Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Power
Uploaded by
Johnpaul Bayron PagalanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Power
Uploaded by
Johnpaul Bayron PagalanCopyright:
Available Formats
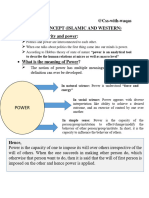
POWER
- ability to achieve a desired outcome and in politics, is usually thought of as a relationship.
- a capacity that A has to influence the behaviour of B, so that B acts in accordance with A’s wishes.
- get someone to do something you want done.
- make things happen in the way you want.
NATURE OF POWER:
1. Power is used in relational sense.
2. Power is not concentrated at any particular centre.
3. In a class-society there are diverse interests and each power represents a particular interest,
4. Power is a conditional power.
5. Power is a very complex notion.
DIMENSIONS OF POWER:
1. ISSUE 2. AGENDA 3. MANIPULATION
TYPES OF POWER:
1. Economic Power- the measurement of the ability to control events by virtue of material advantage.
2. Social Power- based upon informal community opinions, family position, honour, prestige and pattern of
consumption & lifestyle.
3. Political Power- based upon the relationships to the legal structure, party affiliation and extensive
bureaucracy.
- Involves the power to tax and power to distribute resources to the citizen.
4. Military Power- involve the use of physical coercion.
5. Ideological Power- involves power on ideas and beliefs.
6. Distributional Power- ability of individuals to get others to help them pursue their own goals.
7. Collective Power- exercised by social groups
- It may be exercised by one social group over another.
You might also like
- Politics and GovernmentDocument4 pagesPolitics and GovernmentDanielle CondesNo ratings yet
- Week 4 in A NutshellDocument11 pagesWeek 4 in A NutshellHugo Martiniano de NoronhaNo ratings yet
- Power and AccountabilityDocument22 pagesPower and AccountabilityClangClang Obsequio-ArintoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Power Fact SheetDocument5 pagesLesson 3 - Power Fact SheetWinnona Sofia JandayanNo ratings yet
- Concepts and Institutions-1Document2 pagesConcepts and Institutions-1DebashritaNo ratings yet
- Polsci Notes 02 20 2020Document2 pagesPolsci Notes 02 20 2020Keshia AsayasNo ratings yet
- Concept Notes With Formative Activities: Philippine Politics and GovernanceDocument9 pagesConcept Notes With Formative Activities: Philippine Politics and GovernanceSheena Mae RuezoNo ratings yet
- Power, Authority, Legitimcay - 2020Document38 pagesPower, Authority, Legitimcay - 2020Tasnova Zaman 1911260630No ratings yet
- LESSON 1 Ethics / EtikaDocument3 pagesLESSON 1 Ethics / EtikaPEÑA ALIAH EUNICE C.No ratings yet
- Características Dimensiones HofstedeDocument9 pagesCaracterísticas Dimensiones HofstedeJaz WoolridgeNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance: Nature, Dimension, Types, and Consequences of PowerDocument12 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance: Nature, Dimension, Types, and Consequences of PowerKristine RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 4 PowerDocument21 pages4 PowerAaliyah DumangasNo ratings yet
- PPGG Module 1 - FinaleDocument11 pagesPPGG Module 1 - FinalePhean ArañoNo ratings yet
- Philippine Politics and Governance LESSON3Document25 pagesPhilippine Politics and Governance LESSON3mae lynette tuvallesNo ratings yet
- Chappter 3 4 Politics GovernanceDocument41 pagesChappter 3 4 Politics GovernanceCijesNo ratings yet
- Presentation3-Module 3 Power Its Nature, Dimenstions, Types, and ConsequencesDocument22 pagesPresentation3-Module 3 Power Its Nature, Dimenstions, Types, and ConsequencesEmelinda Camillo AlhabsiNo ratings yet
- CFLM22Document12 pagesCFLM22CRIMY PIENo ratings yet
- Power:: Ability To Influence Something ElseDocument5 pagesPower:: Ability To Influence Something ElseZain Ul AbideenNo ratings yet
- 3-The-Concept-of-Power and Their LimitationsDocument40 pages3-The-Concept-of-Power and Their LimitationsRica Jeanne V. EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PPGDocument4 pagesReviewer in PPGMichelle GumarangNo ratings yet
- Politics 5,6 - 7Document9 pagesPolitics 5,6 - 7Eleazar De TorresNo ratings yet
- Whole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Senior High School GradeDocument15 pagesWhole Brain Learning System Outcome-Based Education: Senior High School GrademarkNo ratings yet
- Sse14 Premil NotesDocument4 pagesSse14 Premil NotesJing Jing DelaraNo ratings yet
- Jeza B. Magalang - PPG DLP 4th WeekDocument3 pagesJeza B. Magalang - PPG DLP 4th WeekJeza MagalangNo ratings yet
- Understanding PowerDocument37 pagesUnderstanding PowerRamjit Kumar100% (1)
- Pointers in Ucsp 2nd QuarterDocument7 pagesPointers in Ucsp 2nd QuarterMari Cris MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Power State ActivityDocument3 pagesPower State ActivityLiezl BULJATINNo ratings yet
- Mob - Unit 4Document46 pagesMob - Unit 4Yash PednekarNo ratings yet
- UCSP ReviewerDocument4 pagesUCSP ReviewernahatdoganNo ratings yet
- Ucsp NotesDocument3 pagesUcsp NotesfrnzHSNNo ratings yet
- Power: Define Power (Learning Competencies)Document8 pagesPower: Define Power (Learning Competencies)Kristine TusanNo ratings yet
- Learning Module IN Philippine Politics and Governance 11 Quarter 1: Week 4-5Document6 pagesLearning Module IN Philippine Politics and Governance 11 Quarter 1: Week 4-5Rostelito CatalonNo ratings yet
- Intro To Philoso Q1 W3Document69 pagesIntro To Philoso Q1 W3Mark CatiponNo ratings yet
- Organizational Control and PowerDocument22 pagesOrganizational Control and PowerJessa Quiño EscarpeNo ratings yet
- Phil. Gov. LS 4 PDFDocument6 pagesPhil. Gov. LS 4 PDFVanessa PanagaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Political IdeologiesDocument2 pagesLesson 2 Political IdeologiesアンジェロドンNo ratings yet
- Power and Politics - Organizational BehaviourDocument6 pagesPower and Politics - Organizational Behaviournits_85100% (3)
- DLP 2 Community Power StructureDocument5 pagesDLP 2 Community Power StructureKEn Laurence MagonciaNo ratings yet
- Unit 6Document25 pagesUnit 6Eshetu AlemuNo ratings yet
- 3 - Nature - Forms - and - Consequences - of - Power (Autosaved)Document55 pages3 - Nature - Forms - and - Consequences - of - Power (Autosaved)Jerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- UdERStaNDING cULTURE, sOCIETY & POLITICSDocument18 pagesUdERStaNDING cULTURE, sOCIETY & POLITICSAhms NavarroNo ratings yet
- The Concept of Power in IRDocument10 pagesThe Concept of Power in IRUswa AzharNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Phil. Politics-Week 3Document11 pagesModule 3 Phil. Politics-Week 3Shendy AcostaNo ratings yet
- Power: Prepared By: Group 4 (GAS 12 - 2)Document36 pagesPower: Prepared By: Group 4 (GAS 12 - 2)Mark OngasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics (Grade 12) Mrs. Ana Lyn D. de Leon Subject TeacherDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics (Grade 12) Mrs. Ana Lyn D. de Leon Subject TeacherSelvin A Crisostomo100% (1)
- Pol GovDocument4 pagesPol GovmayaNo ratings yet
- PHILGOV Lesson 4Document2 pagesPHILGOV Lesson 4Robert AquinoNo ratings yet
- Political SelfDocument21 pagesPolitical SelfJulienne NicholeNo ratings yet
- Gibs 10 Organizational Power and PoliticsDocument7 pagesGibs 10 Organizational Power and PoliticsM FauzanNo ratings yet
- POWER by Vikas BarodiyaDocument21 pagesPOWER by Vikas BarodiyaVikas BarodiyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Power & PoliticsDocument7 pagesAssignment of Power & Politicschandrica banik100% (1)
- Power National PowerDocument35 pagesPower National PowerTrâm Ái TrịnhNo ratings yet
- Power in World PoliticsDocument22 pagesPower in World Politicssafder aliNo ratings yet
- P1 Ch4 Political ConceptsDocument24 pagesP1 Ch4 Political ConceptsAhmadNo ratings yet
- Power and LeadershipDocument3 pagesPower and LeadershipSTA. FE NHS ICTNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Political PowerDocument9 pagesWeek 3 - Political PowerKRISTINE ANGELI BARALNo ratings yet
- Philippines Politics: and GovernanceDocument11 pagesPhilippines Politics: and GovernanceJud Den100% (1)
- Political Ideologies: Sittie Nadja B. RondaDocument38 pagesPolitical Ideologies: Sittie Nadja B. RondaFahad SBNo ratings yet
- PowerDocument1 pagePowerJohnpaul Bayron PagalanNo ratings yet
- Political IdeologiesDocument1 pagePolitical IdeologiesJohnpaul Bayron PagalanNo ratings yet
- PowerDocument1 pagePowerJohnpaul Bayron PagalanNo ratings yet
- PowerDocument1 pagePowerJohnpaul Bayron PagalanNo ratings yet
- Political IdeologiesDocument1 pagePolitical IdeologiesJohnpaul Bayron PagalanNo ratings yet
- DIASSDocument14 pagesDIASSJohnpaul Bayron Pagalan100% (1)
- PPG Week FG - Historical Background of Philippine Democratic PoliticsDocument5 pagesPPG Week FG - Historical Background of Philippine Democratic PoliticsElmira NiadasNo ratings yet