Professional Documents
Culture Documents
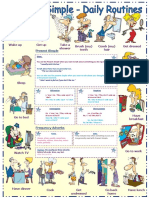
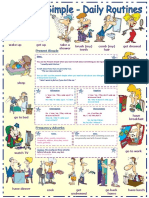
Daily Routines
Uploaded by
Lucía Maribel TeranCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
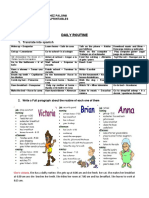
Daily Routines
Uploaded by
Lucía Maribel TeranCopyright:
Available Formats
Daily routines
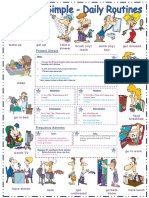
I usually get up at 6:30 am every morning. I take shower at 7:00
o’clock. I get dresses at 7:15 am. I do breakfast at 8:00 o’clock. After
that I brush my teeth. I study English at 9:00 o’clock. I finish to
study English at 11:00 o’clock. I return at home at 11:15 am. I
always have a lunch at 1:00 o’clock. After that I listen to music at
2:00 oclock. I go to work at 3:00 o’clock. I usually play with my dog
at 3:30 pm. I also surf in the internet at 4:00 o’cloock. Then I go with
my family to the mall at 6:00 o’clock. I have dinner at 6:30 pm. After
that I return at home at 7:30 pm. Also I watch tv with my family at
8:00 o’clock. Then I go to bed at 10:00 o’clock. First I go to sleep at
11:15 pm.
Daily routine
Spanish English
DAILY ROUTINE
despertar to wake someone up
Su madre la despierta a las ocho. Her mother wakes her up at 8 o'clock.
despertarse to wake up
Me despierto muy temprano. I wake up very early.
Levantarse to get up
hacer la cama to make the bed
Vestirse to get dressed
Preparase to get ready
Ducharse to have a shower
Bañarse to have a bath
Lavarse to have a wash
lavarse los dientes to clean your teeth
cepillarse los dientes to brush your teeth
lavarse el pelo / la cabeza to wash your hair
secarse el pelo to dry your hair
cepillarse el pelo to brush your hair
Peinarse to comb your hair
secarse las manos to dry your hands
Afeitarse to have a shave
limpiarse los zapatos to clean your shoes
maquillarse / pintarse to put on makeup
ponerse las lentillas to put in your contact lenses
ponerse la dentadura postiza;
to put in your false teeth
ponerse los dientes postizos
desayunar / tomar el desayuno to have breakfast
almorzar / comer to have lunch
Cenar to have dinner
hacer la comida to cook lunch, to get lunch ready
dar de comer al gato / perro to feed the cat / dog
regar las plantas to water the plants
poner la radio / televisión to switch on the radio / televisión
escuchar el radio to listen to the radio
ver la televisión / tele to watch television / telly
ir al colegio / al trabajo / a la universidad to go to school / work / university / the
/ a la oficina office
tomar / coger* el autobús / tren to catch the bus / train
empezar a trabajar / entrar a trabajar to start work
llegar a casa to get home (from work)
ir a casa to go home
desvestirse / desnudarse to get undressed
Acostarse to go to bed
poner el despertador to set the alarm clock
tomarse un descanso / echarse una siesta to have a rest
Dormirse to fall asleep
quedarse dormido to oversleep
pasar la noche en vela to have a sleepless night
tener insomnio / sufrir de insomnio to suffer from insomnia
*Note: Be very careful with these two verbs depending on which Spanish speaking
country you are in.
In Spain, it is very common to use the verb "coger".
However, this has a completely different, sexual meaning in certain South American
countries. So, if you are in South America, it's safer to use "tomar".
DAILY ROUTINE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
¿A qué hora te levantas? What time do you get up?
¿Con qué frecuencia vas al cine?
How often do you go to the cinema?
¿Cada cuánto vas al cine?
Voy al cine una vez / dos veces a la I go to the cinema once / twice a week /
semana / al mes / al año. month / year.
A veces / Nunca voy al teatro. I sometimes / never go to the theatre.
Voy al teatro a menudo. I often go to the theatre.
¿Cuánto tardas en llegar al trabajo? How long does it take you to get to work?
¿Dónde vives? Where do you live?
¿Cuánto café bebes? How much coffee do you drink?
¿Qué sueles desayunar? What do you usually have for breakfast?
¿Cómo llegas al colegio? How do you get to school?
¿A qué hora te acuestas? What time do you go to bed?
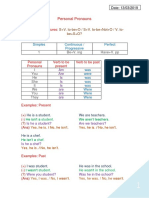
A NOTE ON REFLEXIVE VERBS
A lot of these verbs are reflexive e.g. to wash my hair = lavarse el pelo.
In English, the verb does not change but the possessive adjective before hair changes
to reflect who is doing the action.
In Spanish, the verb is reflexive and changes to reflect who is doing the action.
Note: normally in Spanish, it is not normally necessary to use the subject pronoun (Yo,
Tú, Él, Ella, Nosotros, Vosotros, Ellos, Ellas). However, if you need to distinguish
between a girl and a boy then it is possible to include it (see below).
Me lavo el pelo. I wash my hair.
Te lavas el pelo. You wash your hair.
Se lava el pelo He washes his hair.
Se lava el pelo. She washes her hair.
Nos lavamos el pelo. We wash our hair.
Os laváis el pelo. You wash your hair.
Se lavan el pelo. They wash their hair.
Él se lava el pelo por la mañana pero ella He washes his hair in the morning but she
se lava el pelo por la tarde. washes her hair in the afternoon.
You might also like
- Psych 1xx3 Quiz AnswersDocument55 pagesPsych 1xx3 Quiz Answerscutinhawayne100% (4)
- Christos A. Ioannou & Dimitrios A. Ioannou, Greece: Victim of Excessive Austerity or of Severe "Dutch Disease"? June 2013Document26 pagesChristos A. Ioannou & Dimitrios A. Ioannou, Greece: Victim of Excessive Austerity or of Severe "Dutch Disease"? June 2013Christos A IoannouNo ratings yet
- Exercicios Inglês 6º Ano p15Document1 pageExercicios Inglês 6º Ano p15carlbispNo ratings yet
- Present Past Simple Vs Past Present Continuous RevisionDocument14 pagesPresent Past Simple Vs Past Present Continuous RevisionMarta Norton CondeNo ratings yet
- Listening comprehension worksheetDocument2 pagesListening comprehension worksheetKhinPhyuPhyu KhaingNo ratings yet
- Ficha 5 SM InglesDocument69 pagesFicha 5 SM InglesCarmenMartinNo ratings yet
- Daily routine of a famous footballerDocument10 pagesDaily routine of a famous footballerElsaMariaMalheiroNo ratings yet
- Daily routines under 40 charactersDocument1 pageDaily routines under 40 charactersLópez Sánchez JonásNo ratings yet
- ANCIENT HISTORY Started When People Invented - This Was in AboutDocument3 pagesANCIENT HISTORY Started When People Invented - This Was in AboutAlba CubilloNo ratings yet
- Stopwatch 4 Standard Test U1 1bguDocument3 pagesStopwatch 4 Standard Test U1 1bguDiego Samaniego100% (1)
- Unit 3 Yummy TesteDocument5 pagesUnit 3 Yummy TesteFernando Santos Pastores AlemãesNo ratings yet
- Physical and Psychological Description: Fast Worksheet 4Document2 pagesPhysical and Psychological Description: Fast Worksheet 4cisternNo ratings yet
- (Lê o Texto.) : True FalseDocument4 pages(Lê o Texto.) : True Falseluprof tpNo ratings yet
- Asking For and Giving DirectionsDocument6 pagesAsking For and Giving DirectionsMilenitha RangelNo ratings yet
- Tercer Grado InglesDocument68 pagesTercer Grado InglesAlejandra DCPNo ratings yet
- Apoio Ao Estudo: Past Simple - Irregular Verbs (Unit 5)Document2 pagesApoio Ao Estudo: Past Simple - Irregular Verbs (Unit 5)Paula PereiraNo ratings yet
- My name is Julia, a 10-year-old who wants to be a teacherDocument1 pageMy name is Julia, a 10-year-old who wants to be a teacherNicole TorresNo ratings yet
- Daily Routine and QuestionsDocument4 pagesDaily Routine and QuestionsLeidy Johanna Sotelo LopezNo ratings yet
- Daily Routine - Rutina DiariaDocument5 pagesDaily Routine - Rutina DiariaYoselinRamosNo ratings yet
- Aily Routine - Rutina DiariaDocument5 pagesAily Routine - Rutina DiariaAnonymous wWgeW44No ratings yet
- Daily RoutineDocument4 pagesDaily RoutineJust ShowNo ratings yet
- Daily routines in Spanish and EnglishDocument3 pagesDaily routines in Spanish and EnglishJuan EchavarríaNo ratings yet
- Daily Routine - Rutina DiariaDocument5 pagesDaily Routine - Rutina DiariaIvancito Iinanovich HuamanNo ratings yet
- Daily Routine VocabularyDocument3 pagesDaily Routine VocabularyAkili ArmaniNo ratings yet
- RutinasDocument2 pagesRutinasKevin Jonathan Mendez LopezNo ratings yet
- Daily Activities at HomeDocument6 pagesDaily Activities at HomeAlexander BacilioNo ratings yet
- VOCABULARY Daily RoutineDocument3 pagesVOCABULARY Daily Routinecristylersam7No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Page 37 Lesson B4A LIST OF DAILY ACTIVITIES (PRESENT)Document1 pageUnit 4 Page 37 Lesson B4A LIST OF DAILY ACTIVITIES (PRESENT)alfonso compradorNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Page 36 Lesson B1A LIST OF DAILY ACTIVITIES (PRESENT)Document1 pageUnit 4 Page 36 Lesson B1A LIST OF DAILY ACTIVITIES (PRESENT)alfonso compradorNo ratings yet
- Unit 7. Activities and RoutinesDocument17 pagesUnit 7. Activities and RoutinesDeyvis Sanchez PerezNo ratings yet
- Present Tense & Daily RoutinesDocument13 pagesPresent Tense & Daily Routineslizbeth lilianaNo ratings yet
- Portfolio of EvidenceDocument28 pagesPortfolio of EvidenceEduardo RamosNo ratings yet
- English 1-Clase 3Document4 pagesEnglish 1-Clase 3Liz Estefany Pacompia ChambillaNo ratings yet
- Español Inglés Español InglésDocument8 pagesEspañol Inglés Español InglésKris LMNo ratings yet
- Evaluation SpeakingDocument4 pagesEvaluation SpeakingJessica SuastesNo ratings yet
- English Work: Verbs-Simple Present TenseDocument4 pagesEnglish Work: Verbs-Simple Present Tensepaulo lynchNo ratings yet
- English To SpanishDocument2 pagesEnglish To SpanishkvijayvinoNo ratings yet
- Daily routines and activities in Spanish and EnglishDocument5 pagesDaily routines and activities in Spanish and EnglishDalia Alvarenga100% (2)
- Https:API.schoology.comv1attachment1620217851source76ce5ee7cfc246acb538633fd78bd5ccDocument4 pagesHttps:API.schoology.comv1attachment1620217851source76ce5ee7cfc246acb538633fd78bd5cccrazyunicorngal12345No ratings yet
- Daily RoutineDocument10 pagesDaily RoutineAngiePamelaLozadaBalcazarNo ratings yet
- SpanishReflexiveVerbsandDailyRoutines PDFDocument5 pagesSpanishReflexiveVerbsandDailyRoutines PDFDylan FrazierNo ratings yet
- Verbes PronominauxDocument3 pagesVerbes Pronominaux111961No ratings yet
- Team Engagement Meeting Ideas by SlidesgoDocument8 pagesTeam Engagement Meeting Ideas by SlidesgoLaura LombanaNo ratings yet
- Routine DailyDocument1 pageRoutine DailyDoménica LópezNo ratings yet
- Present Simple: Wake Up Get Up Take A Shower Comb (My) Hair Get Dressed Brush (My) TeethDocument3 pagesPresent Simple: Wake Up Get Up Take A Shower Comb (My) Hair Get Dressed Brush (My) TeethAzuna77No ratings yet
- How To Form The Perfect TenseDocument9 pagesHow To Form The Perfect TenseKribsyNo ratings yet
- Daily Routine ProjectDocument3 pagesDaily Routine Projectmaría camila ortiz canoNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Tense Daily RoutineDocument3 pagesPresent Simple Tense Daily RoutinePedro RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Daily Routine: 1. Translate Into SpanishDocument3 pagesDaily Routine: 1. Translate Into SpanishJORGE LEONARDO BOLIVAR ZAMBRANONo ratings yet
- VOCABULARIO Y EXPRESIONES ESENCIALESDocument18 pagesVOCABULARIO Y EXPRESIONES ESENCIALESYuliana VeraNo ratings yet
- 10 Page A Level Grammar Reviewpart B Grammar Guides 105985Document10 pages10 Page A Level Grammar Reviewpart B Grammar Guides 105985Sardariu AlexNo ratings yet
- Present Simple Workshop 2019Document3 pagesPresent Simple Workshop 2019Surlye100% (1)
- Lesson 2:: Daily ActivitiesDocument5 pagesLesson 2:: Daily ActivitiesJein PatilaNo ratings yet
- 3 Material - RoutinesDocument6 pages3 Material - RoutinesJHON JAIRO HIDALGO ARTEAGANo ratings yet
- Present Simple Affimative FormDocument10 pagesPresent Simple Affimative FormEDU ALONSO CASTILLO VILELANo ratings yet
- WorkbookDocument10 pagesWorkbookJorge CardenasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 04Document44 pagesLesson 04Alexander FloresNo ratings yet
- French Exam Revision GuideDocument7 pagesFrench Exam Revision GuideMahi Jayesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Simple Present and Adverbs of FrequencyDocument5 pagesSimple Present and Adverbs of FrequencyNatalia GomezNo ratings yet
- Simple - Present-Daily-Routines & Frequency-AdverbsDocument3 pagesSimple - Present-Daily-Routines & Frequency-Adverbsalexander vegaNo ratings yet
- Daily Spanish Routines and ActivitiesDocument3 pagesDaily Spanish Routines and ActivitiesNandoNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 Daily RoutineDocument24 pagesUNIT 3 Daily RoutineJimy PeraltaNo ratings yet
- A4 and b1Document6 pagesA4 and b1Lucía Maribel TeranNo ratings yet
- DialogueDocument1 pageDialogueLucía Maribel TeranNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronauns: Sentence StructuresDocument3 pagesPersonal Pronauns: Sentence StructuresLucía Maribel TeranNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronauns: Sentence StructuresDocument3 pagesPersonal Pronauns: Sentence StructuresLucía Maribel TeranNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronauns: Sentence StructuresDocument3 pagesPersonal Pronauns: Sentence StructuresLucía Maribel TeranNo ratings yet
- Personal Pronauns: Sentence StructuresDocument3 pagesPersonal Pronauns: Sentence StructuresLucía Maribel TeranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Managing Quality (Sesi 3)Document68 pagesChapter 6 Managing Quality (Sesi 3)Nurmala SariNo ratings yet
- UnitTest D10 Feb 2024Document26 pagesUnitTest D10 Feb 2024dev.shah8038No ratings yet
- 1.1 Enterprise AssessmentDocument1 page1.1 Enterprise AssessmentGermanRobertoFongNo ratings yet
- B.Ed Syllabus NEW 2015-16 PDFDocument170 pagesB.Ed Syllabus NEW 2015-16 PDFVikas KuthadiNo ratings yet
- Crashing Pert Networks: A Simulation ApproachDocument15 pagesCrashing Pert Networks: A Simulation ApproachRavindra BharathiNo ratings yet
- Forecast Time Series-NotesDocument138 pagesForecast Time Series-NotesflorinNo ratings yet
- Gfk-1383a 05012Document108 pagesGfk-1383a 05012occhityaNo ratings yet
- Engagement LetterDocument1 pageEngagement LetterCrystal Jenn Balaba100% (1)
- JMPRTraininga I5545e PDFDocument500 pagesJMPRTraininga I5545e PDFmvptoxNo ratings yet
- Lecture Euler EquationDocument33 pagesLecture Euler EquationYash RajNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Task 3 - A C P I WK 2Document8 pagesTutorial Task 3 - A C P I WK 2BM70621 Alya Zahirah Binti AziziNo ratings yet
- IEC61508 GuideDocument11 pagesIEC61508 Guidesrbehera1987No ratings yet
- Technology Class ResumeDocument4 pagesTechnology Class Resumeapi-259588430No ratings yet
- Hotel Engineering Facilities: A Case Study of Maintenance PerformanceDocument7 pagesHotel Engineering Facilities: A Case Study of Maintenance PerformanceHoh Pui KeiNo ratings yet
- Constructivism improves a lesson on nounsDocument6 pagesConstructivism improves a lesson on nounsOlaniyi IsaacNo ratings yet
- Training Report On Machine LearningDocument27 pagesTraining Report On Machine LearningBhavesh yadavNo ratings yet
- Api RP 2a WSD 1pdf - CompressDocument1 pageApi RP 2a WSD 1pdf - CompressRamesh SelvarajNo ratings yet
- Nitobond SBR (Latex)Document4 pagesNitobond SBR (Latex)Samarakoon Banda100% (1)
- Arduino Programming Step by Step Guide To Mastering Arduino Hardware and SoftwareDocument109 pagesArduino Programming Step by Step Guide To Mastering Arduino Hardware and SoftwareMohan100% (3)
- Heather Bianco 2016 Resume Revised PDFDocument3 pagesHeather Bianco 2016 Resume Revised PDFapi-316610725No ratings yet
- X-Ray Generator Communication User's Manual - V1.80 L-IE-4211Document66 pagesX-Ray Generator Communication User's Manual - V1.80 L-IE-4211Marcos Peñaranda TintayaNo ratings yet
- Classical Fields 2Document2 pagesClassical Fields 2Jonathan SanchezNo ratings yet
- Pick Pack Ship Public APIDocument19 pagesPick Pack Ship Public APIgauravpuri198050% (2)
- LINDA ALOYSIUS Unit 6 Seminar Information 2015-16 - Seminar 4 Readings PDFDocument2 pagesLINDA ALOYSIUS Unit 6 Seminar Information 2015-16 - Seminar 4 Readings PDFBence MagyarlakiNo ratings yet
- HFH ch04Document11 pagesHFH ch04Harikrishan RNo ratings yet
- Concurrent AuditorDocument67 pagesConcurrent AuditorAjoydeep DasNo ratings yet
- Inna Phos Diammonium Phosphate MSDSDocument9 pagesInna Phos Diammonium Phosphate MSDSjosephNo ratings yet
- Radio Codes and ConventionsDocument2 pagesRadio Codes and Conventionsapi-570661298No ratings yet