Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Expt. 1 Thevinin's and Nortons Eqv Circuit
Expt. 1 Thevinin's and Nortons Eqv Circuit
Uploaded by
Venky MaxOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Expt. 1 Thevinin's and Nortons Eqv Circuit
Expt. 1 Thevinin's and Nortons Eqv Circuit
Uploaded by
Venky MaxCopyright:
Available Formats
Simulation # 1
Thevenin And Norton
Equivalent Circuits
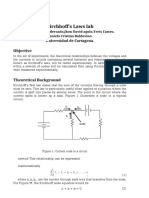
Electrical circuits simulation laboratory
Department of Electronic engineering
NIT Rourkela
Aim of the Expt.:
1. To obtain the Thevenin’s and Norton equivalent circuits of the circuit provided
2. Simulate those circuits and compare their performance to the original circuit
Theory:
Statement of Thevenin’s theorem:
An active network having two terminals A and B can be replaced by a constant-voltage
source having an e.m.f. (Vth) and an internal resistance ‘Rth’. The value of E is equal to the
open circuit p.d. between A and B, ‘Rth’ is the resistance of the network measured between A
and B with the load disconnected and the source emf replaced by their internal resistance.
Internal resistance
o Voltage Source -> Short circuit
o Current source -> Open circuit
Figure 1 Thevenin's Eqv. circuit
Statement of Norton’s theorem:
The current which flows in any branch of a network is the same as that which would flow in
the branch if it were connected across a source of electrical energy, the short circuit current of
which is equal to the current that would flow in short circuit across the branch, and the
internal resistance of which is equal to the resistance which appear across the open circuited
branch terminals.
ISS R N = R TH
Figure 2 Norton's Eqv. circuit
Circuit Diagram:
Simulation:
1. Solve the given circuit (refer Error: Reference source not found) manually and find
the Thevinin’s and Norton’s equivalent circuit across AB. Determine current through
load resistance (50Ω) using both the methods.
2. Run the simulation for original circuit and obtain the load voltages V o and Io for load
resistor RL = 25 Ω, 50 Ω, 100 Ω.
3. Simulate the Thevenin equivalent circuit and the Norton equivalent circuit
4. For each of the three load resistors specified, obtain the load voltage and current for
each case.
Questions:
1. Tabulate and Compare the simulation results of load voltages and currents among
three circuits.
Sl. RL Original Thevinin’s Rth=R Norton’s
No. (Ω) circuit N
VAB IAB Vth IAB Rth=RN Isc IAB
1 25
2 50
3 100
2. Compare Thevenin’s and Norton’s equivalent circuit.
3. For given circuit, find the value of RL at which the current taken by the load circuit is
5 A.
4. For given circuit, what should be the value of RL so that maximum power is delivered
to the load?
5. State maximum power transfer theorem.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Netflix Premium Cookie 6Document2 pagesNetflix Premium Cookie 6Venky MaxNo ratings yet
- Nord CookiesDocument4 pagesNord CookiesVenky MaxNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Power and Energy For Passive Components by Graphical MethodDocument4 pagesCalculation of Power and Energy For Passive Components by Graphical MethodVenky MaxNo ratings yet
- XCFNNDocument105 pagesXCFNNVenky MaxNo ratings yet
- Scanned With CamscannerDocument8 pagesScanned With CamscannerVenky MaxNo ratings yet
- Torrents Downloaded From Worlwidetorrents - EuDocument1 pageTorrents Downloaded From Worlwidetorrents - EuRavi Stephen100% (2)
- Wa0000Document6 pagesWa0000Venky MaxNo ratings yet
- STEMpedia STEM Education Curriculum EducatorsDocument30 pagesSTEMpedia STEM Education Curriculum EducatorsKamal MahmudovNo ratings yet
- Ch11 Workbook ON Science 9Document14 pagesCh11 Workbook ON Science 9mllupoNo ratings yet
- Parallel Resonance and Parallel RLC Resonant CircuitDocument9 pagesParallel Resonance and Parallel RLC Resonant CircuitRoboconDKNo ratings yet
- IB Physics Review-Electric CircuitsDocument7 pagesIB Physics Review-Electric CircuitsyawahabNo ratings yet
- (PART-B) Unit 5: Generation of Impulse Voltage and CurrentDocument27 pages(PART-B) Unit 5: Generation of Impulse Voltage and CurrentAlfred OkacheNo ratings yet
- Sistemas de Potencia Dodge DurangoDocument244 pagesSistemas de Potencia Dodge Durangomatias quezadaNo ratings yet
- II SEMSTER BOS Approved SyllabusDocument59 pagesII SEMSTER BOS Approved SyllabusGnanarajNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of RF CMOS aTTENUATORSDocument15 pagesAnalysis and Design of RF CMOS aTTENUATORSDejanNo ratings yet
- VC15B+/VC17B+ Digital Multimeter User Manual: NOT Exceed The "Maximum Value" Indicated in The SpecificationDocument2 pagesVC15B+/VC17B+ Digital Multimeter User Manual: NOT Exceed The "Maximum Value" Indicated in The SpecificationDiegoM.ArdissoneNo ratings yet
- High and Low Voltage Cutoff With Delay and AlarmDocument2 pagesHigh and Low Voltage Cutoff With Delay and Alarmadnanshahzad521No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3 Measurement of VoltageDocument10 pagesExperiment No. 3 Measurement of VoltageLynndon VillamorNo ratings yet
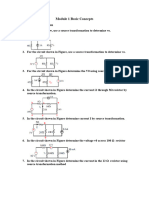
- Theory:: Figure: Verification of Voltages and Currents in Different Branches in A Ladder NetworkDocument4 pagesTheory:: Figure: Verification of Voltages and Currents in Different Branches in A Ladder NetworkAhmed Nesar Tahsin ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and InductorsDocument31 pagesCapacitors and InductorsJucimar BrilhanteNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus - TLE 9Document13 pagesCourse Syllabus - TLE 9Ian JamesNo ratings yet
- Us 4936961Document8 pagesUs 4936961PratikNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics (EL-313) : Complex Engineering Problem (CEP)Document13 pagesPower Electronics (EL-313) : Complex Engineering Problem (CEP)RidaNo ratings yet
- According To The IEC 60909: From Open ElectricalDocument15 pagesAccording To The IEC 60909: From Open Electricalcgalli2100% (1)
- Instruction Manual: VS-606V7 SeriesDocument166 pagesInstruction Manual: VS-606V7 Seriesmax_ingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 CapacitorsDocument11 pagesChapter 9 CapacitorsnNo ratings yet
- Pei QBDocument12 pagesPei QBchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument42 pagesDepartment of Electronics & Communication Engineeringnikhilvatsa20068212No ratings yet
- VFTO in 550 KV GIS PDFDocument9 pagesVFTO in 550 KV GIS PDFCarlos Lino Rojas AgüeroNo ratings yet
- Circuito CCLDocument15 pagesCircuito CCLArellys LizamaNo ratings yet
- Power QualityDocument44 pagesPower QualityLalit Gaur100% (1)
- SCC ManualDocument564 pagesSCC ManualIvan JeremicNo ratings yet
- EE405 LecturesDocument202 pagesEE405 LecturesAbdoooNo ratings yet
- 192 EE1029 Midterm Group2Document4 pages192 EE1029 Midterm Group2Thao Vo VanNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff LabDocument8 pagesKirchhoff LabandreaNo ratings yet
- Source TransformationDocument5 pagesSource Transformationraovinayakm2No ratings yet
- Basic Electronics Practive Assignment Diode1Document2 pagesBasic Electronics Practive Assignment Diode1YASHNo ratings yet