Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Arithmetic Sequence-Missing K
Uploaded by
Mom Gie0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views1 pageThe value of k that makes k-2, 5k+12, 6-k an arithmetic sequence is -2. The terms of the arithmetic sequence are -4, 2, 8. The common difference is 6. The next term in the sequence is 14.
Original Description:
Arithmetic Sequence
Original Title
Arithmetic Sequence-missing k
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe value of k that makes k-2, 5k+12, 6-k an arithmetic sequence is -2. The terms of the arithmetic sequence are -4, 2, 8. The common difference is 6. The next term in the sequence is 14.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
33 views1 pageArithmetic Sequence-Missing K
Uploaded by
Mom GieThe value of k that makes k-2, 5k+12, 6-k an arithmetic sequence is -2. The terms of the arithmetic sequence are -4, 2, 8. The common difference is 6. The next term in the sequence is 14.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
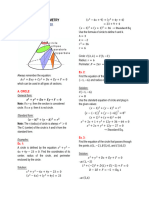
Problem:
Find the value of k and the next term if k-2,5k + 12, 6-k will form an arithmetic sequence.
Given:
First term, a₁ = k-2
Second term, a₂ = 5k + 12
Third term, a₃ = 6 - k
Find the value of k using the formula for the common difference, d:
a₂ - a₁ = a₃ - a₂
(5k + 12) - (k - 2) = (6 - k) - (5k + 12)
5k + 12 - k + 2 = 6 - k - 5k - 12
4k + 14 = - 6k - 6
(4k + 14 ⇒ common difference expression between a₂ and a₁)
(-6k - 6 ⇒ common difference expression between a₃ and a₂)
Combine the like terms:
4k + 14 = - 6k - 6
6k + 4k = -6 - 14
10k/10 = -20/10
k = -2
The value of k is -2.
Substitute, k = -2:
a₁ = k-2 a₂ = 5k + 12 a₃ = 6 - k To determine the common difference, d:
a₁ = (-2)-2 a₂ = 5(-2) + 12 a₃ = 6 - (-2) a₂ - a₁ = a₃ - a₂
a₁ = -4 a₂ = -10 + 12 a₃ = 6 + 2 2 - (-4) = 8 - 2
a₂ = 2 a₃ = 8 2+4 = 6
6=6
The arithmetic sequence when k = -2: d=6
-4, 2, 8
The common difference, d= 6.
Find the next term, a₄/fourth term:
As expression: Substitute k = -2:
a₄ = a₃ + d (common difference between a₃
and a₂ a₄ = -7(-2)
a₄ = 6 - k + (-6k - 6) a4 = 14
a₄ = 6 - k - 6k - 6
a₄ = -7k
Answer:
The value of k = -2.
The next term is a₄=-7k or a₄ = 14.
The sequence: -4, 2, 8, 14
You might also like
- Special ProjectDocument23 pagesSpecial ProjectLeo Ipo100% (1)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Obligation and Contracts Art 1156 To 1178 Civil Code of The Philippines - Republic Act No 386Document3 pagesObligation and Contracts Art 1156 To 1178 Civil Code of The Philippines - Republic Act No 386Mom Gie100% (7)
- Quadratic Equation: Very Short Answer Type QuestionsDocument26 pagesQuadratic Equation: Very Short Answer Type QuestionsMadhur MaheshwaryNo ratings yet
- U S A Mathematical Talent Search: 1/2/10. Determine The Unique Pair of Real NumbersDocument10 pagesU S A Mathematical Talent Search: 1/2/10. Determine The Unique Pair of Real Numbersสฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- QuarticDocument10 pagesQuarticlalasoisNo ratings yet
- MS Equations Y8 8.6Document3 pagesMS Equations Y8 8.6sNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 1 Real Numbers Get PDFDocument37 pagesRD Sharma Solutions For Class 10 Chapter 1 Real Numbers Get PDFAbhilash C UNo ratings yet
- Maths Mania # 044: DIRECTIONS: For The Following Questions, Four Options Are Given. Choose The Correct OptionDocument4 pagesMaths Mania # 044: DIRECTIONS: For The Following Questions, Four Options Are Given. Choose The Correct OptionTUSHAR JALANNo ratings yet
- Suggested Solution To Homework 5: SEEM 4480 Decision Methodology and Applicatons Xuedong He, Fall 2017Document3 pagesSuggested Solution To Homework 5: SEEM 4480 Decision Methodology and Applicatons Xuedong He, Fall 2017Gladys Gladys MakNo ratings yet
- Numerical Research of Bending Flexible PlatesDocument9 pagesNumerical Research of Bending Flexible PlatesMahesh GarlankaNo ratings yet
- Round 2 SolutionsDocument10 pagesRound 2 Solutionskepler1729No ratings yet
- RS Aggarwal Solution Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Exercise 4DDocument13 pagesRS Aggarwal Solution Class 10 Maths Chapter 4 Quadratic Equations Exercise 4DThe Time ParadoXNo ratings yet
- Thermo Stat3Document4 pagesThermo Stat3Hagere EthiopiaNo ratings yet
- Operator Based Questions: Chapter - 8Document7 pagesOperator Based Questions: Chapter - 8DBS AuthorityNo ratings yet
- Part - A Section - I: CLASS X (2020-21) Mathematics Standard (041) Sample Paper-07Document11 pagesPart - A Section - I: CLASS X (2020-21) Mathematics Standard (041) Sample Paper-07Anand Balakrishnan100% (1)
- Mathematics - 10 Set-2 Answers PDFDocument17 pagesMathematics - 10 Set-2 Answers PDFGolu SinghNo ratings yet
- QED Vertex CorrectionDocument19 pagesQED Vertex CorrectionMehmet HelvaNo ratings yet
- POLYNOMIALSDocument1 pagePOLYNOMIALSAnushka ManatwalNo ratings yet
- Alan Clanak 16Document12 pagesAlan Clanak 16alanfilipinNo ratings yet
- Number System Practice Sheet 2Document15 pagesNumber System Practice Sheet 2baba yagaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 1S - DR Paul May: Calculus Question For January Exam 2006Document2 pagesChemistry 1S - DR Paul May: Calculus Question For January Exam 2006masyuki1979No ratings yet
- ch2 Worksheet 4Document1 pagech2 Worksheet 4ns2496147No ratings yet
- A Generalization of The Parallelogram Law To Higher DimensionsDocument7 pagesA Generalization of The Parallelogram Law To Higher Dimensionsarun rajaramNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Question Bank Class X For Summative Assessment-II 2014Document138 pagesMathematics Question Bank Class X For Summative Assessment-II 2014Apex Institute92% (12)
- Assignments 1 and 2 Discrete MathematicaDocument2 pagesAssignments 1 and 2 Discrete MathematicaShivam PathakSNo ratings yet
- Ellipticl IntegralDocument28 pagesEllipticl IntegralSanthi KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Exam Set ADocument3 pagesExam Set AgregNo ratings yet
- Review Q2 Chapters 9 and 1Document4 pagesReview Q2 Chapters 9 and 1Jeronimo Jr. NacordaNo ratings yet
- Suxcvcxt XCVXCVXCRDocument31 pagesSuxcvcxt XCVXCVXCRKelli FloresNo ratings yet
- Notes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1Document15 pagesNotes Important Questions Answers 12th Math Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1shahidNo ratings yet
- Algebra ReviewDocument9 pagesAlgebra ReviewRyanCallejaNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer Term2Document6 pagesMath Reviewer Term2Tautoan VlogNo ratings yet
- ExampleDocument4 pagesExampleFatima Aliana MautanteNo ratings yet
- F 5 Maths Revision ChapterDocument37 pagesF 5 Maths Revision ChapterWilliam KohNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Maths .12Document31 pagesQuestion Bank Maths .12tulsiram ahirwarNo ratings yet
- Project 5Document13 pagesProject 5Niamat UllahNo ratings yet
- Practice For Precal PDFDocument9 pagesPractice For Precal PDFsharonNo ratings yet
- 3d Geometry Jee (2020-21) Questions and SolutionsDocument11 pages3d Geometry Jee (2020-21) Questions and SolutionsFight With MeNo ratings yet
- Functions and Equations - SolutionsDocument6 pagesFunctions and Equations - Solutionsscribd-in-actionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Simultaneous EquationsDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Simultaneous EquationsAaliya NafeesaNo ratings yet
- Revision Quadratic Equations Challenging: A) X X B) X XDocument5 pagesRevision Quadratic Equations Challenging: A) X X B) X XStijn WinkelerNo ratings yet
- Model Answer For Combined Mathematics I - 2013 AL Paper PDFDocument18 pagesModel Answer For Combined Mathematics I - 2013 AL Paper PDFThiwanka De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Nota Dan Latihan Quadratic EquationsDocument10 pagesNota Dan Latihan Quadratic Equationsjkj1370100% (3)
- Mock 2021 Compulsory Part Paper 2 SolutionsDocument7 pagesMock 2021 Compulsory Part Paper 2 Solutionskiuspy72No ratings yet
- Junior DocsDocument5 pagesJunior Docsjevanjunior0% (1)
- MATEMATIK Soalan Ujian 1Document5 pagesMATEMATIK Soalan Ujian 1mus mustafaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections 1Document41 pagesConic Sections 1Chaz grant borromeoNo ratings yet
- Functions Part 1Document17 pagesFunctions Part 1mnashish619No ratings yet
- M105 Week 2Document14 pagesM105 Week 2Ma. Loraine DurasNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry - Wrob212Document5 pagesAnalytic Geometry - Wrob212bryan04avilesNo ratings yet
- Parcijalni Ispit IM1 S RješenjimaDocument4 pagesParcijalni Ispit IM1 S RješenjimaherminaNo ratings yet
- S4 MTC Past PaperDocument3 pagesS4 MTC Past PaperjalgatkuothgangNo ratings yet
- 02.algebraic FormulaeDocument4 pages02.algebraic Formulaechia poh hooiNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Solved Problems PDFDocument10 pagesQuadratic Equation Solved Problems PDFRakesh RajNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Week 10 - Laplace Transform Part 2 ActivitiesDocument11 pagesActivity 1: Week 10 - Laplace Transform Part 2 ActivitiessiarwafaNo ratings yet
- K.V. JMO 2014 SolutionsDocument11 pagesK.V. JMO 2014 SolutionsPremMehtaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Reviewer - Force and MotionDocument3 pagesGrade 8 Reviewer - Force and MotionMom Gie100% (2)
- REVIEWER - SCIENCE Grade 9Document4 pagesREVIEWER - SCIENCE Grade 9Mom GieNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - KMT Gas BehaviorDocument2 pagesReviewer - KMT Gas BehaviorMom GieNo ratings yet
- James Mill EconomistDocument2 pagesJames Mill EconomistMom GieNo ratings yet
- Operations of Signed NumbersDocument1 pageOperations of Signed NumbersMom GieNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 9 - 3rd GradingDocument1 pageMath Grade 9 - 3rd GradingMom Gie50% (2)
- HELE Grade 5-2nd QuarterDocument4 pagesHELE Grade 5-2nd QuarterNanay Gi100% (2)
- Energy Sources - PhilippinesDocument1 pageEnergy Sources - PhilippinesMom GieNo ratings yet