Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simply Processor.: Atx (Advanced Technology Extended
Uploaded by
Ayla Devi Onne0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views2 pageswords are not mine
Original Title
Handy Computer Acronyms
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentwords are not mine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
39 views2 pagesSimply Processor.: Atx (Advanced Technology Extended
Uploaded by
Ayla Devi Onnewords are not mine
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Handy Computer Acronyms ROM: Read-Only Memory
SATA: Serial Advanced Technology Attachment
AGP: Accelerated Graphics Port SCSI: Small Computer System Interface
ATX (Advanced Technology eXtended SIMM: Single In-Line Memory Module
BIOS: Basic Input-Output Services SMART: Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology
CD: Compact Disc SMPS, or switched-mode power supply
CD-R: Compact Disc Recordable SO-DIMM: Small Outline Dual In-Line Memory Module
CD-ROM: Compact Disc Read-Only Memory SPOF: Single Point of Failure
CD-RW: Compact Disc Re-Writable SRAM: Static Random Access Memory
CPU: The Central Processing Unit, Microprocessor, or sRGB: Standard Red Green Blue
simply Processor. SSD: Solid State Drive
DDR: Double Data Rate UPS: Uninterruptible Power Supply
DDR2: Double Data Rate 2. USB: Universal Serial Bus.
DDR3: Double Data Rate Type 3. VGA: Video Graphics Array
DDR4: Double Data Rate Type 4. VDU: Visual Display Unit
DIMM: Dual In-Line Memory Module VRAM: Video Random Access Memory
DV: Digital Video CMOS (Complementary Metal Oxide Semi-Conductor)
DVD: Digital Versatile Disc
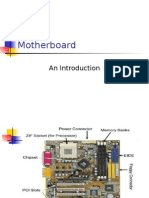
DVD+R: Digital Versatile Disc Recordable Parts of A Motherboard
DVD+RW: Digital Versatile Disk Rewritable
DVD-R: Digital Versatile Disc Recordable
DVD-RAM: Digital Versatile Disc Random Access Memory
DVD-RW: Digital Versatile Disk Rewritable
DVI: Digital Video Interface
ECC: Error Correction Code
EIDE: Enhanced Integrated Drive Electronics
FSB: Front Side Bus
HDD: Hard Disk Drive
HDMI: High-Definition Multimedia Interface
HDTV: High-Definition Television
I/O: Input/Output
ID10T: Pronounced "Eye Dee Ten Tee
IDE: Integrated Device Electronics
IEEE: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IGP: Integrated Graphics Processor
IRQ: Interrupt Request
ISA: Industry Standard Architecture 1. BIOS and CMOS – storage of information and settings of
LAN: Local Area Network the mother board.
LCD: Liquid Crystal Display 2. Input/Output Ports - follow a standard PC color coding.
LUN: Logical Unit Microphone- pink
MAC Address: Media Access Control Address Speakers and Headphones- green
MBR: Master Boot Record Monitor- Older motherboards are equipped
MCA: Micro Channel Architecture with a solid blue VGA port at the back but
MOBO: A cooler way to say "motherboard." newer motherboards use the HDMI and black
NIC: Network Interface Card or white DVI port as standard.
NTFS: New Technology File System. Ethernet network cable- colorless port
NVMe SSD: An SSD drive with a very fast interface Keyboard and Mouse- PS/2 port (Keyboard-
NVRAM: Non-Volatile Random Access Memory purple; Mouse- green)
OSD: On Screen Display USB devices- USB 2.0 colorless port
PCB: Printed Circuit Board USB 3.0 solid blue port
PCI: Peripheral Component Interconnect 3. IDE and SATA connector (Storage Device Connectors)
PCIe: Peripheral Component Interconnect Express The internal storage device connectors are where you will
PCI-X: Peripheral Component Interconnect Extended connect your storage devices.
PCMCIA: Personal Computer Memory Card International
Association
PEBKAC: Problem Exists Between Keyboard and Chair
PMU: Power Management Unit
PROM: Programmable Read-Only Memory
PS/2: Personal System/2
PSU: Power supply unit
RAID: Redundant Array of Independent Disks
RAM: Random-Access Memory
RDRAM: Rambus Dynamic Random Access Memory
4. Power Connectors- draws out the needed power directly
from the power supply.
5. Cabinet Connections -connect the Power Switch, the LED
power indicator, the Reset Switch, the HDD.
6. CPU Socket - where the processing and transfer of data
happens.
7. Expansion Card Slots - add a new component to the
motherboard
Video card slot
Network card slot
Modem card slot
Audio card slot
Video Card Slot
Aside from the integrated graphics from APUs and other
Intel CPUs with integrated graphics, the video card slot lets
you upgrade the graphical output and performance of your
computer. This goes to the high data slots, like the PCIe slot
or AGP slot. Ports include, but are not limited to, (depends
on the card):
HDMI
DVI
DisplayPort
Network Card Slot
Network card slot is where you put the Network Interface
Card (NIC). This allows you to connect to other computer
networks via LAN or the internet. It has an RJ-45 port at the
back.
Modem Card Slot
This is where you connect your network card so you can
connect to the internet through the telephone line.
Obviously, this is an older technology than the above NIC.
This typically has 2 RJ-11 connectors to connect to the
telephone.
Audio Card Slot
This is where audio cards fit. They basically convert
electrical signals to the audio signals or sound that we can
hear. Depending on the type of audio there will be different
types of ports found at the back. But it usually has several
3.5mm ports used for the following:
Microphone
Speaker
Recorder
Gaming Joystick
8. RAM (Memory) Slots
RAM, or Random Access Memory, slots are one of the most
important parts on a motherboard.
The RAM slots are, unsurprisingly, where you place the
RAM modules. There is the SIMM slot (Single in-line
memory module) that only supports 32-bit bus and there is
the DIMM slot (Dual inline memory module) that can
simultaneously run with a 64-bit bus.
DDR3 (Double Data Rate 3th Generation) was once the
standard with RAM, but this has slowly been replaced
with DDR4 (Double Data Rate 4th Generation). While DDR3
is still surprisingly effective, DDR4 is slowly becoming the
standard. Moreover, most motherboards don’t support
both DDR3 and DDR4, so there are compatibility and future
proofing concerns.
When it comes to gaming, there’s still an active debate
whether you need 8GB or 16GB of DDR4.
You might also like
- Computer Hardware-Related AcronymsDocument3 pagesComputer Hardware-Related Acronymsghoul ciprianoNo ratings yet
- Handy Computer Acronyms and Abbreviations ExplainedDocument8 pagesHandy Computer Acronyms and Abbreviations ExplainedMaverick Borres Romo ChoiiNo ratings yet
- PlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6From EverandPlayStation Architecture: Architecture of Consoles: A Practical Analysis, #6No ratings yet
- Computer Acronyms and AbbreviationsDocument5 pagesComputer Acronyms and AbbreviationsJeian Ashley A. MaasinNo ratings yet
- Latest Basic Computer Hardware Interview QuestionsDocument3 pagesLatest Basic Computer Hardware Interview QuestionsSahil ThakurNo ratings yet
- Computer Basics DefinitonDocument8 pagesComputer Basics DefinitonJeetender nath100% (1)
- Essential computer component and technology definitionsDocument3 pagesEssential computer component and technology definitionsJennylyn BaladjayNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1SMART ENGRZNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsDocument78 pagesFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsVencent BuellNo ratings yet
- My TM PresentationfDocument23 pagesMy TM PresentationfCarlo Salvani TablatinNo ratings yet
- Glossary Computer HardwareDocument5 pagesGlossary Computer HardwareNahid MamunNo ratings yet
- Familiarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and PeripheralsDocument98 pagesFamiliarization With The Various Computer Systems' Components and Peripheralsjuliet brusola100% (1)
- Computer Hardware and Software FundamentalsDocument34 pagesComputer Hardware and Software FundamentalsJhayden BlueNo ratings yet
- CHS Set2 W4-6Document136 pagesCHS Set2 W4-6Omar Sharif CuyuganNo ratings yet
- Workshop On Computer HardwareDocument18 pagesWorkshop On Computer HardwareMohd RizwanNo ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionDocument14 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and Its FunctionBrenda Macanlalay Asuncion80% (5)
- Motherboard Parts and Ohs PoliciesDocument5 pagesMotherboard Parts and Ohs PoliciesnikkoNo ratings yet
- Technical Lesson 1Document63 pagesTechnical Lesson 1PAUL GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Know The Common IT Acronyms: June 2014Document7 pagesKnow The Common IT Acronyms: June 2014the deanNo ratings yet
- Computer ApplicationsDocument21 pagesComputer ApplicationsdudungNo ratings yet
- Computer Ports - Cases Power Supply - MOBODocument97 pagesComputer Ports - Cases Power Supply - MOBONhoj Bener StreqsNo ratings yet
- Hard Ware Note BookDocument22 pagesHard Ware Note BookSrini VasuluNo ratings yet
- Identifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and FunctionsDocument31 pagesIdentifying Motherboard Hardware Parts and FunctionsNhil Cabillon QuietaNo ratings yet
- 27 Main Parts of Motherboard and Its FunctionDocument30 pages27 Main Parts of Motherboard and Its FunctionAngelica CarbonquilloNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 2Document12 pagesInformation Sheet 2Manuelo VangieNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 - Parts of The MotherboardDocument41 pagesLesson 5 - Parts of The MotherboardAnthonyNo ratings yet
- BIOS or Basic Input Output SystemDocument13 pagesBIOS or Basic Input Output SystemSaymon Casilang SarmientoNo ratings yet
- The essential components of a PC motherboardDocument28 pagesThe essential components of a PC motherboardshikhasajuNo ratings yet
- BIOS InstallationDocument5 pagesBIOS InstallationArif ShaikhNo ratings yet
- A+ Cert Chapter 1 MiscDocument4 pagesA+ Cert Chapter 1 Misc123456No ratings yet
- ReportDocument8 pagesReportapi-3734554100% (1)
- Motherboard components and portsDocument32 pagesMotherboard components and portsAnanduNo ratings yet
- Motherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryDocument8 pagesMotherboard The Heart of The Computer: Microprocessors Sockets Soldering Embedded System Main MemoryJhay Consolacion WalkerNo ratings yet
- The MotherboardDocument3 pagesThe Motherboardbryan ramosNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware Servicing NC IIDocument21 pagesComputer Hardware Servicing NC IIShe Ma RieNo ratings yet
- Singkatan Dunia KomputerDocument3 pagesSingkatan Dunia KomputerFinza SabangNo ratings yet
- Motherboard components explainedDocument12 pagesMotherboard components explainedTuesept Anne Vargas UrgenteNo ratings yet
- Parts of The System UnitDocument43 pagesParts of The System Unitroy nueraNo ratings yet
- 27 Main Parts of Motherboard and its Function ExplainedDocument24 pages27 Main Parts of Motherboard and its Function ExplainedVictor M. MorcilloNo ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument3 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardRodel Romero100% (2)
- Parts of Computer MotherboardDocument27 pagesParts of Computer MotherboardAling Alma Domiquel Abainza100% (1)
- Itws 2Document33 pagesItws 2rg22No ratings yet
- JammyDocument2 pagesJammyPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- A+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationDocument40 pagesA+ Hardware Tutorial Topic 1: Installation, Configuration, and Up GradationLindasharon AwourNo ratings yet
- Motherboard HandoutDocument5 pagesMotherboard HandoutJudea SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Computer Hardware ServicingDocument44 pagesComputer Hardware ServicingSodnal M. OdeloNo ratings yet
- Parts of A MotherboardDocument9 pagesParts of A Motherboardapi-251392462No ratings yet
- Motherboard ConnectorsDocument5 pagesMotherboard Connectorsmohitpar128No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The MotherboardDocument4 pagesParts and Functions of The MotherboardWilliam Paras InteNo ratings yet
- Netking: Ahsan Jameel KhanDocument20 pagesNetking: Ahsan Jameel KhanIshq Ek BaarNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10Document4 pagesParts of The Motherboard: Ashley Abogado Computer 10DeathNo ratings yet
- Motherboard and Other PartsDocument32 pagesMotherboard and Other PartsJom's Mijares100% (1)
- Motherboard Components... CSEDocument28 pagesMotherboard Components... CSEAtulay Mahajan100% (1)
- Netking: Ahsan Jameel KhanDocument20 pagesNetking: Ahsan Jameel KhanAhsan JameelNo ratings yet
- Types of HDD, Motherboards, Ports and SlotsDocument5 pagesTypes of HDD, Motherboards, Ports and SlotsSudeep OnemNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument30 pagesSeminarShweta Vishwakarma100% (1)
- CHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - IcsDocument70 pagesCHAPTER 2 - COMPUTER HARDWARE - Icsruzanna abu bakarNo ratings yet
- Computer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsDocument29 pagesComputer Motherboard and Its Constituent ComponentsRajendra PatilNo ratings yet
- How to Subnet a Network AddressDocument9 pagesHow to Subnet a Network AddressAyla Devi OnneNo ratings yet
- AC-PJMA Constitution Promotes Management SkillsDocument7 pagesAC-PJMA Constitution Promotes Management SkillsAyla Devi OnneNo ratings yet
- The God StealerDocument2 pagesThe God StealerJerald Lazarte Tadia92% (13)
- Department of Labor and EmploymentDocument4 pagesDepartment of Labor and EmploymentAyla Devi OnneNo ratings yet
- Dead Stars ScriptDocument8 pagesDead Stars ScriptAyla Devi OnneNo ratings yet
- Dead Stars ScriptDocument10 pagesDead Stars ScriptYna Alexandra100% (4)
- Comprehensive Handbook of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests With Nursing Implications by Davis 3rd EditionDocument18 pagesComprehensive Handbook of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests With Nursing Implications by Davis 3rd EditionMaria EdelNo ratings yet
- The God StealerDocument2 pagesThe God StealerJerald Lazarte Tadia92% (13)
- Serif Photo x7Document18 pagesSerif Photo x7Ayla Devi OnneNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer PartsDocument1 pageBasic Computer PartsAyla Devi OnneNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document3 pagesPresentation 1Ayla Devi OnneNo ratings yet
- Serif Photo Plus X7 Review - A Solid Image Editor For WindowsDocument3 pagesSerif Photo Plus X7 Review - A Solid Image Editor For WindowsAyla Devi OnneNo ratings yet
- Customer Experience Management A Handbook To Acquire and Retain Valuable CustomersDocument10 pagesCustomer Experience Management A Handbook To Acquire and Retain Valuable CustomersFranco Garcia VillenaNo ratings yet
- Deep Sea Electronics PLC: Complex Solutions Made SimpleDocument66 pagesDeep Sea Electronics PLC: Complex Solutions Made SimplepdealersNo ratings yet
- Install Windows From A USB Flash DriveDocument2 pagesInstall Windows From A USB Flash DriveJoaoNo ratings yet
- RelNot Opis OPisDocument59 pagesRelNot Opis OPisxxxNo ratings yet
- User Manual - Argentina Tax ReportingDocument9 pagesUser Manual - Argentina Tax ReportingIrina Castro100% (1)
- Geh 6706Document168 pagesGeh 6706Anojan BalaNo ratings yet
- Stm32Cubeide Installation Guide: User ManualDocument18 pagesStm32Cubeide Installation Guide: User ManualMatheus Santana CedoNo ratings yet
- Commodore Magazine Vol-08-N09 1987 SepDocument132 pagesCommodore Magazine Vol-08-N09 1987 SepSteven DNo ratings yet
- Sokkia DT4 Electronic Theodolite ManualDocument27 pagesSokkia DT4 Electronic Theodolite Manualheri purwokoNo ratings yet
- Menoufiya University Postgraduate ConstitutionDocument102 pagesMenoufiya University Postgraduate ConstitutionAhmedNo ratings yet
- Standing Abs WorkoutsDocument4 pagesStanding Abs WorkoutsMIIIBNo ratings yet
- Error Detection - RecoveryDocument35 pagesError Detection - RecoveryjayakrrishnanNo ratings yet
- Project Cost Management Plan Excel TemplateDocument14 pagesProject Cost Management Plan Excel TemplateDessy Lina - Marketing Executive BalikpapanNo ratings yet
- DO-C10072-CT Premet X (Issue 3)Document2 pagesDO-C10072-CT Premet X (Issue 3)Wisnu PrambudiNo ratings yet
- E6430 - QAL81 La-7782pDocument66 pagesE6430 - QAL81 La-7782pVincent TonNo ratings yet
- Product Manual 26011 (Revision C) : Load Sharing ModuleDocument36 pagesProduct Manual 26011 (Revision C) : Load Sharing Moduleincore1976No ratings yet
- Updated Transformers Notes 6th Sem EEE CAEDDocument42 pagesUpdated Transformers Notes 6th Sem EEE CAEDdeepu kumarNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of A Cost Effective Automatic Controller For Spray-Pyrolysis Technique To Deposit Thin FilmsDocument4 pagesFabrication of A Cost Effective Automatic Controller For Spray-Pyrolysis Technique To Deposit Thin Filmsbipul ahmedNo ratings yet
- MA4254 Discrete OptimizationDocument69 pagesMA4254 Discrete OptimizationmengsiongNo ratings yet
- Exploring Microsoft Office Word 2007 Ch1Document28 pagesExploring Microsoft Office Word 2007 Ch1crazybobblaskeyNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations, Acronyms and Common TermDocument28 pagesAbbreviations, Acronyms and Common TermyatishNo ratings yet
- Acr-4001 Imm EngDocument8 pagesAcr-4001 Imm EngNicusor MiertescuNo ratings yet
- DR8.21 ITIL Presentation Service TrainingDocument41 pagesDR8.21 ITIL Presentation Service TrainingKshitiz SaxenaNo ratings yet
- Billing EngineerDocument2 pagesBilling EngineerMahesh KurkundaNo ratings yet
- Polygraphy Midterm LectureDocument99 pagesPolygraphy Midterm Lecturejetlee estacionNo ratings yet
- Majesco Limited: Insurance Tech Company ProfileDocument3 pagesMajesco Limited: Insurance Tech Company ProfileSanjay Kanchan PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Verification of Reliability Assessment Techniques For Fuel Cell-Based Hybrid Power System For ShipsDocument26 pagesComparison and Verification of Reliability Assessment Techniques For Fuel Cell-Based Hybrid Power System For ShipsMuhammad KurniawanNo ratings yet
- The MIB Includes The System Information Transmitted On BCH. Signalling Radio Bearer: N/A Rlc-Sap: TM Logical Channel: BCCH Direction: Network To UEDocument5 pagesThe MIB Includes The System Information Transmitted On BCH. Signalling Radio Bearer: N/A Rlc-Sap: TM Logical Channel: BCCH Direction: Network To UESreenath VenkataNo ratings yet
- Gate Controller Manual: AAD03010 Frequency Control SystemDocument17 pagesGate Controller Manual: AAD03010 Frequency Control SystemKen LeeNo ratings yet
- Chip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Quest to Dominate the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (227)
- Chip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyFrom EverandChip War: The Fight for the World's Most Critical TechnologyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (82)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Core 1 Exam 220-1101 and Core 2 Exam 220-1102Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersFrom EverandAmazon Web Services (AWS) Interview Questions and AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- CompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002From EverandCompTIA A+ Complete Review Guide: Exam Core 1 220-1001 and Exam Core 2 220-1002Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Computer Science: A Concise IntroductionFrom EverandComputer Science: A Concise IntroductionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionFrom Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (6)
- Hacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxFrom EverandHacking With Linux 2020:A Complete Beginners Guide to the World of Hacking Using Linux - Explore the Methods and Tools of Ethical Hacking with LinuxNo ratings yet
- Model-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodFrom EverandModel-based System and Architecture Engineering with the Arcadia MethodNo ratings yet
- From Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionFrom EverandFrom Cell Phones to VOIP: The Evolution of Communication Technology - Technology Books | Children's Reference & NonfictionNo ratings yet
- iPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XFrom EverandiPhone X Hacks, Tips and Tricks: Discover 101 Awesome Tips and Tricks for iPhone XS, XS Max and iPhone XRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- 2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersFrom Everand2018 (40+) Best Free Apps for Kindle Fire Tablets: +Simple Step-by-Step Guide For New Kindle Fire UsersNo ratings yet
- Dancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldFrom EverandDancing with Qubits: How quantum computing works and how it can change the worldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The No Bull$#!£ Guide to Building Your Own PC: No Bull GuidesFrom EverandThe No Bull$#!£ Guide to Building Your Own PC: No Bull GuidesNo ratings yet
- Cancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionFrom EverandCancer and EMF Radiation: How to Protect Yourself from the Silent Carcinogen of ElectropollutionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Kindle Fire Owner's Manual: The ultimate Kindle Fire guide to getting started, advanced user tips, and finding unlimited free books, videos and apps on Amazon and beyondFrom EverandKindle Fire Owner's Manual: The ultimate Kindle Fire guide to getting started, advanced user tips, and finding unlimited free books, videos and apps on Amazon and beyondRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)