Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control System: For Thepurpose of Obtaining A Desired Output With Desired Performance, Given A Specified
Uploaded by
IlyasRaza0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageControl systems must be designed to be stable to ensure the natural response decays over time rather than growing uncontrolled. The design process involves determining system requirements, drawing functional diagrams, modeling the system mathematically, reducing the model, and analyzing and designing to meet specifications for stability, transient response, and steady-state performance.
Original Description:
control
Original Title
Control System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentControl systems must be designed to be stable to ensure the natural response decays over time rather than growing uncontrolled. The design process involves determining system requirements, drawing functional diagrams, modeling the system mathematically, reducing the model, and analyzing and designing to meet specifications for stability, transient response, and steady-state performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views1 pageControl System: For Thepurpose of Obtaining A Desired Output With Desired Performance, Given A Specified
Uploaded by
IlyasRazaControl systems must be designed to be stable to ensure the natural response decays over time rather than growing uncontrolled. The design process involves determining system requirements, drawing functional diagrams, modeling the system mathematically, reducing the model, and analyzing and designing to meet specifications for stability, transient response, and steady-state performance.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
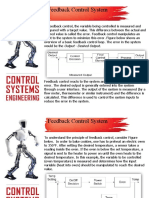
Control system
1. Analysis is the process by which a system's performance is determined.
2. Design is the process by which a system'sperformance is created or changed.
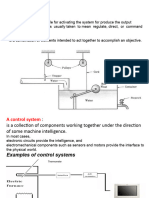
3. A control system consists of subsystems and processes (or plants) assembled
for thepurpose of obtaining a desired output with desired performance, given
a specified.
4. t the total responseof a system is the sum of the natural response and the
forced respons.
5. If natural response is so much greater than the forced responsethat the
system is no longer controlled. This condition, called instability
6. Control systems must be designed to be stable. That is, their natural responsemust decay
to zero as time approaches infinity, or oscillate. In many systems thetransient response
you see on a time response plot can be directly related to the natural response. Thus, if
the natural response decays to zero as time approachesinfinity, the transient response
will also die out, leaving only the forced response. If the system is stable, the proper
transient response and steady-state error characteristics can be designed. Stability is our
third analysis and design objective..
7. The design of a control system follows these steps:
Step 1 Determine a physical system and specifications from requirements.
Step 2 Draw a functional block diagram.
Step 3 Represent the physical system as a schematic.
Step 4 Use the schematic to obtain a mathematical model, such as a block diagram.
Step 5 Reduce the block diagram.
Step 6 Analyze and design the system to meet specified requirements and specifications
that include stability, transient response, and steady-state performance.
You might also like
- Learning-Based Adaptive Control: An Extremum Seeking Approach – Theory and ApplicationsFrom EverandLearning-Based Adaptive Control: An Extremum Seeking Approach – Theory and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control Systems-Student-2021 - 2022 NewDocument885 pagesIntroduction To Control Systems-Student-2021 - 2022 NewAkpevwe Isire100% (1)
- Control Theory Notes PDFDocument212 pagesControl Theory Notes PDFAmrik SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction PDFDocument7 pagesIntroduction PDFSandeep B RNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control System: Output - Desired OutputDocument13 pagesFeedback Control System: Output - Desired OutputApril BalceNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering 5 (1) - 2Document1 pageControl Systems Engineering 5 (1) - 2ANo ratings yet
- EX1 Review F10Document21 pagesEX1 Review F10amer4411No ratings yet
- FeedCon (Unit 1) PDFDocument17 pagesFeedCon (Unit 1) PDFAbby MacallaNo ratings yet
- Control System Engineering - 1Document22 pagesControl System Engineering - 1Uma MageshwariNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control Systems: Engr. Joey P. Sarmiento, PECEDocument160 pagesFeedback and Control Systems: Engr. Joey P. Sarmiento, PECERAINIER RamosNo ratings yet
- Introduction 23Document16 pagesIntroduction 23Ggfgsgege GegsgsNo ratings yet
- ME4120 Assessment 1Document3 pagesME4120 Assessment 1Janlyn OrnosNo ratings yet
- Control System Engineering - IDocument212 pagesControl System Engineering - IAjit Kumar Kisku100% (1)
- Characteristics of A SystemDocument9 pagesCharacteristics of A SystemKatrina MilianNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument15 pagesIntroductionslo803421No ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering: January 2010Document22 pagesControl Systems Engineering: January 2010khacsau2904No ratings yet
- Introduction To Control SystemDocument47 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemDlan Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Engineering: January 2010Document22 pagesControl Systems Engineering: January 2010Kanugolu Bala Ananth SaiNo ratings yet
- System Analysis and DesignDocument69 pagesSystem Analysis and Designsam mydaxNo ratings yet
- Assignment Control 615.Document12 pagesAssignment Control 615.Hamza zulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Prelim-MODULE 4Document5 pagesPrelim-MODULE 4Celimen, John Renz C.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisJoy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction 1.4 Analysis and Design Objectives AnalysisJoy Rizki Pangestu DjuansjahNo ratings yet
- controlICS CH1Document5 pagescontrolICS CH1Magarsaa Qana'iiNo ratings yet
- CompensationDocument2 pagesCompensationSneha NagarNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering & Instrumentation Assignment # 01 Submitted By: Syed Hamza Zulfiqar Reg # 620/BSME/f16 (B)Document12 pagesControl Engineering & Instrumentation Assignment # 01 Submitted By: Syed Hamza Zulfiqar Reg # 620/BSME/f16 (B)Hamza zulfiqarNo ratings yet
- What Can Be Said About The Controllability and Observability Conditions If The Transfer Function Has PoleDocument6 pagesWhat Can Be Said About The Controllability and Observability Conditions If The Transfer Function Has PoleMengistu BirukeNo ratings yet
- Dynamical System ModelDocument47 pagesDynamical System ModelYeimy QuevedoNo ratings yet
- System DevelopmentDocument24 pagesSystem DevelopmentbernardNo ratings yet
- Unit I: Fundamentals of Control System: Lecturer: D. R. PardeshiDocument18 pagesUnit I: Fundamentals of Control System: Lecturer: D. R. PardeshiDnyaneshwar RajputNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop ResponseDocument8 pagesClosed Loop ResponseJoydeep Choudhury 20UCH030No ratings yet
- Systems Approach Theories-FinalDocument11 pagesSystems Approach Theories-FinalBassam AlqadasiNo ratings yet
- Examples of Control Systems:: Lecture OneDocument4 pagesExamples of Control Systems:: Lecture OnemornyNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit - IDocument10 pagesNotes Unit - IAamin AftabNo ratings yet
- Module 1 and 2Document15 pagesModule 1 and 2Vanvan BitonNo ratings yet
- Chapter V - Building Information SystemsDocument43 pagesChapter V - Building Information SystemsŚüthår KîśhóręNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 ISMDocument32 pagesUnit-3 ISMupkeeratspamNo ratings yet
- Control System 1Document29 pagesControl System 1Gabriel GalizaNo ratings yet
- Session 1 Introduction To Control Systems: Learning OutcomesDocument8 pagesSession 1 Introduction To Control Systems: Learning OutcomesJana DissanayakeNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - Overview of System Analysis & DesignDocument7 pagesLESSON 1 - Overview of System Analysis & DesignGlaiza PudaNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Compressed WatermarkDocument71 pagesControl Engineering Compressed WatermarkBasava RajNo ratings yet
- Control Systems - 1Document18 pagesControl Systems - 1H. ZNADNo ratings yet
- Feedback Control: InherentDocument5 pagesFeedback Control: InherentRabi Shankar ShilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Introduction: Subject: Control PrinciplesDocument5 pagesChapter 1: Introduction: Subject: Control PrinciplesRonaldo KmeNo ratings yet
- Control System ModelingDocument24 pagesControl System ModelingSiva Bala KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Expert Systems For Monitoring and Control: Daniel L. DvorakDocument24 pagesExpert Systems For Monitoring and Control: Daniel L. DvorakMohamed A. ShishtawyNo ratings yet
- Take Home Examprocess Control1Document4 pagesTake Home Examprocess Control1Gehad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Essay / Assignment Title: System Engineering With A Focus On Business ProcessesDocument32 pagesEssay / Assignment Title: System Engineering With A Focus On Business ProcessesAmneet sistersNo ratings yet
- Control System Analysis New CHP 1 and 2Document109 pagesControl System Analysis New CHP 1 and 2KejeindrranNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control SystemsDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemsLeta EmiruNo ratings yet
- Principles of Fault ToleranceDocument16 pagesPrinciples of Fault ToleranceMako KazamaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignDocument14 pagesTopic 1. Introduction To Control Systems DesignxREDCivicCometxNo ratings yet
- Diseño Informe Guía 4Document4 pagesDiseño Informe Guía 4Nancy QuirogaNo ratings yet
- MT0032-Unit-01-System and System ConceptsDocument96 pagesMT0032-Unit-01-System and System ConceptsSocheat BunNo ratings yet
- Report SeminarDocument23 pagesReport SeminarpradnyaekadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Control SystemsDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Control SystemsRahul SandilyaNo ratings yet
- Semi-Markov Models: Control of Restorable Systems with Latent FailuresFrom EverandSemi-Markov Models: Control of Restorable Systems with Latent FailuresNo ratings yet