Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earthquake
Earthquake
Uploaded by
yanoy.mc98Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earthquake
Earthquake
Uploaded by
yanoy.mc98Copyright:
Available Formats
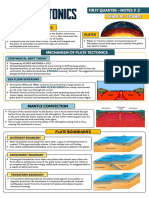
Earthquake – vibration of rocks when the energy stored in them is released
Focus – where earthquake starts
- Immediate area where vibration takes place
Epicenter – directly above the focus
Fault - fracture along which the blocks of crust on either side have moved relative to one another
parallel to the fracture.
Fault plane - planar (flat) surface along which there is slip during an earthquake
Fault scrap -feature on the surface of the earth that looks like a step caused by slip on the fault.
Convection current – movement of materials in earth’s interior, which transfers energy from one
another
Tensional movement – occurs when one convection current moves clockwise, while another current
moves counterclockwise in adjacent but separate areas, tending to pull the
lithosphere above it in opposite directions
Plate Tectonics - that considers the earth's crust and upper mantle to be composed of several large, thin,
relatively rigid plates that move relative to one another.
-tectonic plates is that they are parts of the lithosphere that break up into huge rock
slabs, or crustal plates .
Sea-floor spreading - happens at the mid-oceanic ridge where a divergent boundary is causing two
plates to move away from one another resulting in spreading of the sea floor. As
the plates move apart, new material wells up and cools onto the edge of the plates.
You might also like
- 6 10cd 2 0 Explain Stemscopedia EnglishDocument8 pages6 10cd 2 0 Explain Stemscopedia Englishapi-266033006No ratings yet
- Introduction To Engineering GeologyDocument84 pagesIntroduction To Engineering GeologyTan U-ShangNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument1 pageEarthquakeyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4luisloredoperez156No ratings yet
- Earthquake and FaultsDocument1 pageEarthquake and FaultsTricia BautistaNo ratings yet
- Lebs ScienceDocument9 pagesLebs ScienceVince Casison Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Science g10Document4 pagesScience g10Julia Amor DestuaNo ratings yet
- 1 Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Mountain RangesDocument26 pages1 Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Mountain RangesCrisanta GanadoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument5 pagesPlate Tectonic TheoryDenise Anne SolidadNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesPlate TectonicsNicole TaroyNo ratings yet
- 10.1 Study Notes - Moving ContinentsDocument6 pages10.1 Study Notes - Moving Continents「。R I C E 。」No ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience ReviewerFiona MiralpesNo ratings yet
- Hand OutsDocument6 pagesHand OutsMJ DejosNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics VocabularyDocument4 pagesPlate Tectonics VocabularyShabir RahimoonNo ratings yet
- Tectonic EarthquakeDocument25 pagesTectonic EarthquakeMark Aaron AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- L6 Earths Driving ForcesDocument30 pagesL6 Earths Driving ForcesgabwastedNo ratings yet
- DSTMDocument18 pagesDSTMDesh Deepak kantNo ratings yet
- Shear Stress: FaultDocument2 pagesShear Stress: Faultbae joohyunNo ratings yet
- Plates Volcanoes EarthquakesDocument45 pagesPlates Volcanoes EarthquakesAbigail HernandezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledIanNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonic Theory States That The EarthDocument2 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory States That The EarthPRINTDESK by DanNo ratings yet
- Summary (Chapter 1)Document7 pagesSummary (Chapter 1)Vina PardedeNo ratings yet
- Science Plate BoundariesDocument3 pagesScience Plate BoundariesAshley VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plate Tectonic Earth Interior Science 10 q1Document14 pagesLecture Plate Tectonic Earth Interior Science 10 q1echevarrialorainneNo ratings yet
- G10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsDocument2 pagesG10 Science Notes - Plate TectonicsCairo DiazNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 - Plate TectonicsDocument1 pageNotes 2 - Plate TectonicsSabrina May LabradorNo ratings yet
- Plates Tectonics 2Document57 pagesPlates Tectonics 2Mark LourenceNo ratings yet
- Q1C2L5 Plate TectonicsDocument25 pagesQ1C2L5 Plate TectonicsCher Z 2No ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesEarth Science ReviewerBenz Nicolf CasadorNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience ReviewerMarinelle Joy PALADANo ratings yet
- Science 8 4Document17 pagesScience 8 4Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- Continental Volcanic ArcDocument4 pagesContinental Volcanic ArcsalesNo ratings yet
- Milfa FilesDocument2 pagesMilfa Filesjolfa fradejasNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics NotesDocument7 pagesPlate Tectonics Notesmahsa tNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledeissa rigiNo ratings yet
- Voc 3 8th 2020-03-23 at 10.47.04 AMDocument8 pagesVoc 3 8th 2020-03-23 at 10.47.04 AMJasir June DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 Lesson 1 Relationship Between Faults and EarthquakeDocument22 pagesQuarter 2 Lesson 1 Relationship Between Faults and EarthquakeJose BundalianNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Plates NotesDocument3 pagesTectonic Plates NotesAngelica CamilonNo ratings yet
- Grade10 Lesson 4Document21 pagesGrade10 Lesson 4Ka KlasmeytNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceIciss Yumi AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- The Theory of Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesThe Theory of Plate TectonicsjhemzNo ratings yet
- Continental Volcanic ArcDocument1 pageContinental Volcanic ArcRenmarie LaborNo ratings yet
- All About PlatesDocument15 pagesAll About PlatesAshara FlynnNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKESDocument10 pagesEARTHQUAKESLuke .J. WuteteNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics PPDocument30 pagesPlate Tectonics PPdazwerk123No ratings yet
- Earthquake EngineeringDocument28 pagesEarthquake EngineeringMaryll TapiaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics 122447Document12 pagesPlate Tectonics 122447mkwa811No ratings yet
- Inbound 4455879487521745204Document1 pageInbound 4455879487521745204Jezell Ann Marie YuNo ratings yet
- Earth's Interior, Continental Drift & Plate TectonicsDocument32 pagesEarth's Interior, Continental Drift & Plate Tectonicssyrine mendozaNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3ADocument5 pagesPlate Tectonics: Name: Krisia Marie Amac Bsge 3AMark Rienzo HingpisNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes For Week 2 - General Geology PDFDocument35 pagesLecture Notes For Week 2 - General Geology PDFRuby LenNo ratings yet
- Plates PowerpointDocument9 pagesPlates Powerpointapi-233082297No ratings yet
- General Science NotesDocument15 pagesGeneral Science Notesomgpop100% (2)
- Understanding The Pieces: Tectonic PlatesDocument17 pagesUnderstanding The Pieces: Tectonic PlatesPrincess Micaela MalolosNo ratings yet
- Week-3 - Plate TectonicsDocument81 pagesWeek-3 - Plate TectonicsRashid AhmedovNo ratings yet
- The Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetDocument32 pagesThe Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetsshoeburrahmanNo ratings yet
- Portfolio in Science: Name: Leila Rose Junio Section: 10 Fleming Teacher: Mrs TabiraoDocument7 pagesPortfolio in Science: Name: Leila Rose Junio Section: 10 Fleming Teacher: Mrs TabiraoChristian FloresNo ratings yet
- Earth's Interior, Continental Drift & Plate TectonicsDocument32 pagesEarth's Interior, Continental Drift & Plate TectonicsOmar NajmNo ratings yet
- Geology For Civil EngineersDocument5 pagesGeology For Civil EngineersTania Cate AranteNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Advocacy SampleDocument3 pagesAdvocacy Sampleyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Fs1 Virtual Classroom Observation Sheets Observation No.Document3 pagesFs1 Virtual Classroom Observation Sheets Observation No.yanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Literary Language: English Elect 1: Stylistic and Discourse Analysis Semantic MapDocument1 pageLiterary Language: English Elect 1: Stylistic and Discourse Analysis Semantic Mapyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Preparation: (C/o Gabi, Enobio, Penaso, Calope,)Document4 pagesPreparation: (C/o Gabi, Enobio, Penaso, Calope,)yanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Shaina AdvocacyDocument4 pagesShaina Advocacyyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Advocacy YeyDocument5 pagesAdvocacy Yeyyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Marrian Chriselle S. Tapa: NameDocument2 pagesMarrian Chriselle S. Tapa: Nameyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Plaque of Recogni Tion: For Winning CHAMPION in "GINTONG BOSES NG COED 2020"Document4 pagesPlaque of Recogni Tion: For Winning CHAMPION in "GINTONG BOSES NG COED 2020"yanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Corona Virus 2019: Stay at Home Wear Your MaskDocument1 pageCorona Virus 2019: Stay at Home Wear Your Maskyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Human Rights Law Against Gender-Based Violence The Anti-Rape Law of 1997Document4 pagesHuman Rights Law Against Gender-Based Violence The Anti-Rape Law of 1997yanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Virtual Chorale Contest. On Behalf of The SSG, I Am Sending This Message To InviteDocument1 pageVirtual Chorale Contest. On Behalf of The SSG, I Am Sending This Message To Inviteyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Marrian Chriselle S. Tapa Bsed-EnglishDocument4 pagesMarrian Chriselle S. Tapa Bsed-Englishyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Inside Out (Intonation)Document5 pagesInside Out (Intonation)yanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Article XivDocument3 pagesArticle Xivyanoy.mc98100% (1)
- Human Rights Law Against Gender-Based Violence The Anti-Rape Law of 1997Document4 pagesHuman Rights Law Against Gender-Based Violence The Anti-Rape Law of 1997yanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument1 pageEarthquakeyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- Factors That Influence The Acquisition of ReadingDocument1 pageFactors That Influence The Acquisition of Readingyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- TechnologyDocument2 pagesTechnologyyanoy.mc98No ratings yet
- El 6 Lsitening FinalDocument4 pagesEl 6 Lsitening Finalyanoy.mc98No ratings yet