizalDocument10 pagesLife of Jose RizalThiody Hope MongasNo ratings yet
- Module 8: Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways MetabolismDocument4 pagesModule 8: Enzymes & Metabolic Pathways MetabolismThiody Hope Mongas100% (2)
- Molecular Composition of CellsDocument3 pagesMolecular Composition of CellsThiody Hope Mongas100% (1)
- Mitosis and Meiosis NotesDocument12 pagesMitosis and Meiosis NotesThiody Hope Mongas100% (1)
- Parts of Plant Cell and Its FunctionsDocument2 pagesParts of Plant Cell and Its FunctionsThiody Hope Mongas50% (2)
- Lesson Plan in Biotechniques (Staining)Document13 pagesLesson Plan in Biotechniques (Staining)Ronel Pasalo Medina BatanganNo ratings yet
- MIC254 Lab Report Enumeration of E. coliDocument9 pagesMIC254 Lab Report Enumeration of E. coliAnis NatashaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Physiological SystemsDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Physiological SystemsLim SuxingNo ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet - Exercise 2 PDFDocument5 pagesLab Worksheet - Exercise 2 PDFmariammanutdNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Lesson 21 Archaea, Bacteria and VirusesDocument31 pages7th Grade Lesson 21 Archaea, Bacteria and VirusesPamela Ribeiro GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Casadio Et Al-2012-Journal of Raman SpectrosDocument11 pagesCasadio Et Al-2012-Journal of Raman SpectrosJoão Henrique Ribeiro BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Microstructural Characterization of a Modified 2219 Aluminum AlloyDocument6 pagesMicrostructural Characterization of a Modified 2219 Aluminum Alloycargetoianu2357No ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology Journal (PCI) 2021 (3) ModifiedDocument72 pagesPharmaceutical Microbiology Journal (PCI) 2021 (3) ModifiedAishwarya PatilNo ratings yet
- MC3 Microbiology and Parasitology NotesDocument15 pagesMC3 Microbiology and Parasitology NotesKim Erida QuezonNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesDocument10 pagesClass 11 Biology Chapter 8 - Revision NotesHARKIRIT KAUR100% (1)
- THE CELL ProjectDocument4 pagesTHE CELL ProjectKaylee Lopez Student - KnightdaleHSNo ratings yet
- Benson's Microbiological Applications Laboratory Manual in General Microbiology - Alfred E Brown-395-396Document2 pagesBenson's Microbiological Applications Laboratory Manual in General Microbiology - Alfred E Brown-395-396Luz IzaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 Scientific Paper (A Microbiological Survey of The Different Representative Organisms of Bacteria)Document4 pagesExercise 2 Scientific Paper (A Microbiological Survey of The Different Representative Organisms of Bacteria)Theresa LambayonNo ratings yet
- Histology MCQs - Epithelial Tissue - WikiLecturesDocument8 pagesHistology MCQs - Epithelial Tissue - WikiLecturesIsaac OnigbindeNo ratings yet
- What I Know About Cell OrganellesDocument14 pagesWhat I Know About Cell OrganellesLyka Mae BenitoNo ratings yet
- A True Macro Fluorescence Imaging System: MacroviewDocument8 pagesA True Macro Fluorescence Imaging System: MacroviewPrabavathy NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Special Stains For Histopathology LaboratoryDocument2 pagesSpecial Stains For Histopathology LaboratorySophiaAniceteNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure - Class 9th Grade Biology Science Project Free PDF DownloadDocument19 pagesCell Structure - Class 9th Grade Biology Science Project Free PDF Downloadh8631259No ratings yet
- Revealing Hidden Interfaces in Organic SemiconductorsDocument7 pagesRevealing Hidden Interfaces in Organic SemiconductorsalkanderiNo ratings yet
- Microtomy 1pdfDocument38 pagesMicrotomy 1pdfSneha KumariNo ratings yet
- Sol-Gel Deposition of (Ti, Ru)O2 and (Ti, Ru, Ir)O2 Oxide CoatingsDocument7 pagesSol-Gel Deposition of (Ti, Ru)O2 and (Ti, Ru, Ir)O2 Oxide CoatingsAnkit GarachNo ratings yet
- Surface Finish Guide: Measurements, Effects & InstrumentsDocument5 pagesSurface Finish Guide: Measurements, Effects & InstrumentsFachryal HiltansyahNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Report - Exercise 4 - Isolation and Cultivation of MicroorganismsDocument18 pagesPost Lab Report - Exercise 4 - Isolation and Cultivation of MicroorganismsDara KwonNo ratings yet
- The Main Themes of MicrobiologyDocument31 pagesThe Main Themes of MicrobiologyJhon VincentNo ratings yet
- Viruses Their ReplicationDocument39 pagesViruses Their ReplicationYsabella LlanetaNo ratings yet
- Viral Structure and Characterization MethodsDocument3 pagesViral Structure and Characterization MethodsKeanne GanironNo ratings yet
- Microbes in Our Lives: A Guide to MicroorganismsDocument12 pagesMicrobes in Our Lives: A Guide to MicroorganismsBeatrix Adrianna PabulayanNo ratings yet
- Engineering failure analysis proceduresDocument12 pagesEngineering failure analysis proceduressafeer ahmadNo ratings yet
- Summary of Protein CrystallographyDocument7 pagesSummary of Protein Crystallographykptbce09No ratings yet
- BIOL 3162 Lab 2-Introduction To Microbial Biotech Techniques ADocument7 pagesBIOL 3162 Lab 2-Introduction To Microbial Biotech Techniques Arube10000No ratings yet
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- Alex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessFrom EverandAlex & Me: How a Scientist and a Parrot Discovered a Hidden World of Animal Intelligence—and Formed a Deep Bond in the ProcessNo ratings yet
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationFrom EverandWater: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and CivilizationRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (37)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (63)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)