Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CT 5 Ans e
Uploaded by
WP YiuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CT 5 Ans e
Uploaded by
WP YiuCopyright:
Available Formats
Marking scheme
5 Metabolism and enzymes
A. Multiple-choice questions (10 marks)
1. A 2. C 3. C 4. C 5. B
6. A 7. C 8. A 9. D 10. A
(1 mark each)
B. Short questions (12 marks)
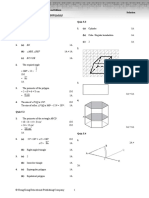
1. (a) Concentration of substrate (1)
(b) Concentration of enzyme (1)
(c) (i) Z (1)
(ii) X (1)
(d) (i) The enzyme activity and slope of the curve are lower then that of the original curve. (1)
(ii) There is no enzyme activity even the substrate concentration increase as the enzyme is
denatured. (1)
enzyme Y
activity
10 oC
X 100 oC
substrate concentration
(Total: 6 marks)
3. (a) Babies cannot (fully) digest proteins in their food / Allows babies to absorb proteins more easily.
(1)
(b) protease (1)
(c) (i) B (1)
It can digest all / 100% protein (1)
at the lowest temperature (15 oC). (1)
(ii) reduces production cost / uses less energy / preserves more nutritional value (1)
(Total: 6 marks)
HKDSE BIOLOGY—Concepts and Applications
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd. Chapter Test 5-M1
C. Structured questions (18 marks)
1. (a) Effect of sucrase concentration
on the rate of sucrose digestion
Time required to
digest the sucrose
(second)
Sucrase concentration (%)
(4)
(b) The time required to digest sucrose decreases when the concentration of sucrase increases. (2)
More active sites are available to bind with sucrase. (1)
(c) It is because this is the optimum temperature for most enzymes to work / to minimise the effect
of temperature on enzyme action. (1)
o
(d) Use a water bath of 40 C (1)
(Total: 9 marks)
2. (a) (i) Vinegar has low pH / is acidic. (1)
Enzymes involved in the browning process are denatured. (1)
(ii) Low temperature decreases the enzyme activity. (1)
Enzymes involved in the browning process are inactivated and the browning process occurs
at a slower rate. (1)
(b) Any five of the following: (max. 5)
Cut apple into cubes with the same size (1)
The apple cubes are cut from same apple (1)
The apple cubes are treated under same condition – e.g. temperature / volume of pH solution
(1)
Immerse the apple cubes into solutions of varying pH (minimum 3 different pH) (1)
Explain how pH is to be controlled – e.g. use of buffers / dilute acid and dilute alkali and
water (1)
Compare colour after set time period (1)
Repetitions (1)
Plot graph / use of table / display results in some acceptable way (1)
(Total: 9 marks)
HKDSE BIOLOGY—Concepts and Applications
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd. Chapter Test 5-M2
D. Essay (11 marks)
Enzyme concentration (max. 3)
Rate of reaction increases with increasing enzyme concentration (1)
More active sites are available to bind with the substrate (1)
The rate increases as long as substrate molecules are in excess (1)
The rate decreases when substrate molecules are used up (1)
Temperature (max. 3)
Enzyme works well in a narrow range of temperature (1)
Enzyme works best at the optimum temperature (1)
Rate of reaction increases with increasing temperature (1)
Higher temperature provides more (kinetic) energy for enzyme and substrate (1)
Enzyme and substrate move faster and collide more frequently (1)
The chance of forming enzyme-substrate complex increases (1)
High temperature may denature the enzyme (1)
Low temperature may inactivate the enzyme (1)
Inhibitor (max. 2)
Inhibitor will decrease the rate of enzymatic reaction (1)
Case 1
Inhibitor has similar shape to substrate (1)
The inhibitor fit / occupy the active site for short time / temporary / reversible (1)
prevents the substrate from binding with the active site (1)
The rate determined by the concentration of inhibitor (1)
The effect of the inhibitor can be reversed by increasing substrate concentration (1)
Case 2
Inhibitor does not compete for the active sites with substrates (1)
They bind to the enzyme at a different place other than the active site (1)
The shape of the enzyme molecule changes (1)
The active site no longer fits the substrate(s), thereby reducing or stopping enzyme activity (1)
Increasing the concentration of substrates cannot resume the rate of enzyme reaction (1)
Communication (max. 3)
HKDSE BIOLOGY—Concepts and Applications
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd. Chapter Test 5-M3
You might also like
- All About SelfDocument10 pagesAll About SelfWP YiuNo ratings yet
- LH - Ap - bk10 - L - Ans (Set 1)Document4 pagesLH - Ap - bk10 - L - Ans (Set 1)WP YiuNo ratings yet
- Answer EngDocument6 pagesAnswer EngWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Answer EngDocument18 pagesAnswer EngWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Applications of Percentages (1) : What Percentage of Each Whole Figure Below Is The Shaded Part?Document2 pagesApplications of Percentages (1) : What Percentage of Each Whole Figure Below Is The Shaded Part?WP YiuNo ratings yet
- 7 TiyuDocument18 pages7 TiyuWP YiuNo ratings yet
- A Christmas Carol: by Charles DickensDocument38 pagesA Christmas Carol: by Charles DickensTom ScottNo ratings yet
- Document 2Document2 pagesDocument 2WP YiuNo ratings yet
- 4A05 Section 1 Quiz E MarkingDocument1 page4A05 Section 1 Quiz E MarkingWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Education Bureau: 1. D C 3. C 4. B 5. C 6. ADocument3 pagesEducation Bureau: 1. D C 3. C 4. B 5. C 6. AWP YiuNo ratings yet
- 325234Document3 pages325234WP YiuNo ratings yet
- Int P601e1Document12 pagesInt P601e1WP YiuNo ratings yet
- Comp A Set 1.2 IdeasBankDocument3 pagesComp A Set 1.2 IdeasBankWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Eunice 2 CDocument2 pagesEunice 2 CWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Extra 08Document8 pagesExtra 08WP YiuNo ratings yet
- 1A Ch05 On2016 Quiz5.1 EDocument1 page1A Ch05 On2016 Quiz5.1 EWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Document 16 RDocument2 pagesDocument 16 RWP YiuNo ratings yet
- 4A05 Section 2 Quiz E MarkingDocument1 page4A05 Section 2 Quiz E MarkingWP YiuNo ratings yet
- 1A Ch05 On2016 Sol EDocument3 pages1A Ch05 On2016 Sol EWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Able OF Ontents: Warm-Up ExerciseDocument3 pagesAble OF Ontents: Warm-Up ExerciseWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Section Quiz 5.2: Suggested Solutions Marks RemarksDocument1 pageSection Quiz 5.2: Suggested Solutions Marks RemarksWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - TestDocument5 pagesChapter 5 - TestWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Section Quiz 5.2: Suggested Solutions Marks RemarksDocument1 pageSection Quiz 5.2: Suggested Solutions Marks RemarksWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Moment of A ForceDocument17 pagesChapter 5 Moment of A ForceWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Able OF Ontents: Warm-Up ExerciseDocument3 pagesAble OF Ontents: Warm-Up ExerciseWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Overall Plan: China and The WorldDocument33 pagesOverall Plan: China and The WorldWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Thinking Skill: Comprehension Thinking Strategy: Flow ChartDocument1 pageThinking Skill: Comprehension Thinking Strategy: Flow ChartWP YiuNo ratings yet
- Sore:: Difficulty Remembering Order Tasks Hate Soggy Try Eat Quickly Voice Started Spent TimeDocument1 pageSore:: Difficulty Remembering Order Tasks Hate Soggy Try Eat Quickly Voice Started Spent TimeWP YiuNo ratings yet
- 2011-Mathematics II KeyDocument1 page2011-Mathematics II KeyWP YiuNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research: Narendra P. SinghDocument8 pagesMutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research: Narendra P. SinghAndrea bedoya vasquezNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 15-ENZYMESDocument4 pagesWorksheet 15-ENZYMESNaz BasaranNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive TransportDocument2 pagesActive and Passive TransportMaricon TubonNo ratings yet
- Copy of Quiz-Glycolysis and FermentationDocument6 pagesCopy of Quiz-Glycolysis and FermentationParisa YahyaieNo ratings yet
- Genetic EngineeringDocument5 pagesGenetic Engineeringapi-247770724No ratings yet
- Biotech Q4 Weke 5 6Document23 pagesBiotech Q4 Weke 5 6Arins Zae BajamundiNo ratings yet
- The NF-KB PathwayDocument4 pagesThe NF-KB PathwayAndri Praja Satria100% (1)
- DNA Polymerase IIIDocument24 pagesDNA Polymerase IIIAhmad JavaidNo ratings yet
- Biology SL Paper 2 3 PDFDocument8 pagesBiology SL Paper 2 3 PDFAna OlveraNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Global H3K27me Enhances HER2ErbB2 Targeted Therapy2019Cell ReportsOpen Access PDFDocument18 pagesReduction of Global H3K27me Enhances HER2ErbB2 Targeted Therapy2019Cell ReportsOpen Access PDFLorena RamosNo ratings yet
- DNA Extraction: Qualitative Estimation of Genomic DNADocument32 pagesDNA Extraction: Qualitative Estimation of Genomic DNAPAWANKUMAR S. K.No ratings yet
- BiotechnologyDocument10 pagesBiotechnologymike_pangNo ratings yet
- Transcription Kezia Joice BautistaDocument43 pagesTranscription Kezia Joice BautistaKeziajoicee Bautista0% (1)
- NCBI HandbookDocument391 pagesNCBI HandbookRohnWoodNo ratings yet
- Chapter FourDocument75 pagesChapter Fourkel GetanehNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Purification of Putative Pentr4:Campari ClonesDocument10 pagesIsolation and Purification of Putative Pentr4:Campari ClonesBrittani HyltonNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument6 pagesRespiration in PlantsAadil ShakulNo ratings yet
- Unit VII - Nucleic Acids - MCONDocument30 pagesUnit VII - Nucleic Acids - MCONikram ullah khanNo ratings yet
- Bachelor of Science in BiochemistryDocument5 pagesBachelor of Science in Biochemistryho.caroline112No ratings yet
- Bacterial Staining TechniquesDocument3 pagesBacterial Staining TechniquesSeerat FatimaNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 - Introduction Qand HistoryDocument37 pagesLec 1 - Introduction Qand HistorySatyam AryaNo ratings yet
- Proteomics: Higher 3 (2017) (Syllabus 9815)Document12 pagesProteomics: Higher 3 (2017) (Syllabus 9815)Lester LimNo ratings yet
- How Many Plants in The List Given Below Have Tap Root Modifications - Banyan, VandaDocument9 pagesHow Many Plants in The List Given Below Have Tap Root Modifications - Banyan, VandaroseNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Notes - CellsDocument3 pagesO Level Biology Notes - CellsRakib Ahsan86% (7)
- M Scan BrochureDocument8 pagesM Scan BrochureM-ScanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids, Peptides and ProteinsDocument41 pagesAmino Acids, Peptides and ProteinsHeraNo ratings yet
- Y Chromosome Fact SheetDocument1 pageY Chromosome Fact SheetTzuyu TchaikovskyNo ratings yet
- 15.1-Worksheet 2Document3 pages15.1-Worksheet 2Remas NBNo ratings yet
- Basic EndocrinologyDocument43 pagesBasic EndocrinologyAnanya MajilaNo ratings yet
- AAV9-mediated Schwann Cell-Targeted Gene Therapy Rescues A Model of Demyelinating NeuropathyDocument17 pagesAAV9-mediated Schwann Cell-Targeted Gene Therapy Rescues A Model of Demyelinating NeuropathyCarlos Meza HernandezNo ratings yet