Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Injection Systems: Basic Functions
Uploaded by
pramodOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Injection Systems: Basic Functions
Uploaded by
pramodCopyright:
Available Formats
Injection Systems
Basic Functions
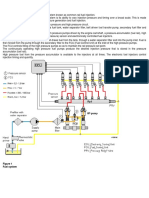
The basic functions of a diesel injection system can be broken down into four sub functions:
Fuel delivery (low pressure side) from the tank through the fuel filter to high pressure
generation. This function is assumed by the ‘‘low pressure circuit’’ subsystem, which is
generally equipped with the components of pre-filter, main filter (heated if necessary), feed
pump and control valves. The low pressure circuit connects the vehicle tank to the high
pressure system feed and return by lines through the low pressure components. The
functionally determinative pressure and flow specifications of the connected high and low
pressure components must be observed.– High pressure generation and fuel delivery (high
pressure side) to the metering point or in an accumulator with high efficiency during
compression. Optimal steady state and dynamic injection pressure both have to be provided
as a function of the engine operating point. The required injected fuel quantity and system-
dependent control and leak quantities have to be delivered. This function is assumed by the
high pressure pump and, depending on the system, an accumulator. Valves are installed in the
high pressure circuit to control the mass flows and pressures. In advanced injection systems,
they are electronically actuated.
High pressure generation and fuel delivery (high pressure
Side) to the metering point or in an accumulator with high efficiency during compression.
Optimal steady state and dynamic injection pressure both have to be provided as a function of
the engine operating point. The required injected fuel quantity and system-dependent control
and leak quantities have to be delivered. This function is assumed by the high pressure pump
and, depending on the system, an accumulator. Valves are installed in the high pressure circuit
to control the mass flows and pressures. In advanced injection systems, they are
electronically actuated.
– Fuel metering that precisely meters the fuel mass into the combustion chamber as a
function of speed and engine load and is supported by exhaust gas after treatment systems.
Advanced injection systems meter fuel with the aid of electrically actuated solenoid or piezo
valves mounted on the high pressure pumps or directly on the injectors.
– Fuel preparation by optimally utilizing the pressure energy for primary mixture formation
for the purpose of a fluid spray that is optimally distributed in the combustion chamber in
terms of time and location. The fuel is prepared in the injection nozzle. The metering valve’s
interaction with the nozzle needle control and the routing of the flow from the nozzle inlet
until its discharge at the nozzle holes are of key importance.
You might also like
- Cummins ISX Fuel System 02-05Document18 pagesCummins ISX Fuel System 02-05g665013100% (21)
- Bosch CP3 OperationDocument6 pagesBosch CP3 OperationGianfranco Danna Gálvez100% (3)
- SC SystemDocument80 pagesSC Systemgillian marbebe0% (1)
- Komat'Su - HPI Fuel SystemDocument76 pagesKomat'Su - HPI Fuel SystemKarthik Rao100% (2)
- BSP YellDocument1 pageBSP Yelljesha fabio-abarcaNo ratings yet
- Common Rail SystemDocument30 pagesCommon Rail SystemJunaidi Juna Westborneo100% (3)
- Fuel System D6EDocument1 pageFuel System D6EPreett Rajin Menabung100% (14)
- Shop Management ModuleDocument31 pagesShop Management ModuleEllen WaminalNo ratings yet
- Vehicle Electrical ActuatorsDocument40 pagesVehicle Electrical ActuatorsBence M Zoltan100% (1)
- Weber Injection-Ignition SystemDocument27 pagesWeber Injection-Ignition SystemjohnvandurenNo ratings yet
- Electronic Diesel Fuel System (Common Rail)Document30 pagesElectronic Diesel Fuel System (Common Rail)Katu2010100% (1)
- AT 111 - Module 6 Servicing Automotive BatteryDocument28 pagesAT 111 - Module 6 Servicing Automotive BatteryJeffrey Segarra NicomedesNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Servicing Automotive Battery 1Document52 pages2 1 Servicing Automotive Battery 1Jayson Cayabyab100% (3)
- Module 2-Test & Repair FinalDocument24 pagesModule 2-Test & Repair FinalCharmaine Mae RetizaNo ratings yet
- Catering Management: CAM 301 Bs Hospitality ManagementDocument37 pagesCatering Management: CAM 301 Bs Hospitality Managementfelize padllaNo ratings yet
- The Overall Motronic SystemDocument12 pagesThe Overall Motronic SystemKanagasundram JathursajanNo ratings yet
- Steely Dan Lyrics InterpretationsDocument298 pagesSteely Dan Lyrics Interpretationsmilnak100% (3)
- Bosch Fuel System Common RailDocument4 pagesBosch Fuel System Common RailAlaa saidNo ratings yet
- Engine Lubrication SystemDocument6 pagesEngine Lubrication SystemWaqar Younas NumberdarNo ratings yet
- Common Rail Fuel Injection SystemDocument56 pagesCommon Rail Fuel Injection SystemMarcos Maciel100% (1)
- Module 4. Leadership in NursingDocument33 pagesModule 4. Leadership in NursingSang Hyun JungNo ratings yet
- WSH Healthcare GuidelinesDocument75 pagesWSH Healthcare GuidelinesJohn KurongNo ratings yet
- Actividad Carta Al Director 8 BásicoDocument13 pagesActividad Carta Al Director 8 BásicomariaNo ratings yet
- Engine Characteristics: UEC33LSE-Eco-C2 Technical Data 1.4 Eco-Engine SystemDocument6 pagesEngine Characteristics: UEC33LSE-Eco-C2 Technical Data 1.4 Eco-Engine Systembritties69No ratings yet
- Activity Sheet SampleDocument5 pagesActivity Sheet SampleDhan GregorioNo ratings yet
- Automotive CBCDocument82 pagesAutomotive CBCAllan Tomas100% (1)
- SAG - Automotive Servicing NC IDocument3 pagesSAG - Automotive Servicing NC IROJANE F. BERNAS, PhD.No ratings yet
- Compensating Devices of CarbutetorDocument8 pagesCompensating Devices of Carbutetoratulsemilo0% (1)
- Chapter 6 NotesDocument13 pagesChapter 6 NotesPankaj Gaurav100% (1)
- Business Plan Preparation Midterm ExamDocument5 pagesBusiness Plan Preparation Midterm ExamDiane DominiqueNo ratings yet
- Force Feed SystemsDocument4 pagesForce Feed SystemsputerinuritaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan - Demo Business EnterpriseDocument2 pagesLesson Plan - Demo Business EnterpriseMaritess MunozNo ratings yet
- 2.session PlanDocument2 pages2.session PlanMayeng LogagayNo ratings yet
- Automotive-Pecs Lo1-Activity-SheetsDocument6 pagesAutomotive-Pecs Lo1-Activity-SheetsJumar BaldrezNo ratings yet
- Automotive Servicing Grade 7-8 PECS - Align One's PECS With That of A PractitionerentrepreneurDocument3 pagesAutomotive Servicing Grade 7-8 PECS - Align One's PECS With That of A PractitionerentrepreneurrodNo ratings yet
- AUTOMOTIVE SET A Mastery TestDocument5 pagesAUTOMOTIVE SET A Mastery TestRon louise PereyraNo ratings yet
- Analysis of The Macro EnvironmentDocument16 pagesAnalysis of The Macro EnvironmentsaintangelleNo ratings yet
- Servicing Ignition SytemDocument55 pagesServicing Ignition SytemYvan LopezNo ratings yet
- 4 Tec Troubleshooting ChartDocument11 pages4 Tec Troubleshooting ChartnelsoncoNo ratings yet
- Progress Chart Bread and Pastry Production NC Ii: Basic CompetenciesDocument4 pagesProgress Chart Bread and Pastry Production NC Ii: Basic CompetenciesLovely TaguasNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification in Automotive ServicingDocument1 pageTable of Specification in Automotive ServicingBilly Joe ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Automobile Cooling System Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesAutomobile Cooling System Lesson PlanAyobami olaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Ignition SystemDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The Ignition SystemJestoni100% (2)
- Recitation CardDocument1 pageRecitation CardGenesis AgcaoiliNo ratings yet
- 4 Differences Between GDP and GNPDocument5 pages4 Differences Between GDP and GNPAmpy SasutonaNo ratings yet
- Fuel Feed SystemDocument26 pagesFuel Feed SystemKarnal 0388No ratings yet
- Detroit Diesel DD Three Filter SystemDocument170 pagesDetroit Diesel DD Three Filter Systemcristian picadoNo ratings yet
- Indirect Fuel InjectionDocument3 pagesIndirect Fuel InjectionFrigura IulianNo ratings yet
- Common RailDocument30 pagesCommon RailAnonymous 9QkTHFNo ratings yet
- SSP 020 Common - RailDocument30 pagesSSP 020 Common - Railvenkateshyadav2116No ratings yet
- 6 Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection SystemsDocument34 pages6 Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection Systemsloganathanpalani100% (1)
- CRDIDocument31 pagesCRDIJawahar Raj100% (3)
- 1 Gasoline Electronic Direct Injection System1Document40 pages1 Gasoline Electronic Direct Injection System1EZHILARASAN RNo ratings yet
- Experiment No: 2 Fuel Pump & InjectorsDocument4 pagesExperiment No: 2 Fuel Pump & InjectorsAjay JachakNo ratings yet
- FuelInjection SystemDocument24 pagesFuelInjection SystemCharlyn FloresNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument11 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentJunaid YNo ratings yet
- Gasoline Electronic Fuel Injection SystemsDocument35 pagesGasoline Electronic Fuel Injection SystemsatulsemiloNo ratings yet
- FCMDocument4 pagesFCMMansoor Ahmad100% (1)
- High PressureDocument9 pagesHigh Pressurezozo0424No ratings yet
- Electronic Fuel Injection by Dr.S.John AlexisDocument32 pagesElectronic Fuel Injection by Dr.S.John AlexisJ Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- bài thầy đứcDocument23 pagesbài thầy đứcnguyenductai.lop93.lhpNo ratings yet
- Common Rail Injection System Pressure ControlDocument3 pagesCommon Rail Injection System Pressure ControlSilvio MadetyNo ratings yet
- Automobile EnggDocument43 pagesAutomobile EnggV V DEVADASNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machine PPTTDocument28 pagesHydraulic Machine PPTTFaisal SaifNo ratings yet
- Saa6d140e-3 Shop ManualDocument18 pagesSaa6d140e-3 Shop Manualjannievanstaden783No ratings yet
- Standing EnukleasiiDocument3 pagesStanding Enukleasiig_meilisaNo ratings yet
- 8Document7 pages8Crystal MurrayNo ratings yet
- 12 Chapter 04Document42 pages12 Chapter 04Lokesh Ujjainia UjjainiaNo ratings yet
- Living With The Himalayan MastersDocument27 pagesLiving With The Himalayan MastersLauren Hughes0% (3)
- Travel Book Mini 2 PreviewDocument0 pagesTravel Book Mini 2 PreviewAndrysNo ratings yet
- XML Extensible Markup LanguageDocument59 pagesXML Extensible Markup LanguagevssNo ratings yet
- An Empirical Analysis of Money Demand Function in Nepal: Birendra Bahadur BudhaDocument17 pagesAn Empirical Analysis of Money Demand Function in Nepal: Birendra Bahadur BudhaIsmith PokhrelNo ratings yet
- Lista de Peças Empilhadeira Elétrica Epn1655 - Sas MovimentaçãoDocument71 pagesLista de Peças Empilhadeira Elétrica Epn1655 - Sas MovimentaçãoCleber AndradeNo ratings yet
- Đề Ôn Thi Vào 10 2Document7 pagesĐề Ôn Thi Vào 10 2Quỳnh PhạmNo ratings yet
- "Once Saved Always Saved": Are They Biblical?Document41 pages"Once Saved Always Saved": Are They Biblical?jarrodjohnNo ratings yet
- Micro Economy (BA II)Document113 pagesMicro Economy (BA II)Janahvi JanardhanNo ratings yet
- ATV12HU15M2Document2 pagesATV12HU15M2choirulfachruddinNo ratings yet
- October Month Vocabulary The Hindu Editorial Part-1Document10 pagesOctober Month Vocabulary The Hindu Editorial Part-1sauravNo ratings yet
- RPH Chem f5 22.07.2020 5S1Document1 pageRPH Chem f5 22.07.2020 5S1yeopeeNo ratings yet
- Cooling Water Requirement For Molding MachinesDocument5 pagesCooling Water Requirement For Molding MachinesPinak ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Protac Cyanoacrylate AdhesivesDocument4 pagesProtac Cyanoacrylate AdhesivesIgorNo ratings yet
- Specification For Aluminum-Alloy Sand Castings: SB-26 /SB-26MDocument17 pagesSpecification For Aluminum-Alloy Sand Castings: SB-26 /SB-26MHernan RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 2 NotesmatthewNo ratings yet
- Kabale University Government Sponsorship Admission List For Academic Year 2020Document9 pagesKabale University Government Sponsorship Admission List For Academic Year 2020The Campus Times100% (1)
- EI Laying OFC 310107Document21 pagesEI Laying OFC 310107agmtechnical100% (1)
- LKPD 2-Understanding Explanation TextDocument3 pagesLKPD 2-Understanding Explanation TextSabina TuankottaNo ratings yet
- Acid-And Acid/Heat Coagulated Cheese: J A Lucey, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USADocument8 pagesAcid-And Acid/Heat Coagulated Cheese: J A Lucey, University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, USAمیلاد قاسمیNo ratings yet
- Instructional Design Project Outline Christy HughesDocument3 pagesInstructional Design Project Outline Christy Hughesapi-560842067No ratings yet
- Trend-Graph-Đã Chuyển ĐổiDocument8 pagesTrend-Graph-Đã Chuyển ĐổiNguyễn Minh ChâuNo ratings yet
- DOE Acc ReportDocument24 pagesDOE Acc ReportElena LegaspiNo ratings yet