Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Normal Probe Range Calibration (Work Instruction) : TH TH
Uploaded by
Bhadresh PatelOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Normal Probe Range Calibration (Work Instruction) : TH TH
Uploaded by
Bhadresh PatelCopyright:
Available Formats
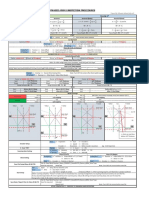
Normal Probe Range Calibration ( work instruction )
1. Select proper ( Normal ) probe & connect with the Machine.
2. Switch on the Machine.
3. Check the Mode ( Single / Dual )
a. Note : To change the mode, go to 5th Menu & 4th Raw, change the mode & come back.
4. Set the Range.
5. Set the velocity 5920 m/s.
6. Set the delay 0.0.
7. Set the gain over 40 db. ( db should be > 40 ).
8. Set the Initial pulse at zero division with the help of zero control.
9. Apply couplant on the reference thickness.
10. Put the probe on the reference thickness.
11. Set lower thickness echo ( left side echo) with zero control & higher thickness echo ( right side
echo) with velocity control.
Range calibration steps.
Ex. Range 0 to 100 mm, Normal probe, 4 Mhz, dia 10 mm, Ref. thk : 25 mm V1 Block.
1. 100 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 10 mm.
2. 25 ÷ 10 = 2.5, 50 ÷ 10 = 5, 75 ÷ 10 = 7.5, 100 ÷ 10 = 10.
Zero control Velocity control
Ex. Range 0 to 125 mm, Normal probe, 4 Mhz, dia 10 mm, Ref. thk : 25 mm Al Block.
1. 125 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 12.5 mm.
2. 25 ÷ 12.5 = 2, 50 ÷ 12.5 = 4, 75 ÷ 12.5 = 6, 100 ÷ 12.5 = 8, 125 ÷ 12.5 = 10
Zero control Velocity control
Ex. Range 0 to 150 mm, Normal probe, 4 Mhz, dia 10 mm, Ref. thk : 50 mm V1 Block.
1. 150 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 15 mm.
2. 50 ÷ 15 = 3.3, 100 ÷ 15 = 6.6, 150 ÷ 15 = 10.
Zero control Velocity control
Practice work.
1. Range 0-175 mm, Ref thk 25 mm.
2. Range 0-200 mm, Ref thk 50 mm.
3. Range 0-600 mm, Ref thk 100 mm.
4. Range 0-800 mm, Ref thk 100 mm.
5. Range 0-160 mm, On job calibration. ( No reference thk. Available ).
TR Probe Range Calibration ( work instruction )
1. Select proper ( TR ) probe & connect with the Machine.
2. Switch on the Machine.
3. Check the Mode ( Single / Dual )
a. Note : To change the mode, go to 5th Menu & 4th Raw, change the mode & come back.
4. Set the Range.
5. Set the velocity 5920 m/s.
6. Set the delay 0.0.
7. Set the gain over 40 db. ( db should be > 40 ).
8. Set the Initial pulse at zero division with the help of zero control.
9. Apply couplant on the reference thickness.
10. Put the probe on the reference thickness.
11. Set lower thickness echo ( left side echo) with zero control & higher thickness echo ( right side
echo) with velocity control.
Range calibration steps.
Ex. Range 0 to 20 mm, TR probe, 4 Mhz, dia 10 mm, Ref. thk : 4 & 10 mm VW Block.
1. 20 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 2 mm.
2. 4 ÷ 2 = 2, 10 ÷ 2 = 5.
Zero control Velocity control
Ex. Range 0 to 30 mm, TR probe, 4 Mhz, dia 10 mm, Ref. thk : 6 & 9 mm VW Block.
1. 30 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 3 mm.
2. 6 ÷ 3 = 2, 9 ÷ 3 = 3.
Zero control Velocity control
Ex. Range 0 to 50 mm, TR probe, 4 Mhz, dia 10 mm, Ref. thk : 25 & 50 mm AL Block.
1. 50 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 5 mm.
2. 25 ÷ 5 = 5, 50 ÷ 5 = 10.
Zero control Velocity control
Practice work
1. Range 0-15 mm, Ref thk. 6 & 9 VW Block.
2. Range 0-10 mm, Ref thk. 5 & 10 VW Block.
Angle Probe Range Calibration ( work instruction )
1. Select proper ( Angle ) probe & connect with the Machine.
2. Switch on the Machine.
3. Check the Mode ( Single / Dual )
a. Note : To change the mode, go to 5th Menu & 4th Raw, change the mode & come back.
4. Set the Range.
5. Set the velocity 3250 m/s.
6. Set the delay 0.0.
7. Set the gain over 40 db. ( db should be > 40 ).
8. Set the Initial pulse at zero division with the help of zero control.
9. Apply couplant on the reference thickness.
10. Put the probe on the reference thickness.
11. Set lower thickness echo ( left side echo) with zero control & higher thickness echo ( right side
echo) with velocity control.
Range calibration steps.
Ex. Range 0 to 100 mm, Angle probe, 4 Mhz, 8 x 9 mm, Ref. Radius : 25 mm V2 Block.
1. 100 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 10 mm.
2. 25 ÷ 10 = 2.5, 100 ÷ 10 = 10.
Zero control Velocity control ( 3250 m/s )
Ex. Range 0 to 125 mm, Angle probe, 4 Mhz, 8 x 9 mm, Ref. Radius : 50 mm V2 Block.
1. 125 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 12.5 mm.
2. 50 ÷ 12.5 = 4, 125 ÷ 12.5 = 10.
Zero control Velocity control ( 3250 m/s )
Ex. Range 0 to 150 mm, Angle probe, 4 Mhz, 8 x 9 mm, Ref. Radius : 25 mm V2 Block.
1. 150 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 15 mm.
2. 25 ÷ 15 = 1.6, 100 ÷ 15 = 6.6.
Zero control Velocity control ( 3250 m/s )
Practice work
1. Range 0 – 125 mm, Ref Radius 25 mm V2 block.
2. Range 0 – 150 mm, Ref Radius 50 mm V2 block.
3. Range 0 – 175 mm, Ref Radius 25 mm V2 block.
4. Range 0 – 175 mm, Ref Radius 50 mm V2 block
5. Range 0 – 200 mm, Ref Radius 25 mm V2 block
6. Range 0 – 200 mm, Ref Radius 50 mm V2 block
Angle probe range calibration & block scanning
Ex. Weld thk 15 mm , Angle 70°
Part A
½ V = Thk / cosθ
= 15 / cos 70° = 43.85 mm
V = 87.71 mm
1 ½ V = 131.56 mm ( So minimum range should be 131.56 mm, but we will take 150 mm round figure)
Part B
Range 0 to 150 mm, Angle probe, 4 Mhz, 8 x 9 mm, Ref. Radius : 25 mm V2 Block.
1. 150 mm ÷ 10 div, therefore 1 div = 15 mm.
2. 25 ÷ 15 = 1.6, 100 ÷ 15 = 6.6.
Zero control Velocity control ( 3250 m/s )
Part C
½ Skip distance = Thk x tanθ
= 15 x tan 70° = 41.21 mm
Full skip distance = 82.42 mm
1 ½ skip distance = 123.63 mm ( so we should scan 123.63 mm both side from weld centre. )
Part D
Set the db for scanning.
Beam path (bp) = ________ division x 1 div. value. ( for this Ex. It is 15 mm ).
Surface distance (sd) = bp x sinθ ( for this Ex. It is sin70° = 0.93 )
Depth (d) = bp x cosθ ( for this Ex. It is cos70° = 0.34 )
Depth > Thk, then 2 Thk – d
Depth > 2 Thk, d – 2 Thk
You might also like
- Home Education Resources NDT Course Material Ultrasound: Calibration MethodsDocument7 pagesHome Education Resources NDT Course Material Ultrasound: Calibration MethodspanduranganraghuramaNo ratings yet
- En 14096-1 Final DraftDocument11 pagesEn 14096-1 Final Draftrizwankhanzhi100% (1)
- What Is NDT ?: Detection of Damage Before BreakdownDocument40 pagesWhat Is NDT ?: Detection of Damage Before BreakdownAnik hasan BadhonNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic TestingDocument4 pagesUltrasonic TestingSyahmie AzreeNo ratings yet
- 38 MM DAC Block - Master SUDHANDocument5 pages38 MM DAC Block - Master SUDHANmaxpan maxNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of Weld RadiographsDocument8 pagesInterpretation of Weld RadiographsMyk MamykinNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument13 pagesInterview QuestionsWalter RuedaNo ratings yet
- UT Shear Wave Skip Distances and Search For Indications LabDocument4 pagesUT Shear Wave Skip Distances and Search For Indications Lab1248a9a9a1q3we71No ratings yet
- RT Examination CheckpointsDocument1 pageRT Examination CheckpointsSantanu SahaNo ratings yet
- Updated Asnt-Ndt Level - II in RT Ut MT PTDocument4 pagesUpdated Asnt-Ndt Level - II in RT Ut MT PTJason RogersNo ratings yet
- ISO Specifications for Non-Destructive TestingDocument4 pagesISO Specifications for Non-Destructive Testingskynyrd75No ratings yet
- High Temperature Ultrasonic ScanningDocument7 pagesHigh Temperature Ultrasonic ScanningscribdmustaphaNo ratings yet
- Austenitic Weld Inspection Solution OverviewDocument17 pagesAustenitic Weld Inspection Solution OverviewRupam BaruahNo ratings yet
- Omniscan TofdDocument4 pagesOmniscan Tofdsdmkl85No ratings yet
- 08 Omniscan ConventionsDocument11 pages08 Omniscan ConventionsLương Hồ VũNo ratings yet
- ECHOGRAPH Ultrasonic Probes Brochure SummaryDocument4 pagesECHOGRAPH Ultrasonic Probes Brochure Summarycarlos100% (1)
- Radiography: Limitations of Rt-MethodDocument25 pagesRadiography: Limitations of Rt-MethodvcpNo ratings yet
- Radiograph Interpretation GuideDocument36 pagesRadiograph Interpretation GuideMaverikbjNo ratings yet
- M.E.Forge Tech: Ultrasonic Inspection ReportDocument1 pageM.E.Forge Tech: Ultrasonic Inspection ReportK.s. Raghavendra KumarNo ratings yet
- IQI Standards of RTDocument1 pageIQI Standards of RTHiren Panchal100% (1)
- Ultrasonic Testing Training (UT) : Level-IIDocument8 pagesUltrasonic Testing Training (UT) : Level-IIAn IkhrandiNo ratings yet
- Pentrmeter SpecificationDocument30 pagesPentrmeter SpecificationJayeshNo ratings yet
- Visual Inspection Guide for WeldsDocument11 pagesVisual Inspection Guide for WeldsAldy Bagus PratamaNo ratings yet
- Major Differences Between API 5L PSL 1 & PSL 2 PipesDocument1 pageMajor Differences Between API 5L PSL 1 & PSL 2 PipesvijayachiduNo ratings yet
- DPI (Dye Penetrant Inspection) : Main PurposedDocument9 pagesDPI (Dye Penetrant Inspection) : Main PurposedAgung Prastyo WibowoNo ratings yet
- RT ProcedureDocument10 pagesRT ProcedureSandeep SundriyalNo ratings yet
- NDT Code Book Made Easy For AsmeDocument398 pagesNDT Code Book Made Easy For AsmeJosé Pablo Espinoza SolísNo ratings yet
- Comparison ASTM A 3388 & ISO 11496Document1 pageComparison ASTM A 3388 & ISO 11496Rahul MoottolikandyNo ratings yet
- Overview of NDT Methods & ApplicationsDocument7 pagesOverview of NDT Methods & Applicationsgeorgescribd1103No ratings yet
- Draft Wps Astm A 743 GR - Ca6nmDocument2 pagesDraft Wps Astm A 743 GR - Ca6nmIlham PaneNo ratings yet
- Dac CurveDocument24 pagesDac Curvesantu_23No ratings yet
- Inspection of Composite Rocket Nozzle PDFDocument10 pagesInspection of Composite Rocket Nozzle PDFHari KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing ManualDocument88 pagesUltrasonic Testing ManualphillipskincaidNo ratings yet
- Iqi TableDocument3 pagesIqi TableverdiblueNo ratings yet
- Beamtool Scan Plan Inspection Layout: 50Mm 289Mm 223Mm 0Mm Steel 1020 3.24Mm/Μs 5.89Mm/ΜsDocument3 pagesBeamtool Scan Plan Inspection Layout: 50Mm 289Mm 223Mm 0Mm Steel 1020 3.24Mm/Μs 5.89Mm/Μsநந்த குமார் சம்பத் நாகராஜன்No ratings yet
- 0455e - Welding Inspector Visual Acuity Record PDFDocument1 page0455e - Welding Inspector Visual Acuity Record PDFAbu HanifaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18-UTDocument50 pagesLecture 18-UTsamrn850% (2)
- Circ-it configured Environmental SpecificationsDocument2 pagesCirc-it configured Environmental SpecificationsMarcos Kaian Moraes RodriguesNo ratings yet
- Visual Testing: - Asme - Section 5 (NDT) - Section 5 - Article 9 (VT)Document29 pagesVisual Testing: - Asme - Section 5 (NDT) - Section 5 - Article 9 (VT)MAXX ENGINEERS100% (1)
- Material Specifications and Mechanical PropertiesDocument1 pageMaterial Specifications and Mechanical PropertiesSagarKBLNo ratings yet
- A General Review of The Causes and Acceptance of Shape ImperfectionsDocument7 pagesA General Review of The Causes and Acceptance of Shape ImperfectionsMuhammed SulfeekNo ratings yet
- Liquid Penetrant InspectionDocument83 pagesLiquid Penetrant InspectionAzhar GulzarNo ratings yet
- LPT As Per Asme & IsoDocument2 pagesLPT As Per Asme & IsosbmmlaNo ratings yet
- Gray Shades PDFDocument1 pageGray Shades PDFbgonzalez1981No ratings yet
- PA Probe Catalog en 201304Document24 pagesPA Probe Catalog en 201304Durgamadhaba Mishra100% (2)
- Cast Steel GradesDocument5 pagesCast Steel Gradessohan_miyawala1906No ratings yet
- UT Chapter 11Document70 pagesUT Chapter 11knizam1971100% (1)
- Phased Array Ut PDFDocument32 pagesPhased Array Ut PDFgueridiNo ratings yet
- General and technical data on the Rotoscan ultrasonic pipeline inspection systemDocument15 pagesGeneral and technical data on the Rotoscan ultrasonic pipeline inspection systemElsayed AbdeenNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Examination ProcedureDocument20 pagesRadiographic Examination ProcedureMohanadNo ratings yet
- DGS DGS MethodDocument6 pagesDGS DGS MethodAlzaki AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Spec Sheet - Handler 187Document4 pagesSpec Sheet - Handler 187Hobart Welding ProductsNo ratings yet
- Procedure PAUT PDFDocument1 pageProcedure PAUT PDFScribd ScribdNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Test Procedure1Document8 pagesUltrasonic Test Procedure1MHDNo ratings yet
- MA 40 ManualDocument18 pagesMA 40 ManualJOSE ABRAHAM GONZALEZNo ratings yet
- USFD of Rails and WeldsDocument9 pagesUSFD of Rails and WeldsVISWANADH KUCHIBHOTLANo ratings yet
- Performing Transmitter Hum and Noise Measurement Per TIA-603-CDocument7 pagesPerforming Transmitter Hum and Noise Measurement Per TIA-603-CJim0% (1)
- Specifications: DESCRIPTION: Electret Condenser Microphone Part Number: Cma-6542PfDocument4 pagesSpecifications: DESCRIPTION: Electret Condenser Microphone Part Number: Cma-6542PfIordache AdrianNo ratings yet
- Piezoelectronic Buzzers: Pin Terminal/lead Without Oscillator CircuitDocument8 pagesPiezoelectronic Buzzers: Pin Terminal/lead Without Oscillator CircuitSrinu SrinivasaraoNo ratings yet
- E50P Carenado Prodigy G1000Document33 pagesE50P Carenado Prodigy G1000Jesús Sánchez100% (1)
- GP1850 Service Manual - FurunoDocument24 pagesGP1850 Service Manual - FurunoCarlos Proaño100% (1)
- Harsh Iit Kanpur CVDocument3 pagesHarsh Iit Kanpur CVapi-293629330No ratings yet
- Asme Section Ii A Sa-426 PDFDocument6 pagesAsme Section Ii A Sa-426 PDFAnonymous GhPzn1xNo ratings yet
- Inversor Min Growatt 8000 TL XDocument2 pagesInversor Min Growatt 8000 TL XIngenieria 2No ratings yet
- GeoxdrawDocument12 pagesGeoxdrawWelsinsin Kevin SinNo ratings yet
- Colonie Findings With AttmtDocument130 pagesColonie Findings With AttmtTown of Colonie LandfillNo ratings yet
- 520 Um001 - en e PDFDocument244 pages520 Um001 - en e PDFAlanAvtoNo ratings yet
- HITACHI-Spare Parts Price ListDocument481 pagesHITACHI-Spare Parts Price Listrachitmail84% (31)
- NetApp Cluster Mode CDOT 8Document10 pagesNetApp Cluster Mode CDOT 8rahulchaudhry007No ratings yet
- Transformer Protection Relay GRE160 Brochure 12027-1 0Document22 pagesTransformer Protection Relay GRE160 Brochure 12027-1 0tanujaayerNo ratings yet
- Guia Técnico - Tomadas Industriais PDFDocument26 pagesGuia Técnico - Tomadas Industriais PDFNuno HenriquesNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Synthesis of DilantinDocument9 pagesFigure 1 Synthesis of Dilantinstepkim92No ratings yet
- RP 30 2 Selection and Use of Measurement InstrumentDocument212 pagesRP 30 2 Selection and Use of Measurement Instrumentmohammed el erianNo ratings yet
- PCAB CFY 2014 2015 List of ContractorsDocument570 pagesPCAB CFY 2014 2015 List of ContractorsRobert Ramirez100% (4)
- Design of Tank and Tubes - TransformersDocument6 pagesDesign of Tank and Tubes - TransformersAJAY KOSHY PS 18-20No ratings yet
- Model 3410: Shear Beam Load CellsDocument4 pagesModel 3410: Shear Beam Load CellsIvanMilovanovicNo ratings yet
- L Gate User ManualDocument161 pagesL Gate User ManualNguyen Manh ThangNo ratings yet
- Construction materials and supplies itemizationDocument7 pagesConstruction materials and supplies itemizationGintokiNo ratings yet
- Manufacture of UreaDocument86 pagesManufacture of UreamohamedNo ratings yet
- Robot Gripper DesignDocument51 pagesRobot Gripper DesignDug McCallumNo ratings yet
- Ziegler-Mfm-3480 Manual-E1R0Document78 pagesZiegler-Mfm-3480 Manual-E1R0Naveed Syed MohammadNo ratings yet
- Analysys Mason VNGN OSS Framework Sep2015 RMA16 RMA07Document35 pagesAnalysys Mason VNGN OSS Framework Sep2015 RMA16 RMA07Yousuf_Alqeisi100% (1)
- Curriculum Vitae: Working ExperienceDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Working ExperienceSiti AjiraNo ratings yet
- Request For Quotation - Pile WorksDocument2 pagesRequest For Quotation - Pile WorksOsama MZNo ratings yet
- Ground effects on pressure fluctuations in atmospheric boundary layersDocument21 pagesGround effects on pressure fluctuations in atmospheric boundary layersArchie PapNo ratings yet
- Information Systems 363 Stair Chapter 3 11th EditionDocument55 pagesInformation Systems 363 Stair Chapter 3 11th EditionVictoria NguyenNo ratings yet
- Construction checklist for GI trunking installationDocument1 pageConstruction checklist for GI trunking installationMAZHALAI SELVANNo ratings yet
- Restraint System Assembly: With Illustrated Parts ListDocument35 pagesRestraint System Assembly: With Illustrated Parts ListEdwar ZulmiNo ratings yet