Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Bonding-Answers
Uploaded by
JaznMon71%(7)71% found this document useful (7 votes)
7K views2 pagesOriginal Title
Chemical_Bonding-answers.doc
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
71%(7)71% found this document useful (7 votes)
7K views2 pagesChemical Bonding-Answers
Uploaded by
JaznMonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Chemical Bonding Worksheet
Ionic Bond between a Metal and Non-Metal
Covalent Bond between a Non-Metal and Non-Metal
Metallic Bond between a Metal and Metal
Compound Name Oxidation states Bond Type
of each atom
NO2 nitrogen dioxide N = +4 covalent
O = -2
NaCl sodium chloride Na = +1 ionic
Cl = -1
SO2 sulfur dioxide S = +4 covalent
O = -2
PO43- phosphate anion P= +5 covalent
O = -2
MgBr2 magnesium bromide Mg = +2 ionic
Br = -1
CaO calcium oxide Ca = +2 ionic
O = -2
H2O water H = +1 covalent
O = -2
K2O potassium oxide K = +1 ionic
O = -2
Cu-Zn alloy brass Cu = 0 metallic
Zn = 0
O2 oxygen gas O=0 covalent
CuCl2 copper(II) chloride Cu = +2 ionic
Cl = -1
NO2- nitrite anion N = +3 covalent
O = -2
TiO2 titanium (IV) oxide Ti = +4 ionic
O = -2
HF hydrofluoric acid H= +1 covalent
F = -1
Rb2S rubidium sulfide Rb = +1 ionic
S = -2
Au-Pt mixture white gold Au = 0 metallic
Pt = 0
Fe2O3 iron (III) oxide Fe = +3 ionic
O = -2
C6H12O6 glucose C= +4 covalent
H =-1
O= -2
Difference in electronegativity
4.0 1.7 .4 0
Polar-covalent covalent
Ionic bond bond
100% 50% 5% 0%
Percentage Ionic character
Bonding Molecular Name Oxidation states Bond Type
between Formula of each atom
Sulfur and H2S hydrosulfic acid H = +1 covalent
Hydrogen S = -2
Sulfur and Cs2S cesium sulfide Cs= +1 ionic
cesium S = -2
Chlorine and ClBr3 chlorine tri bromide Cl = +3 covalent
bromine Br = -1
Calcium and CaCl2 calcium chloride Ca = +2 ionic
chlorine Cl = -1
Oxygen and H2O water H = +1 polar covalent
hydrogen O = -2
Nitrogen and NH3 ammonia H = +1 polar covalent
hydrogen N = -3
Iodine and I2 solid iodine I=0 covalent
iodine
Copper and CuS copper (II) sulfide Cu = +2 ionic
sulfur S = -2
Hydrogen and HF hydrofluoric acid H= +1 polar covalent
fluorine F = -1
Carbon and CO2 carbon dioxide C = +4 polar covalent
oxygen O = -2
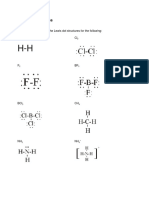
1. Arrange these compounds in order of increasing ionic character of their bonds: LiF, LiBr, KCl, KI
KI, LiBr, KCl, LiF
2. Classify each of the bonds as either ionic or covalent.
a. Al—O I d. Bi—O I g. Na—S C j. Ti—Br C
b. Al—S C e. C—Cl C h. P—O C k. C—O C
c. Bi—Cl C f. N—O C i. S—O C l. Sr—Cl I
3. What force holds the two ions together in an ionic bond?
Electrostatic attractions
4. What is the meaning of the oxidation number of an element that forms an ionic bond?
The charge of each ion (the number of electrons it lost or gained)
5. What is a molecule?
Species formed when 2 or more nonmetals bond covalently
6. How are molecules and polyatomic ions alike? How are they different?
They are both collections of nonmetals covalently bonded
molecules are neutral whereas, polyatomic ions are charged
You might also like
- Electronegativity WorksheetDocument2 pagesElectronegativity WorksheetDn Angel100% (1)
- WORKSHEET Chemical BondingDocument2 pagesWORKSHEET Chemical BondingIsabel Del ValleNo ratings yet
- Empirical and Molecular Formula WorksheetDocument2 pagesEmpirical and Molecular Formula WorksheetHanum100% (2)
- Types of Chemical Reaction Worksheet Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesTypes of Chemical Reaction Worksheet Practice Answerskheil01371% (28)
- Stoichiometry Worksheet+AnswersDocument2 pagesStoichiometry Worksheet+AnswersAnonymous 6MSekAxCnZ0% (3)
- Worksheet-Accuracy and Precision-FinalDocument4 pagesWorksheet-Accuracy and Precision-FinalSabeeh Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- NSC-130 Stoichiometry WorksheetDocument2 pagesNSC-130 Stoichiometry WorksheetAnonymous 6MSekAxCnZNo ratings yet
- Ions & Ionic Bonds (Multiple Choice) QPDocument7 pagesIons & Ionic Bonds (Multiple Choice) QPИРадојичић100% (1)
- Worksheet - Empirical Formulas and Molecular FormulasDocument2 pagesWorksheet - Empirical Formulas and Molecular FormulasWassachol Sumarasingha100% (2)
- Limiting Reactants WorksheetDocument2 pagesLimiting Reactants WorksheetBrandon BaxterNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends WorksheetDocument4 pagesPeriodic Trends Worksheetsyd ricafort50% (6)
- Ionic Bonding Worksheet - Type 1 PracticeDocument2 pagesIonic Bonding Worksheet - Type 1 Practicerichwenekylejc o Evaristo100% (6)
- Naming Ionic CompoundsDocument20 pagesNaming Ionic CompoundsMegan Sarah100% (1)
- Empirical and Molecular Formulas PracticeDocument3 pagesEmpirical and Molecular Formulas PracticeLeeanaNo ratings yet
- Mole ConceptDocument90 pagesMole ConcepthariniNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Molecular & Ionic Compound Structure & PropertiesDocument18 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Molecular & Ionic Compound Structure & PropertiesDragonbariumNo ratings yet
- Bond Polarity and ElectronegativityDocument2 pagesBond Polarity and ElectronegativityJewel Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry Worksheet With AnswersDocument5 pagesStoichiometry Worksheet With Answersapi-298247873100% (1)
- Electron Configuration Multiple Choice Questions For Unit ReviewDocument16 pagesElectron Configuration Multiple Choice Questions For Unit ReviewAli EslamiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding - Practice Questions: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument5 pagesChemical Bonding - Practice Questions: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The QuestionJemina R. B. Espedillon100% (1)
- Empirical and Molecular Formula WorksheetDocument3 pagesEmpirical and Molecular Formula WorksheetAgee AbdullaNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Bonding A KEYDocument3 pagesQuiz - Bonding A KEYManongdo AllanNo ratings yet
- Acid and Base Worksheet 1-07-08 Ans KeyDocument4 pagesAcid and Base Worksheet 1-07-08 Ans KeyShazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice Worksheet For 8th GradeDocument2 pagesProtons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice Worksheet For 8th GradeDrama Music67% (3)
- Balancing Chemical Equations WorksheetDocument99 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations Worksheetkhaled_behery9934100% (3)
- Electron Configuration: Edgar F. CariñoDocument20 pagesElectron Configuration: Edgar F. CariñoLea JotojotNo ratings yet
- Bonding Practice Test PDFDocument15 pagesBonding Practice Test PDFpeterjo raveloNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument36 pagesAcids and Baseschong5680% (5)
- Chemistry Final Worksheet Grade 9Document9 pagesChemistry Final Worksheet Grade 9Lama AshiNo ratings yet
- Acid Base WorksheetDocument2 pagesAcid Base WorksheetBobby Barnes100% (2)
- Separation TechniquesDocument19 pagesSeparation TechniquesLenin Prabhu100% (4)
- Powerpoint Slides - Separation TechniquesDocument66 pagesPowerpoint Slides - Separation Techniquesapi-30590932560% (5)
- Electronegativity Worksheet AnswersDocument2 pagesElectronegativity Worksheet Answerscpliam83% (6)
- States of Matter: Paper 1: Practice TestDocument4 pagesStates of Matter: Paper 1: Practice TestSadaqat UllahNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Covalent Chemical Bonding WS enDocument4 pagesIonic and Covalent Chemical Bonding WS enrajaijahNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and Salts Worksheet 1Document6 pagesAcid Bases and Salts Worksheet 1Pooja Debnath100% (3)
- CHE 123 - Worksheet - Atomic Structure - IonizationDocument6 pagesCHE 123 - Worksheet - Atomic Structure - IonizationJanet UsherNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Grade 10Document88 pagesOrganic Chemistry Grade 10Sai Pranav100% (2)
- LP 9 - Chemical Bonding Summative TestDocument3 pagesLP 9 - Chemical Bonding Summative TestCrislyn Jane PadillaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Alkenes WorksheetDocument2 pagesOrganic Chemistry Alkenes Worksheetoc100% (1)
- 4) Transition Metal Electron Configuration Multiple ChoiceDocument4 pages4) Transition Metal Electron Configuration Multiple ChoiceAnonymous pgjIAZoNo ratings yet
- Balancing Redox Reactions Worksheets 1 & 2 (With Answers)Document2 pagesBalancing Redox Reactions Worksheets 1 & 2 (With Answers)ronnie schwiers50% (4)
- Acids and Bases (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingDocument1 pageAcids and Bases (Grade 9) - Free Printable Tests and Worksheets - HelpTeachingSabu Lazer100% (1)
- Lewis DotDocument9 pagesLewis DotLing Wang100% (1)
- S-C-5-3 - Periodic Trends Worksheet and KEYDocument6 pagesS-C-5-3 - Periodic Trends Worksheet and KEYSanim Choudhury40% (5)
- Date: March 20, 2015 Wicomico High School 5E Lesson Plan Subject: Honors Chemistry Grade: 11th/12th Teacher: Rachel ThorntonDocument3 pagesDate: March 20, 2015 Wicomico High School 5E Lesson Plan Subject: Honors Chemistry Grade: 11th/12th Teacher: Rachel Thorntonapi-28361150088% (8)
- Learning Module: Mole ConceptDocument133 pagesLearning Module: Mole ConceptArnel BoholstNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 1Document60 pagesStoichiometry 1Aryan Anchan0% (1)
- General Chemistry 1: First Quarter-Module 3: Writing and Naming Chemical FormulasDocument19 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: First Quarter-Module 3: Writing and Naming Chemical FormulasAlessandra Gabrielle Garez100% (1)
- Separation Techniques WorksheetDocument2 pagesSeparation Techniques Worksheetmarleigh75% (4)
- Chemical Formula Writing WorksheetDocument4 pagesChemical Formula Writing Worksheetapi-286295321No ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces Worksheet With KeyDocument4 pagesIntermolecular Forces Worksheet With KeyNoreen ClarkNo ratings yet
- Empirical Formula Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesEmpirical Formula Lesson Planjohnrey_lidres100% (4)
- Balancing Chemical EquationDocument4 pagesBalancing Chemical Equationamin_zaman100% (1)
- Stoichiometry and The Mole Concept NotesDocument26 pagesStoichiometry and The Mole Concept Noteshafizhapni93% (30)
- Worksheet 01 Dated 05072021Document1 pageWorksheet 01 Dated 05072021Jeny SharmaNo ratings yet
- 6 Redox Reactions16472475341647342590Document5 pages6 Redox Reactions16472475341647342590Atharva JamsandekarNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry: The Periodic Table and ChargesDocument4 pagesStoichiometry: The Periodic Table and ChargesLei YinNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Numbers, Redox and Half Equations PDFDocument6 pagesOxidation Numbers, Redox and Half Equations PDFRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Corrosion Lecture 1 Material EngineeringDocument14 pagesCorrosion Lecture 1 Material EngineeringBaso Rahmat TarmiziNo ratings yet
- Scitech - Activity 1 Please Read Carefully The Questions and Write Your Answer On The Space Provide MechanicsDocument1 pageScitech - Activity 1 Please Read Carefully The Questions and Write Your Answer On The Space Provide MechanicsJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Youth of PrayerDocument1 pageYouth of PrayerJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Introduction To: ParasitesDocument32 pagesIntroduction To: ParasitesJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Dear SirDocument1 pageDear SirJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Reflection About SDA View 1Document1 pageReflection About SDA View 1JaznMonNo ratings yet
- Academic Disciplines. Pickwick Publications: Ontario, CanadaDocument2 pagesAcademic Disciplines. Pickwick Publications: Ontario, CanadaJaznMonNo ratings yet
- ELS August TestDocument4 pagesELS August TestJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Nature of Man - Seventh-Day Adventist BelieveDocument18 pagesNature of Man - Seventh-Day Adventist BelieveJaznMonNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS IN SCIENCE Teaching in Science EducationDocument16 pagesSYLLABUS IN SCIENCE Teaching in Science EducationJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Empower MeDocument2 pagesEmpower MeJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Chapter 1Document57 pagesMicrobiology Chapter 1Victoria FakiledeNo ratings yet
- Whatis Life PHLSDocument17 pagesWhatis Life PHLSJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Maligayang Araw: Science, Technology and SocietyDocument17 pagesMaligayang Araw: Science, Technology and SocietyJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Activity 2 ScitechDocument1 pageActivity 2 ScitechJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Find Us FaithfulDocument14 pagesFind Us FaithfulJaznMonNo ratings yet
- He Leadeth Me: Vox DilectiDocument35 pagesHe Leadeth Me: Vox DilectiJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Come, Thou Fount of Every Blessing - NWPDFDocument8 pagesCome, Thou Fount of Every Blessing - NWPDFJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument20 pagesKingdom PlantaeJaznMon100% (1)
- Specific Heat WorksheetDocument1 pageSpecific Heat WorksheetJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Share Your FaithDocument7 pagesShare Your FaithJaznMonNo ratings yet
- There Is Always A Place at The TableDocument7 pagesThere Is Always A Place at The TableJaznMonNo ratings yet
- I Will RiseDocument12 pagesI Will RiseJaznMonNo ratings yet
- 414 Mary Did You Know PDFDocument10 pages414 Mary Did You Know PDFeruth987No ratings yet
- Specific Heat WorksheetDocument1 pageSpecific Heat WorksheetJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Satb Because He LivesDocument8 pagesSatb Because He LivesJaznMonNo ratings yet
- HEAT Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesHEAT Practice ProblemsHR Tusher100% (1)
- Atomic Structure PacketDocument11 pagesAtomic Structure PacketJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Bio2 Initial Release 13june PDFDocument94 pagesBio2 Initial Release 13june PDFJojebelle Kate Iyog-cabanletNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium Practice AnswersDocument2 pagesEquilibrium Practice AnswersJaznMonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 KeyDocument16 pagesChapter 17 KeyAriny ZaqiyahNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry 11th Edition Francis Carey Robert Giuliano Janice SmithDocument32 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry 11th Edition Francis Carey Robert Giuliano Janice Smithxavianhatmgzmz9No ratings yet
- Petrom OMV Norm B 2001 Rom Eng Rev.1 2006-12-21Document72 pagesPetrom OMV Norm B 2001 Rom Eng Rev.1 2006-12-21lucianduNo ratings yet
- Acrylic AcidDocument5 pagesAcrylic AcidSavita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Matter Chemical Trends and Bonding Sch3uDocument27 pagesUnit Plan Matter Chemical Trends and Bonding Sch3uapi-350642180No ratings yet
- Titration - Dry Lab - 2020Document6 pagesTitration - Dry Lab - 2020MariaPaulaGonzalezRojasNo ratings yet
- Air Pollution in QuitoDocument14 pagesAir Pollution in Quitoapi-385158934No ratings yet
- Thermo EquipmentDocument8 pagesThermo EquipmentlualineNo ratings yet
- Soils Acid ManagementDocument99 pagesSoils Acid Managementbig john100% (9)
- GVP Specific Protocol Drinking Water FINAL 2015 03 04Document28 pagesGVP Specific Protocol Drinking Water FINAL 2015 03 04Yanuar PaksiNo ratings yet
- Activity Series LabDocument4 pagesActivity Series LabjeffoisawesomeNo ratings yet
- What Is SoilDocument4 pagesWhat Is SoilLiaw Wan TzeNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full C Programming From Problem Analysis To Program Design 8th Edition Malik Solutions Manual PDFDocument36 pagesDwnload Full C Programming From Problem Analysis To Program Design 8th Edition Malik Solutions Manual PDFlucedystu56100% (13)
- Angus Amp 95 Latexpaint TdsDocument5 pagesAngus Amp 95 Latexpaint TdsOng Kok TongNo ratings yet
- The Origin and Zoning of Hypogene and Supergene Fe-Mn-Mg-Sc-U-REE Phosphate Mineralization From The Newly-Discovered Trutzhofmühle ApliteDocument29 pagesThe Origin and Zoning of Hypogene and Supergene Fe-Mn-Mg-Sc-U-REE Phosphate Mineralization From The Newly-Discovered Trutzhofmühle ApliteLuis MartinsNo ratings yet
- Microwave Drying of FruitsDocument11 pagesMicrowave Drying of Fruitsshreya ghoshNo ratings yet
- Seviour Bible 2010Document684 pagesSeviour Bible 2010Murylu Dias dos SantosNo ratings yet
- Sno2 FDocument5 pagesSno2 FLa Viola FiorentinaNo ratings yet
- Aflas EngDocument11 pagesAflas EngVictor Flores ResendizNo ratings yet
- Sunscreen Cleaning ValidationDocument6 pagesSunscreen Cleaning Validationrobbnz29No ratings yet
- Bic Sodio Shandong MSDSDocument7 pagesBic Sodio Shandong MSDSFIORELLA VANESSA MAITA MUCHANo ratings yet
- Mathematics ContentDocument10 pagesMathematics ContentNayive Lancheros0% (3)
- LeadCare II User ManualDocument24 pagesLeadCare II User ManualririmonirNo ratings yet
- The Gas Laws: 1.boyle's Law 2.charles' Law 3.Gay-Lussac's Law 4.avogadro's LawDocument20 pagesThe Gas Laws: 1.boyle's Law 2.charles' Law 3.Gay-Lussac's Law 4.avogadro's Lawdavid jenil nabua100% (1)
- ANSYS Modeling Solidification PDFDocument34 pagesANSYS Modeling Solidification PDFvictoriaNo ratings yet
- Subcooling Superheating and Liquid Suction Heat ExchangerDocument4 pagesSubcooling Superheating and Liquid Suction Heat ExchangerDeniell Joyce MarquezNo ratings yet
- Steel Connection WeldingDocument56 pagesSteel Connection WeldingKentDemeterio100% (2)
- Accepted Manuscript: Computers & EducationDocument32 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Computers & EducationAlpyh ZahrohNo ratings yet
- Akinlua Etal 2007 PDFDocument11 pagesAkinlua Etal 2007 PDFJavierNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2021 February Analysis by MathonGoDocument4 pagesJEE Main 2021 February Analysis by MathonGoAnshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Micellar Catalysis or CatalystDocument39 pagesMicellar Catalysis or CatalystchinuasfaNo ratings yet