0% found this document useful (0 votes)
151 views1 pageTransmission Line Analysis
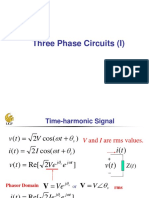
1) Three phase power transmission systems can transmit three times the power of a single phase system with the same current and voltage ratings.
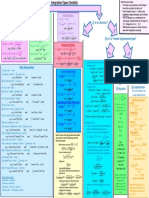
2) Transmission line performance is affected by its length, with shorter lines behaving differently than longer lines. The surge impedance and phase constant are important line parameters.
3) Reactive power flow in transmission lines can be controlled using series capacitors and shunt reactors.
Uploaded by
Tariq MahmoodCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
151 views1 pageTransmission Line Analysis
1) Three phase power transmission systems can transmit three times the power of a single phase system with the same current and voltage ratings.
2) Transmission line performance is affected by its length, with shorter lines behaving differently than longer lines. The surge impedance and phase constant are important line parameters.
3) Reactive power flow in transmission lines can be controlled using series capacitors and shunt reactors.
Uploaded by
Tariq MahmoodCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd