Professional Documents
Culture Documents
c/2 (1-d) /A (This Is Periodic) Then Multiply The Above Answer With 2
c/2 (1-d) /A (This Is Periodic) Then Multiply The Above Answer With 2
Uploaded by
pare121Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
c/2 (1-d) /A (This Is Periodic) Then Multiply The Above Answer With 2
c/2 (1-d) /A (This Is Periodic) Then Multiply The Above Answer With 2
Uploaded by
pare121Copyright:
Available Formats
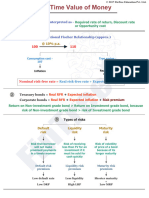
FIXED INCOME SECURITIES
Calculation Of Discount Factors From Swap Rates OBSERVATIONS: PULL TO PAR EFFECT
Interest Rate Swap is a portfolio of long-short bonds & Discount factor curve is always downward PRICE
Swap Rate refers to fixed rate.(i.e. Coupon Rate of a sloping. PREMIUM BOND
Bond Trading At Par) If the spot rate curve is upward sloping,forward
Suppose, d rate curve lies above it & par rate curve lies FV PAR
Maturity Swap Rates before it.
When spot rate curve is downward DISCOUNT BOND
0.5 3% sloping,forward rate curve lies below it & par
1 3.4% rate curve will lie above it. MATURITY
For a disc bond,ytm> coupon rate &
1.5 3.8% PAR RATE ytm is higher for
Par Rate is that coupon rate which makes the bond trade short-term maturity bond.
2 4%
at par.
For a premium bond,ytm<coupon
2.5 4.5%
c/2=(1-dT)/AT {THIS IS PERIODIC} rate & ytm is higher for higher
Then multiply the above answer with 2. maturity bond.
101.5 * d0.5=100.So,d0.5=0.9852. NOTE:
1.7* 0.9852+101.7d1=100.So, d1=0.9668. IMPACT OF MATURITY ON PRICE LOWER COUPON BONDS
d1.5=[100-1.9(0.9852+0.9668)]/101.9.So, d1.5=0.945 ARE MORE VOLATILE.
d2=[100-2(0.9852+0.9668+0.945)]/102.So, d2=0.9236. In a ZCB,ytm=last year’s
d2.5=[100-2.25(3.8206)]/102.25=0.8939 spot rate.
PRICE RETURNS
Calculation Of Spot Rates From Discount Factors One period Gross realized yield
P(1.5)>P(1) If our forecast of =(C+P1-P0)/P0
Consider discount factor as the price of a $1 FV Bond. Short Term rates is Focussing on numerator of price
1/2t
z(t)=[{1/dt} -1]*2 > f(1) & f(1.5),we appreciation.we have P1-P0=
Yes, if coupon
Or should invest at z0.5 P1-x + x-y + y-P0
rate > f(1.5)
USING CALCULATOR: & roll it over.
1 FV If our forecast of Spread rate carry roll
No,if coupon rate Short Term rates is Change change down
df ± PV
2n N <f(1.5) < f(1) & f(1.5),we Old Expected Curren
CPT i/y *2 should invest long spread Term t term
term i.e. at z1.5. To new Structure structu
OBSERVATIONS spread to Actual re to
When the spot rate curve is upward New Term Expect
sloping,swap rate curve(similar to par rates) term Structure ed
lies below it. structur Spread Term
When the spot rate curve is downward RETURN,SPREAD & YIELDS e same same Structu
sloping,swap rate curve(similar to par rates) re,
lies above it. Gross Return=(EVt-BVt-1)/ BVt-1 spread
When spot rate curve is flat,the par rate Where EVt=FV of reinvested coupon amt+Ending same
curve=spot rate. Price CARRY ROLL DOWN
Long term amortizing or callable bonds with high P0=Pt[Rt,St]
FORWARD RATE coupon rate have highest Reinvestment Risks. Y=Pt+1[ R’t+1,St]
Net Return=Gross Return-Financing Cost
For a positive spread, Expected Term Structure
f0.5 0 0.5
Actual market price<model price Choice 1:Realised Forward scenario
f1 0.5 1 For a negative spread, Realised fwd rate=Implied fwd
f1.5 1 1.5 Actual market price>model price st
rate,Gross yield =1 fwd rate i.e.
Tuckman has expressed SPREAD as a spread over f(0,0.5)
INTERPRETATIONS benchmark Forward rate i.e. what needs to be Fwd rates do not include risk prem.
Fwd Rate is the rate fixed today for added to each of the forward rates to ensure If realized fwd rate>implied fwd
borrowing/investing a sum of money later. that model price=market price. rate-Buy ST bond & roll them over
It represents the incremental return, if One would like to buy bond with the higher If realized fwd rate<implied fwd
maturity of our investment is extended. spread,given the features of 2 bonds are exactly rate-Buy LT bond.
If our forecast of Short Term rates is > f(1) & same. Choice 2:Unchanged Term
f(1.5),we should invest at z0.5 & roll it over. YTM(Yield To Maturity) is IRR of a bond i.e. Structure scenario
If our forecast of Short Term rates is < f(1) & single discount rate which makes model New f(0,0.5)=old(0,0.5) whereas in
f(1.5),we should invest long term i.e. at z1.5. price=market price. Choice 1: New f(0,0.5)=old(f0.5,1)
Forward Rate is THE INDIFFERENT RATE i.e. Note-r1=f1, Gross realized return wl depend on
indifferent btw investing at z1 or at z0.5 & r2= Geometric mean of f1 & f2 & so on relation btw bond’s coupon rate &
rolling it over. YTM is a complex average of various spot rates. last fwd rate before bond matures.
It is slightly less than r3 if coupon rates are low. Fwd rates include risk premium.
FORWARD RATE But,if coupon rate is higher, r1 & r2 start getting Choice 3:Unchanged Yield Scenario
[(Bigger 6mth factor/Smaller 6mth factor)1/gap-1]*2 higher weights such that ytm would fall in an Calculate initial ytm.We assume this
upward term structure environment. ytm after one period remains same.
Realised yield =YTM if bond is held to maturity & Gross Return=ytm.Ytm criticized
all intermediate cash flows are reinvested at ytm. bcoz of reinvestment assumption.
Page 7
You might also like
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - FAR (Financial Accounting and Reporting)Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (17)
- Monitoring and Control. Marketing PlanDocument6 pagesMonitoring and Control. Marketing PlanrommelssiNo ratings yet
- PIC - A Prueba de Imaginación Creativa - AdultosDocument3 pagesPIC - A Prueba de Imaginación Creativa - AdultosDominicAlexisTorresPuertaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Interest RatesDocument16 pagesChapter 4 - Interest Ratesuyenbp.a2.1720No ratings yet
- Duration - Convexity and ImmunizationDocument43 pagesDuration - Convexity and Immunizationmedhanshjain53No ratings yet
- Debt Markets N 3Document130 pagesDebt Markets N 3parv salechaNo ratings yet
- FIS PPT Covering Multiple Interest Rate Related Concepts - Cash and DerivativesDocument34 pagesFIS PPT Covering Multiple Interest Rate Related Concepts - Cash and DerivativesAbhinav MahajanNo ratings yet
- SS 14 Mindmaps DerivativesDocument36 pagesSS 14 Mindmaps Derivativeshaoyuting426No ratings yet
- Quantitative MethodsDocument35 pagesQuantitative Methodsphindocha30No ratings yet
- Wharton On Coursera: Introduction To Corporate Finance: DiscountingDocument7 pagesWharton On Coursera: Introduction To Corporate Finance: Discountingjhon doeNo ratings yet
- Study Notes in MAS Capital Budgeting Part 1 PDFDocument2 pagesStudy Notes in MAS Capital Budgeting Part 1 PDFHerald JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Fixed Income - Bonds: Juan Manuel de Los Ríos, CFADocument36 pagesFixed Income - Bonds: Juan Manuel de Los Ríos, CFACarlos AriasNo ratings yet
- BMA 12e SM CH 03 FinalDocument14 pagesBMA 12e SM CH 03 FinalNikhil ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Rates 103 - Duration and Interest Rate RiskDocument22 pagesRates 103 - Duration and Interest Rate Riskssj7cjqq2dNo ratings yet
- Review - Bond & Stock ValuationDocument24 pagesReview - Bond & Stock ValuationkerenkangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document25 pagesChapter 5aman7300No ratings yet
- FINS5513 Lecture T02A (Pre Lecture)Document28 pagesFINS5513 Lecture T02A (Pre Lecture)adri kusnoNo ratings yet
- Convexity and ImmunizationDocument8 pagesConvexity and Immunizationarjun guptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture18 PDFDocument21 pagesLecture18 PDFkate ngNo ratings yet
- Weighted Average Cost of CapitalDocument4 pagesWeighted Average Cost of Capitalamkhan02No ratings yet
- Anatomy CBDocument22 pagesAnatomy CBKarya BangunanNo ratings yet
- BUSI3502: Investments: Risk, Return & The Historical RecordDocument35 pagesBUSI3502: Investments: Risk, Return & The Historical RecordChendurNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 AnswerDocument5 pagesTutorial 5 AnswerSyuhaidah Binti Aziz ZudinNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate Risk NotesDocument157 pagesInterest Rate Risk Notesdaksh.agarwal180No ratings yet
- Teaching Note 97-14: Binomial Pricing of Interest Rate DerivativesDocument12 pagesTeaching Note 97-14: Binomial Pricing of Interest Rate Derivativesaaabbb888No ratings yet
- 03 Midterm SolDocument3 pages03 Midterm Solahsan1379No ratings yet
- Fixed Income Analysis - PDF Good FileDocument15 pagesFixed Income Analysis - PDF Good FilechetandeepakNo ratings yet
- Saunders 7e Biswas DurationApplication PortfolioImmunization Oct2021Document8 pagesSaunders 7e Biswas DurationApplication PortfolioImmunization Oct2021anniekassel1No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5m.vakili.aNo ratings yet
- Session 3 Bond and Interes RateDocument26 pagesSession 3 Bond and Interes RateadamobirkNo ratings yet
- l4b Risk Management Applications of Swaps and SwaptionsDocument24 pagesl4b Risk Management Applications of Swaps and SwaptionsmustapharahNo ratings yet
- Deluded1 - Fin 531 Corporate Finance - BW PDFDocument2 pagesDeluded1 - Fin 531 Corporate Finance - BW PDFZulfiana SetyaningsihNo ratings yet
- Fixed-Income Portfolio ManagementDocument11 pagesFixed-Income Portfolio Managementannie:XNo ratings yet
- Bonds 1Document15 pagesBonds 1Umay PelitNo ratings yet
- FXOL KID v1.2Document5 pagesFXOL KID v1.2israeltampwo2No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document20 pagesChapter 5cedNo ratings yet
- Iapm Iim Jammu #4Document64 pagesIapm Iim Jammu #4Daksh KhullarNo ratings yet
- Session 2 EMBA Interest Rate RiskDocument24 pagesSession 2 EMBA Interest Rate Risksatu tanvirNo ratings yet
- Session 2 EMBA Interest Rate RiskDocument24 pagesSession 2 EMBA Interest Rate Risksatu tanvirNo ratings yet
- Interest Rate RiskDocument23 pagesInterest Rate Riskgio040700No ratings yet
- Fnce 443Document4 pagesFnce 443tranbui1709No ratings yet
- SS 4 Mindmaps EconomicsDocument25 pagesSS 4 Mindmaps Economicshaoyuting426No ratings yet
- Chap009 Part3Document4 pagesChap009 Part3alrajinemerNo ratings yet
- CFIN2 CheatsheetDocument2 pagesCFIN2 Cheatsheetkhushi kumariNo ratings yet
- BFD - Weighted Average Cost of Capital by Ahmed Raza Mir & Taha PopatiaDocument6 pagesBFD - Weighted Average Cost of Capital by Ahmed Raza Mir & Taha PopatiaAiman TuhaNo ratings yet
- Valuation and Risk ModelsDocument28 pagesValuation and Risk ModelsChaitanya JadhavNo ratings yet
- Yield To Maturity: Outline and Suggested ReadingDocument14 pagesYield To Maturity: Outline and Suggested Readingmyshare12009No ratings yet
- 4 FI Derivatives - Forward, FRA, IRSDocument25 pages4 FI Derivatives - Forward, FRA, IRSyveziviNo ratings yet
- Chap 6 - Business ValuationDocument92 pagesChap 6 - Business ValuationAmmar FatehNo ratings yet
- DRM 05Document41 pagesDRM 05Kannan MeiyurNo ratings yet
- Fixed Note 1Document14 pagesFixed Note 1Nuooo KhanNo ratings yet
- Practical Investment Management by Robert.A.Strong Slides ch19Document39 pagesPractical Investment Management by Robert.A.Strong Slides ch19mzqaceNo ratings yet
- Corporate Finance Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesCorporate Finance Cheat SheetMinyu LvNo ratings yet
- 435x Lecture 3 Duration-Based Strategies VfinalDocument42 pages435x Lecture 3 Duration-Based Strategies Vfinalarjunbusiness7012No ratings yet
- Fnce 100 Final Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesFnce 100 Final Cheat Sheethung TranNo ratings yet
- Session 4 - Valuation ConceptsDocument23 pagesSession 4 - Valuation Conceptssanjeet_kaur_10No ratings yet
- Bonds Equity - Financial Modeling #11Document48 pagesBonds Equity - Financial Modeling #11Yash ShahareNo ratings yet
- CHap 5Document6 pagesCHap 5camlansuc09999No ratings yet
- Asset-V1 IMF+FMAx+2T2017+type@asset+block@FMAx M3 CLEAN NewDocument47 pagesAsset-V1 IMF+FMAx+2T2017+type@asset+block@FMAx M3 CLEAN NewkingjaspeNo ratings yet
- Term Structure of Interest Rates: Discrete TimeDocument7 pagesTerm Structure of Interest Rates: Discrete Timedylan.fay6No ratings yet
- United States v. Steven Chin Leung, 360 F.3d 62, 2d Cir. (2004)Document13 pagesUnited States v. Steven Chin Leung, 360 F.3d 62, 2d Cir. (2004)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Kelong Paradise Waterfront ResortDocument2 pagesKelong Paradise Waterfront ResortneslymelllerNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument6 pagesCarbohydratesapi-308598460No ratings yet
- PPA StructuringDocument34 pagesPPA StructuringRaj Tha100% (1)
- Premier 300Document2 pagesPremier 300Malitha PeirisNo ratings yet
- 2017 MMFX PresentationDocument38 pages2017 MMFX PresentationaljaycruzadoNo ratings yet
- Introducción A Los Bioreactores - Reactor BatchDocument14 pagesIntroducción A Los Bioreactores - Reactor BatchMilton SteevenNo ratings yet
- Pes Cambodia Penalty CupDocument34 pagesPes Cambodia Penalty CupKm koNo ratings yet
- Brocade Fibre Channel HBA: Administrator's GuideDocument156 pagesBrocade Fibre Channel HBA: Administrator's GuideAshok BeheraNo ratings yet
- History and Family of Benjamin Thomas Trotter MitchellDocument14 pagesHistory and Family of Benjamin Thomas Trotter MitchellLeena RogersNo ratings yet
- Data Science For Business Leaders: Executive Program SyllabusDocument7 pagesData Science For Business Leaders: Executive Program SyllabusSANTIAGO PUJOL ZABALANo ratings yet
- Timeless Sales Strategies: How To Leverage On Powerful Online and Offline Strategies To Boost Your Sales!Document20 pagesTimeless Sales Strategies: How To Leverage On Powerful Online and Offline Strategies To Boost Your Sales!EpiphaneNo ratings yet
- How To Be A Pilot Junior WebDocument16 pagesHow To Be A Pilot Junior WebNextgen AviationNo ratings yet
- Hot Cracking2Document470 pagesHot Cracking2Ashish PatelNo ratings yet
- Complete Deck of Many ThingsDocument1 pageComplete Deck of Many ThingsErnesto de VegaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal HypocalcemiaDocument8 pagesNeonatal HypocalcemiaCristina Fernández ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Nature and Concept of ManagementDocument3 pagesNature and Concept of ManagementHalimanessa AlontoNo ratings yet
- Copenhagen AccordDocument6 pagesCopenhagen AccordQuercusCOP15No ratings yet
- DJ Shadow Endtroducing ... (33â " Series) PDFDocument71 pagesDJ Shadow Endtroducing ... (33â " Series) PDFtululotres100% (1)
- Psoriasis: Epidemiology, Clinical and Histological Features, Triggering Factors, Assessment of Severity and Psychosocial AspectsDocument21 pagesPsoriasis: Epidemiology, Clinical and Histological Features, Triggering Factors, Assessment of Severity and Psychosocial AspectsRHBeautyCareTambolakaNo ratings yet
- CMS-016 Scope of Work Guide v1 0Document12 pagesCMS-016 Scope of Work Guide v1 0ChrisNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Chapter 3Document56 pagesHeat and Mass Chapter 3Mvelo PhungulaNo ratings yet
- Research Proposal: Management ThesisDocument20 pagesResearch Proposal: Management Thesisdamu9290333337No ratings yet
- Yma D L A: Tunkar ThuvawnDocument4 pagesYma D L A: Tunkar ThuvawnlhkNo ratings yet
- Plumbing10 Q1 Module2of2 SelectMaterials v2Document25 pagesPlumbing10 Q1 Module2of2 SelectMaterials v2EJ AtsilabNo ratings yet
- Luo 2018Document10 pagesLuo 2018yashwitha.nNo ratings yet
- Individual Performance Commitment and Review (Ipcr) Form: DPWH Spms Form No.1ADocument2 pagesIndividual Performance Commitment and Review (Ipcr) Form: DPWH Spms Form No.1AMae Ann GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Group I Study Material, Telugu Medium & English Medium, Sakshieducation2Document1 pageGroup I Study Material, Telugu Medium & English Medium, Sakshieducation2Ravi Kumar MogilsettiNo ratings yet